30-second summary
Electric Charges in Atoms
Electric charges in atoms are carried by protons and electrons.
The atoms are defined as the smallest constituents of ordinary matter, which can be divided without the release of electrically charged particles.
An atom consists of a positively charged nucleus surrounded by negatively charged electrons so that the atom as a whole is electrically neutral.
The electrons in an atom are attracted to the protons in the nucleus by the electromagnetic force. This force binds the electrons inside an electrostatic potential well surrounding the smaller nucleus, which means that an external source of energy is needed for the electron to escape.

About Electric Charges in Atoms
What is electricity? Electricity is defined as “the flow of electrons through simple materials and devices” or “that force which moves electrons.” Scientists think electricity is produced by very tiny particles called electrons and protons. These particles are too small to be seen, but exist as subatomic particles in the atom. To understand how they exist, you must first understand the structure of the atom.
The physical world is composed of combinations of various subatomic or fundamental particles. These are the smallest building blocks of matter. The atoms are defined as the smallest constituents of ordinary matter, which can be divided without the release of electrically charged particles. An atom consists of a positively charged nucleus surrounded by negatively charged electrons so that the atom as a whole is electrically neutral. The proton carries a single unit positive charge equal in magnitude to the electron charge. The neutron is slightly heavier than the proton and is electrically neutral, as the name implies.
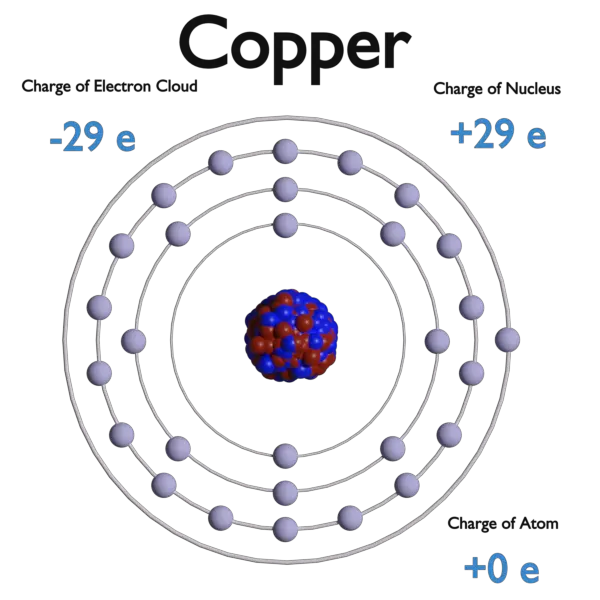
An electron, symbol e−, is one of the fundamental particles that make up matter. The electrons are negatively charged (-1e), almost massless particles that nevertheless account for most of the size of the atom. Their rest mass is equal to 9.109 × 10−31 kg (510.998 keV/c2) (approximately 1/1836 that of the proton). Electrons are located in an electron cloud, which is the area surrounding the nucleus of the atom. The electron cloud model is a model of an atom, in which the atom consists of a small but massive nucleus surrounded by a cloud of rapidly moving electrons. The electron cloud model says that we cannot know exactly where an electron is at any given time, but the electrons are more likely to be in specific areas. Electron cloud model defines the zone of probability describing the electron’s location, because of the uncertainty principle.
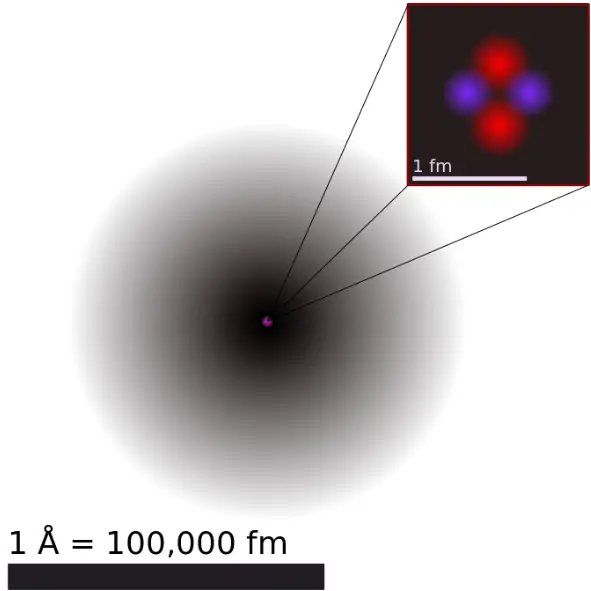
The electrons in an atom are attracted to the protons in the nucleus by the electromagnetic force. This force binds the electrons inside an electrostatic potential well surrounding the smaller nucleus, which means that an external source of energy is needed for the electron to escape.
Sometimes an atom may lose one or more of its electrons or may gain extra electrons, in which case it will have a net positive or negative charge and is called an ion.
Frequently asked questions
The atom’s chemical properties are determined by the number of protons, in fact, by the number and arrangement of electrons. The configuration of these electrons follows the principles of quantum mechanics. The number of electrons in each element’s electron shells, particularly the outermost valence shell, is the primary factor determining its chemical bonding behavior.
An atom consists of a positively charged nucleus surrounded by negatively charged electrons so that the atom as a whole is electrically neutral. The atomic nucleus consists of positively charged protons and neutral neutrons.
The electrons in an atom are attracted to the protons in the nucleus by the electromagnetic force. This force binds the electrons inside an electrostatic potential well surrounding the smaller nucleus, which means that an external source of energy is needed for the electron to escape.

