Explore the world of load cells, their types, applications across industries, working principles, and factors for selection.

Understanding Load Cells
A load cell is a highly precise device that is used to measure force or load. They convert force into an electrical signal that can be measured and standardized. When force is applied to the load cell, it creates a change in electrical resistance which can then be measured and converted into an output signal. This signal is proportional to the force applied and can be interpreted to determine the actual force.
Types of Load Cells
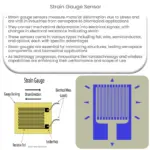
- Strain Gauge Load Cells: The most common type of load cell, strain gauge load cells operate on the principle that the electrical resistance of a material changes when it is strained. A strain gauge load cell typically consists of a spring element to which strain gauges have been securely attached.
- Hydraulic Load Cells: These load cells use a conventional piston and cylinder arrangement to convey a change in pressure by the movement of the piston and a diaphragm arrangement which produces a change in the pressure on a Bourdon tube connected with the load cells. The pressure is then read on a connected pressure gauge.
- Pneumatic Load Cells: Pneumatic load cells are similar to hydraulic load cells in basic principle, but a change in pressure is caused by balancing the load applied with an air pressure.
- Capacitive Load Cells: These load cells work on the principle of capacitance, which is the ability of a system to store a charge. In capacitive load cells, the load applied causes a change in capacitance.
Applications of Load Cells
Load cells are used in a variety of industries for a myriad of applications. Some of the key industries that extensively use load cells include:
- Automotive Industry: Load cells are used for component testing, fatigue testing, and assembly line force testing.
- Aerospace Industry: They are used for structural testing, engine testing, and center of gravity determination.
- Construction Industry: Load cells help in structural load and stress testing, safety testing of lifting equipment, and force measurement in piling operations.
To understand how a load cell works in detail, let’s delve deeper into the science and principles that govern its operation.
The Working Principle of Load Cells
Regardless of the type, all load cells work on a simple principle: they translate a mechanical force into an electrical signal. When a force is applied to the load cell, it results in a deformation of the strain gauge. This deformation causes the electrical resistance to change. This change is then measured and processed by the load cell’s internal electronics to create a readable output.
Strain gauge load cells, for instance, consist of a spring element onto which four strain gauges are bonded. When a load is applied, the spring element bends, causing the strain gauges to elongate or compress. The change in their shape alters the electrical resistance, which is converted into an electrical signal. The greater the load applied, the greater the change in the output signal.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Load Cells
Selecting the right load cell for your application can be challenging. Several factors must be considered:
- Environment: If the load cell is to be used in a harsh environment, it must be robust and resistant to elements such as moisture, dust, and temperature fluctuations.
- Capacity: The maximum load that the load cell is designed to measure safely and accurately, also known as its rated capacity, must align with the requirements of your application.
- Accuracy: The accuracy of a load cell is vital, especially in industries where precision is paramount. It refers to the degree of closeness of the measured weight to the actual weight.
- Physical Size: Depending on the application, the size of the load cell can be a critical factor. The load cell must fit into the available space and be able to handle the physical requirements of the application.
Conclusion
Load cells play a crucial role in a broad range of industries, providing essential data that drives innovation, ensures safety, and aids in quality control. Understanding how they work and the factors to consider when selecting one can help businesses choose the right load cell for their specific needs. Whether it’s the strain gauge load cell used in manufacturing, the hydraulic load cell used in construction, or any other type, the fundamental principle remains the same: converting mechanical force into a measurable electrical signal.