Load cells are transducers that convert mechanical force into electrical signals, enabling precise force and weight measurements in various industries.

Load Cells: Understanding the Essentials and Applications
Introduction
Load cells are essential components in various industries, providing accurate and reliable measurements of force or weight. These transducers convert mechanical force into electrical signals, enabling users to monitor and control processes in real-time. In this article, we’ll explore the fundamental principles behind load cells, the different types available, and their various applications in diverse industries.
Principles of Load Cells
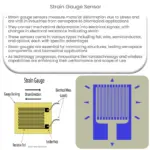
Load cells work based on the principle of strain gauge technology. A strain gauge is a thin, conductive material that changes its electrical resistance when subjected to mechanical deformation (strain). By attaching strain gauges to a load cell’s body, a change in force or weight is detected and converted into an electrical signal proportional to the applied load.
The load cell’s output signal is typically quite small, in the range of millivolts. To convert this low-level signal into a usable form, it must be amplified and conditioned using signal conditioners or amplifiers. The amplified signal can then be displayed, recorded, or transmitted to a control system for further processing and analysis.
Types of Load Cells
Load cells come in various types, each designed to cater to specific applications and environments. The most common types of load cells include:
- Compression Load Cells: These load cells are designed to measure compressive forces. They are commonly used in weighing scales, industrial presses, and other applications where force is applied vertically.
- Tension Load Cells: Tension load cells measure tensile forces or pulling forces. They are often used in crane scales, hanging scales, and force measurement devices for testing materials.
- Beam Load Cells: Beam load cells are commonly used in low-profile weighing applications. They are designed to measure both tension and compression forces and are often found in platform scales and tank weighing systems.
- Single-Point Load Cells: These load cells are specifically designed for platform scales, where they can measure off-center loads accurately. Single-point load cells provide a cost-effective solution for many industrial weighing applications.
- Multi-Axis Load Cells: Multi-axis load cells can measure forces in multiple directions simultaneously. They are used in applications requiring the measurement of complex force vectors, such as robotics, automotive testing, and aerospace research.
Applications of Load Cells
Load cells are utilized in a wide range of industries for their ability to provide accurate and reliable force and weight measurements. Some of the most common applications include:
- Industrial Weighing: Load cells are at the heart of many industrial weighing systems, including platform scales, tank and silo weighing systems, and conveyor belt scales.
- Material Testing: In material testing laboratories, load cells help determine the mechanical properties of materials, such as tensile strength, compressive strength, and fatigue life.
- Force Measurement: Load cells are used in force measurement devices to evaluate the performance of various components and assemblies, like automotive parts, aircraft structures, and medical devices.
- Process Control: In automated manufacturing and production lines, load cells help monitor and control processes, ensuring product quality and consistency.
Choosing the Right Load Cell
Selecting the appropriate load cell for a specific application requires careful consideration of various factors, such as:
- Force or Weight Range: The load cell should be capable of measuring the maximum force or weight expected in the application while maintaining adequate resolution at the lower end of the range.
- Accuracy and Sensitivity: The accuracy and sensitivity of a load cell are crucial for obtaining precise measurements. Consider the maximum error tolerance and the smallest measurable force or weight change required for your application.
- Environment: Environmental factors, such as temperature, humidity, and exposure to dust or chemicals, may affect a load cell’s performance. Choose a load cell with appropriate environmental protection and temperature compensation features.
- Mounting and Installation: Ensure that the load cell’s mechanical design and mounting arrangements are compatible with your application’s requirements, allowing for easy installation and proper force transmission.
- Output Signal: Load cells offer various output signal options, such as analog (mV/V), digital, or wireless. Select the output type that best suits your data acquisition and control system needs.
Load Cell Calibration and Maintenance
To maintain the accuracy and reliability of load cell measurements, regular calibration and maintenance are essential. Calibration involves comparing the load cell’s output signal to known weight or force values, allowing users to adjust the measurement system accordingly. Calibration should be performed periodically or whenever significant changes in the load cell’s performance are suspected.
Proper maintenance of load cells includes regular visual inspections for signs of damage, corrosion, or wear. Additionally, ensure that the load cell and its associated components, such as mounting hardware and electrical connections, are clean and secure. By following appropriate calibration and maintenance procedures, you can ensure the longevity and reliable performance of your load cell system.
Conclusion
Load cells play a vital role in numerous industries, providing accurate and reliable force and weight measurements. Understanding the principles behind load cells, the different types available, and their various applications can help you select the right load cell for your specific needs. By considering factors such as force or weight range, accuracy, environmental conditions, and output signal type, you can optimize your load cell system’s performance. Moreover, regular calibration and maintenance are crucial for maintaining the accuracy and reliability of your load cell measurements.