Strain gauge load cells provide accurate, reliable weight, force, and torque measurements for diverse applications in various industries.

Strain Gauge Load Cell: The Core of Accurate Weight Measurement
Introduction
Strain gauge load cells are widely used in various industries for accurate and reliable measurement of weight, force, and torque. They are the core of many modern weighing systems and are the backbone of applications ranging from laboratory balances to industrial scales. This article delves into the principle of operation, types, and applications of strain gauge load cells, highlighting their significance in today’s technology-driven world.
Principle of Operation
Strain gauge load cells work on the principle of the strain gauge, a device that changes its electrical resistance in response to mechanical deformation. When a load cell is subjected to a force, the strain gauges inside the load cell are either compressed or stretched, causing a change in their electrical resistance. This change in resistance is proportional to the applied force, and by measuring this change, the load cell can determine the weight or force acting on it.
The electrical resistance change is usually very small, so it is necessary to use a Wheatstone bridge circuit to amplify the signal. The Wheatstone bridge is an arrangement of four resistors in a diamond shape, with one or more strain gauges acting as the variable resistors. As the strain gauges change their resistance due to the applied force, the bridge becomes unbalanced, generating a voltage output that can be measured and converted into weight or force readings.
Types of Strain Gauge Load Cells
There are several types of strain gauge load cells, each designed for specific applications and performance requirements. Some common types include:
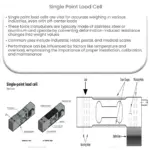
- Single Point Load Cells: These are widely used in platform scales, where the load is applied at a single point on the load cell. They are designed to handle off-center loading and can accommodate large weighing platforms.
- Beam Load Cells: Also known as bending beam or shear beam load cells, they are ideal for low-profile scales and force measurement applications. They are designed to withstand bending or shearing forces and are available in various capacities and sizes.
- Compression Load Cells: These load cells are specifically designed to measure compression forces. They are typically used in applications like truck scales, tank weighing, and industrial process control.
- Tension Load Cells: As the name suggests, tension load cells are designed to measure tensile forces. They are commonly used in crane scales, hanging scales, and cable tension measurement systems.
Applications of Strain Gauge Load Cells
Strain gauge load cells are employed in a vast range of applications due to their versatility, accuracy, and reliability. Some common applications include:
- Industrial weighing systems, such as silo, tank, and hopper scales
- Automotive and aerospace testing for force and torque measurements
- Medical equipment, like patient weighing scales and infusion pumps
- Material testing machines for stress and strain analysis
- Construction and structural health monitoring
Advantages of Strain Gauge Load Cells
Strain gauge load cells offer several advantages that make them the preferred choice for a wide range of applications. Some key benefits include:
- Accuracy: Strain gauge load cells provide high accuracy, making them suitable for applications that require precise weight or force measurements.
- Reliability: They are known for their long-term stability and consistent performance, ensuring reliable measurements over time.
- Wide Capacity Range: Strain gauge load cells are available in various capacities, allowing them to cater to a broad spectrum of applications, from small-scale laboratory balances to large industrial scales.
- Cost-effectiveness: These load cells are relatively affordable compared to other types of load cells, making them an attractive choice for many applications.
- Environmentally Robust: Strain gauge load cells can be designed to withstand harsh environments, such as high temperature, humidity, and corrosive conditions, making them suitable for use in various industries.
Selection Criteria for Strain Gauge Load Cells
Choosing the right strain gauge load cell for a specific application involves considering several factors. Some key selection criteria include:
- Capacity: Select a load cell with a capacity that matches or exceeds the maximum weight or force to be measured.
- Accuracy: Ensure that the load cell’s accuracy meets the requirements of the application. This may involve considering factors such as linearity, hysteresis, and repeatability.
- Environmental Conditions: Consider the environmental conditions the load cell will be exposed to, such as temperature, humidity, and potential exposure to corrosive substances. Choose a load cell with suitable protection or material properties to withstand these conditions.
- Mounting and Installation: Make sure that the load cell’s mounting and installation requirements are compatible with the application’s mechanical setup.
- Cost: While cost is an important factor, it should not compromise the quality and performance of the load cell. Look for a balance between cost and performance to ensure the best value for your investment.
Conclusion
Strain gauge load cells play a critical role in numerous industries, offering accurate and reliable weight, force, and torque measurements. With their versatile design, wide capacity range, and cost-effective nature, these load cells are a popular choice for a vast array of applications. By understanding the types and applications of strain gauge load cells and considering the essential selection criteria, users can ensure that they choose the right load cell for their specific needs, resulting in enhanced performance, reliability, and long-term value.