Bending beam load cells are accurate, reliable devices used for measuring weight and force in various industries and applications.

Bending Beam Load Cell: The Essentials
Introduction
A bending beam load cell is an essential component in many industries and applications, offering an accurate and reliable means of measuring weight and force. In this article, we will explore the basic principles, types, and applications of bending beam load cells.
Principles of Bending Beam Load Cells
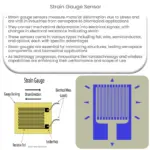
Bending beam load cells work on the principle of strain gauge technology, which is the measurement of the change in electrical resistance due to the deformation of a conductor. As force is applied to the load cell, it causes the bending beam to deflect. This deflection is proportional to the applied force and results in a change in the electrical resistance of the strain gauge. The change in resistance is then converted into an electrical signal that can be easily read and processed.
Construction and Types of Bending Beam Load Cells
Bending beam load cells are typically made from materials such as stainless steel or aluminum, which are known for their strength and resistance to corrosion. The choice of material depends on the specific application and environment in which the load cell will be used.
There are several types of bending beam load cells, including:
- Single-point bending beam load cells: These load cells are designed for single-point weighing applications, where the load is applied to a single point on the load cell. They are commonly used in platform scales, packaging machines, and conveyor systems.
- Double-ended bending beam load cells: These load cells have two points of attachment and are designed for applications where the load is distributed across multiple points. They are commonly used in truck scales, silo weighing systems, and industrial process control.
- Shear beam load cells: This type of load cell is designed to measure the shear force applied to the beam, rather than the bending force. They are commonly used in applications where side loads are present, such as in weighbridges and industrial weighing systems.
Advantages of Bending Beam Load Cells
Bending beam load cells offer several advantages, including:
- Accuracy: They provide highly accurate measurements, with some models offering accuracy levels of up to 0.02% of the rated capacity.
- Reliability: Due to their robust construction and the use of high-quality materials, bending beam load cells are known for their reliability and long service life.
- Versatility: Bending beam load cells are available in a wide range of capacities and configurations, making them suitable for a variety of applications.
Applications of Bending Beam Load Cells
Bending beam load cells are widely used in a variety of industries and applications, such as:
- Industrial weighing: Bending beam load cells are commonly used in industrial weighing systems for process control, batching, and inventory management.
- Transportation: They are used in truck scales and weighbridges to measure the weight of vehicles and their payloads, ensuring compliance with road regulations and avoiding overloading.
- Agriculture: Bending beam load cells are used in agricultural equipment, such as feed mixers and grain silos, to measure the weight of produce and ensure accurate distribution of feed.
- Medical: In medical applications, bending beam load cells are used in patient scales, wheelchair scales, and other devices for accurate weight measurement.
- Packaging: They are used in packaging machines and conveyor systems to ensure accurate filling and labeling of products.
Installation and Calibration
Proper installation and calibration of bending beam load cells are crucial for ensuring accurate and reliable measurements. Some key considerations during installation include:
- Mounting: Bending beam load cells should be mounted on a flat, rigid surface to ensure even distribution of the applied force. Proper mounting hardware, such as load buttons or mounting plates, should be used to secure the load cell in place.
- Load alignment: The load should be applied perpendicular to the sensing element to avoid side-loading, which can lead to inaccurate measurements and potential damage to the load cell.
- Environmental factors: Consideration should be given to environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and vibration, which can affect the performance of the load cell. Some load cells are designed with built-in temperature compensation to minimize the effects of temperature changes.
Calibration is a critical step in ensuring the accuracy of bending beam load cells. A standard procedure involves applying known weights to the load cell and adjusting the output signal until it corresponds to the applied weights. Calibration should be performed periodically to maintain the accuracy of the load cell over time.
Conclusion
Bending beam load cells are a versatile and reliable solution for measuring weight and force in a wide range of applications. Their robust construction, high accuracy, and adaptability to various environments make them an ideal choice for industries such as transportation, agriculture, packaging, and medical. Proper installation and calibration are essential for ensuring the best performance and longevity of these load cells.