Lead-acid batteries are secondary (rechargeable) batteries that consist of a housing, two lead plates or groups of plates, one of them serving as a positive electrode and the other as a negative electrode, and a filling of 37% sulfuric acid (H2SO4) as electrolyte.
Lead and lead dioxide, the active materials on the battery’s p Most of the world’s lead–acid batteries are automobile starting, lighting, and ignition (SLI) batteries, with an estimated 320 million units shipped in 1999. In 1992 about 3 million tons of lead were used in the manufacture of batteries. Industrial fields of applications for lead acid batteries are as traction power for mining vehicles, forklifts and as stationary power sources such as emergency back up power storage (UPS) and signaling stations for railroads and telecommunication.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Lead-acid Batteries
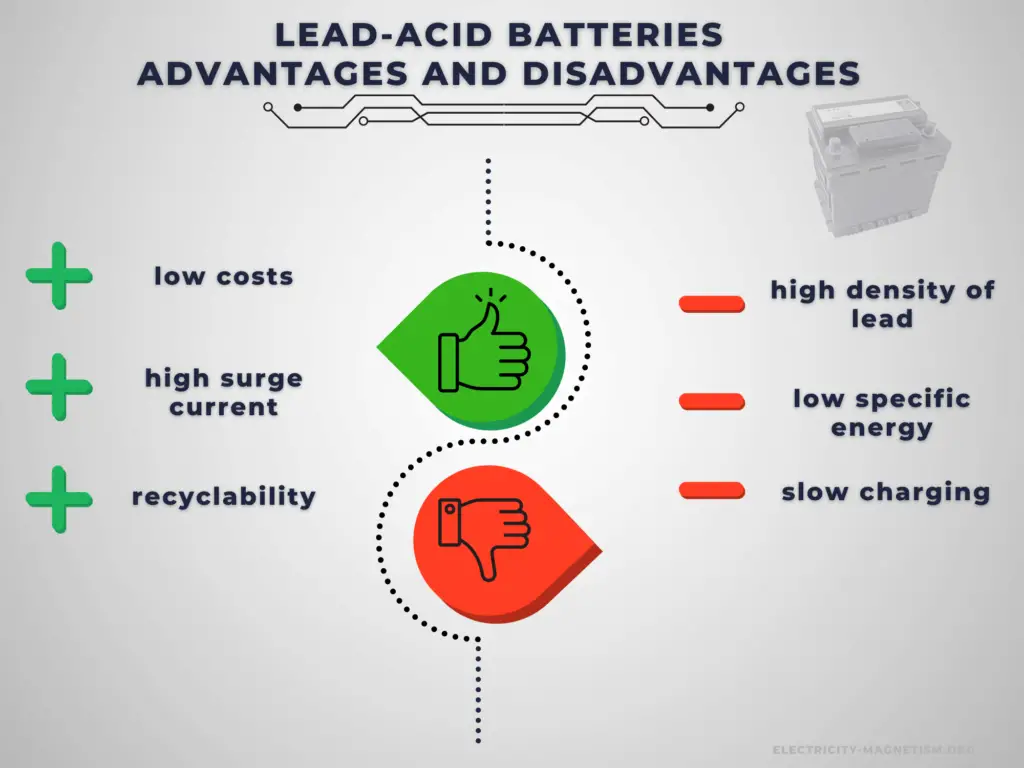
Advantages:
The lead–acid battery is relatively heavy for the amount of electrical energy it can supply. Its low manufacturing cost and its high surge current levels make it common where its capacity (over approximately 10 Ah) is more important than weight and handling issues.
Compared to modern rechargeable batteries, lead–acid batteries have relatively low energy density. Despite this, their ability to supply high surge currents means that the cells have a relatively large power-to-weight ratio. It has become the standard battery for the automotive industry and is commonly used as the power source for starting, lighting, and ignition (SLI) in cars, where it is able to deliver a very high peak current (let’s say about 450 amperes).
Disadvantages:
The disadvantage of this battery chemistry is that it is very sensitive to deep cycling compared to other battery systems, and due to the high density of lead, the specific energy of the batteries is quite low. Charging a lead acid battery system is slow, and it can take up to 16 hours for a full charge. It also requires a current and voltage limiting algorithm, hence limiting the charging current and power. If the charging current is too high, it will cause sulfation which may degrade the performance and cycle life of the battery. Furthermore, the charging voltage must be regulated as the maximum voltage applied is limited by the ambient temperature due to the risk of hydrogen gas generation.
Other Types of Batteries
The following list summarizes notable electric battery types composed of one or more electrochemical cells. Four lists are provided in the table. The first list is a battery classification by size and format. Then, the primary (non-rechargeable) and secondary (rechargeable) cell lists are lists of battery chemistry. The third list is a list of battery applications. The final list is a list of different battery voltages.
Sizes
- AA battery
- AAA battery
- AAAA battery
- C battery
- D battery
- cr1220 battery
- cr1620 battery
- cr1632 battery
- cr1616 battery
- cr2016 battery
- cr2032 battery
- cr2025 battery
- cr2430 battery
- cr2450 battery
- cr123 battery
- cr2 battery
- cr132a battery
- lr1130 battery
- lr41 battery
- lr44 battery
- A23 battery
- a13 battery
- 18650 battery
- 21700 battery

