Pneumatic force sensors convert mechanical force into air pressure signals, offering accurate, reliable measurements in various industries.
Pneumatic Force Sensor: Principles and Applications
Introduction
The pneumatic force sensor is a versatile and cost-effective solution for measuring force in various industrial, manufacturing, and research applications. Pneumatic force sensors are capable of delivering accurate, repeatable, and reliable measurements, making them an attractive option for various industries. This article will explore the principles behind pneumatic force sensors and discuss their various applications.
Principles of Pneumatic Force Sensors
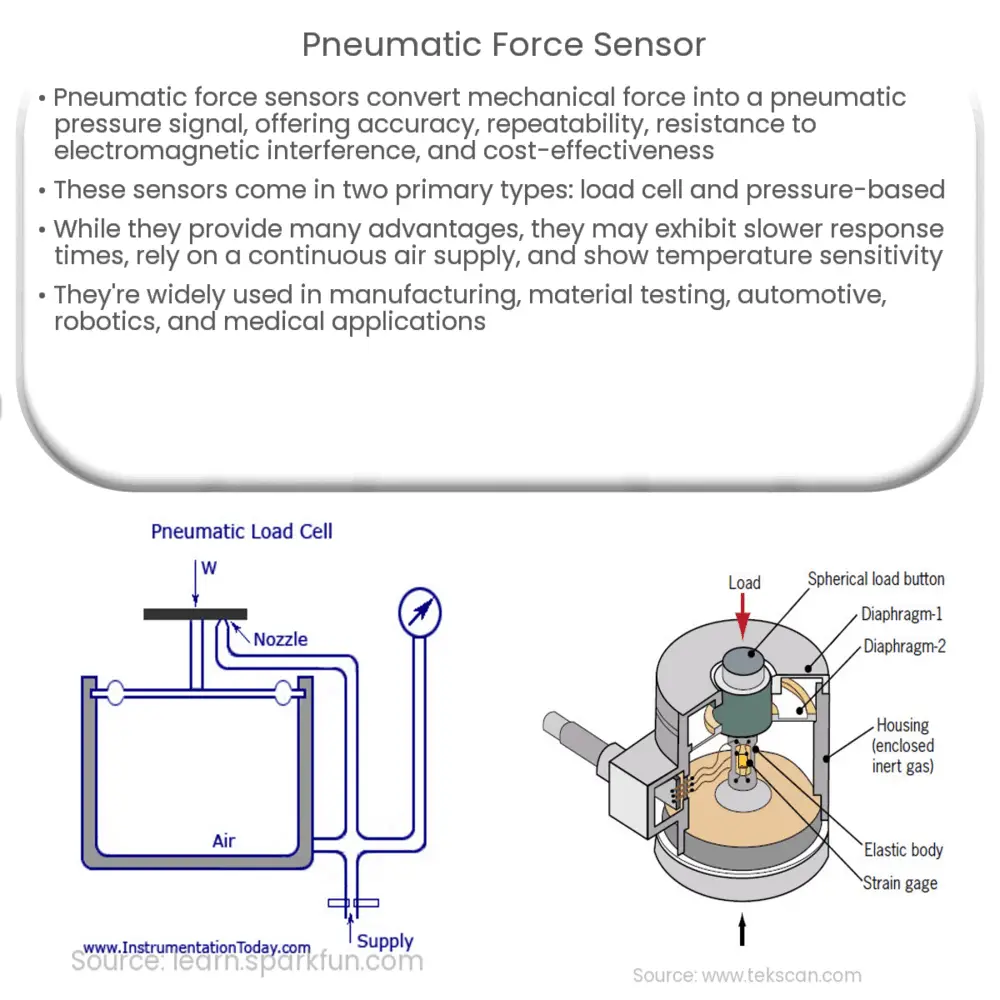
Pneumatic force sensors work on the principle of converting a mechanical force into a pneumatic pressure signal. The sensor is made up of a force-sensitive diaphragm or membrane, which is exposed to a pressurized air source. When an external force is applied to the diaphragm, it deforms, causing a change in the air pressure within the sensor. This change in pressure is then converted into an electrical signal, which can be processed and analyzed to determine the magnitude and direction of the applied force.
There are two primary types of pneumatic force sensors: the load cell and the pressure-based force sensor. The load cell is a mechanical device that measures force through the deformation of a spring element, while the pressure-based force sensor measures force by monitoring the pressure changes within a confined space. Both types of sensors have their own advantages and limitations, making them suitable for different applications.
Advantages of Pneumatic Force Sensors
There are several advantages to using pneumatic force sensors in various applications, including:
- Accuracy and Repeatability: Pneumatic force sensors are capable of providing highly accurate and repeatable measurements, making them suitable for applications requiring precise force measurement.
- Non-electrical: As pneumatic force sensors rely on air pressure rather than electrical signals, they are less susceptible to electromagnetic interference and can be used in environments with high levels of electrical noise.
- Wide Force Range: Pneumatic force sensors can be designed to measure a wide range of forces, from a few newtons to several kilonewtons, making them suitable for a variety of applications.
- Low Maintenance: Due to their simple design and lack of electrical components, pneumatic force sensors typically require less maintenance than other types of force sensors.
- Cost-effectiveness: Pneumatic force sensors are generally more affordable than other types of force sensors, making them an attractive option for budget-conscious applications.
Disadvantages of Pneumatic Force Sensors
While pneumatic force sensors offer several benefits, there are also some disadvantages to consider:
- Slower Response Time: Due to the reliance on air pressure, pneumatic force sensors may have slower response times compared to other types of force sensors, such as strain gauge or piezoelectric sensors.
- Air Supply Dependency: Pneumatic force sensors require a continuous supply of compressed air, which may not be readily available in all environments or applications.
- Temperature Sensitivity: Changes in temperature can affect the performance of pneumatic force sensors, leading to potential measurement inaccuracies if not properly compensated for.
Applications of Pneumatic Force Sensors
Pneumatic force sensors can be used in a wide range of applications across various industries, including:
- Manufacturing and Assembly: Pneumatic force sensors are often used in assembly lines and manufacturing processes to ensure that the correct force is applied during tasks such as pressing, clamping, and fastening.
- Material Testing: Pneumatic force sensors can be used in material testing applications to measure the force required to deform or break materials, providing valuable information on material properties and performance.
- Automotive: In the automotive industry, pneumatic force sensors can be used to measure the force applied to brake pedals, providing data for the development and testing of braking systems.
- Robotics: Pneumatic force sensors can be integrated into robotic systems to enable precise force control during tasks such as grasping, lifting, and manipulating objects.
- Medical: Pneumatic force sensors can be used in medical devices and equipment, such as surgical instruments, to measure and control the force applied during medical procedures.
Conclusion
Pneumatic force sensors are a versatile and cost-effective option for measuring force in a wide range of applications across various industries. By understanding the principles, advantages, and disadvantages of pneumatic force sensors, as well as their potential applications, users can determine if this type of sensor is the best fit for their specific requirements. With proper implementation and maintenance, pneumatic force sensors can provide accurate, reliable, and repeatable force measurements, making them an attractive choice for many applications.




