Explore the role of Differential Pressure Sensors in various industries, their types, working principles, and troubleshooting tips.
Differential Pressure Sensor: An Essential Tool in Measuring Fluid Dynamics
At the heart of many industrial and technological applications lies an unsung hero, the Differential Pressure Sensor. This crucial component functions as the eyes of a system, providing insights into the pressures of various mediums, enabling the systems to function optimally.
A
, often abbreviated as a DP sensor or DPS, is a device that measures the difference in pressure between two points within a system. This difference in pressure is typically expressed in units of force per unit area, such as pounds per square inch (psi) or pascals (Pa).
These devices are utilized in a wide array of applications, from HVAC systems to automobile engines, and even in the medical field. The DPS offers precise measurement and control, ensuring safety, efficiency, and reliability in these systems.
Working Principle of Differential Pressure Sensors
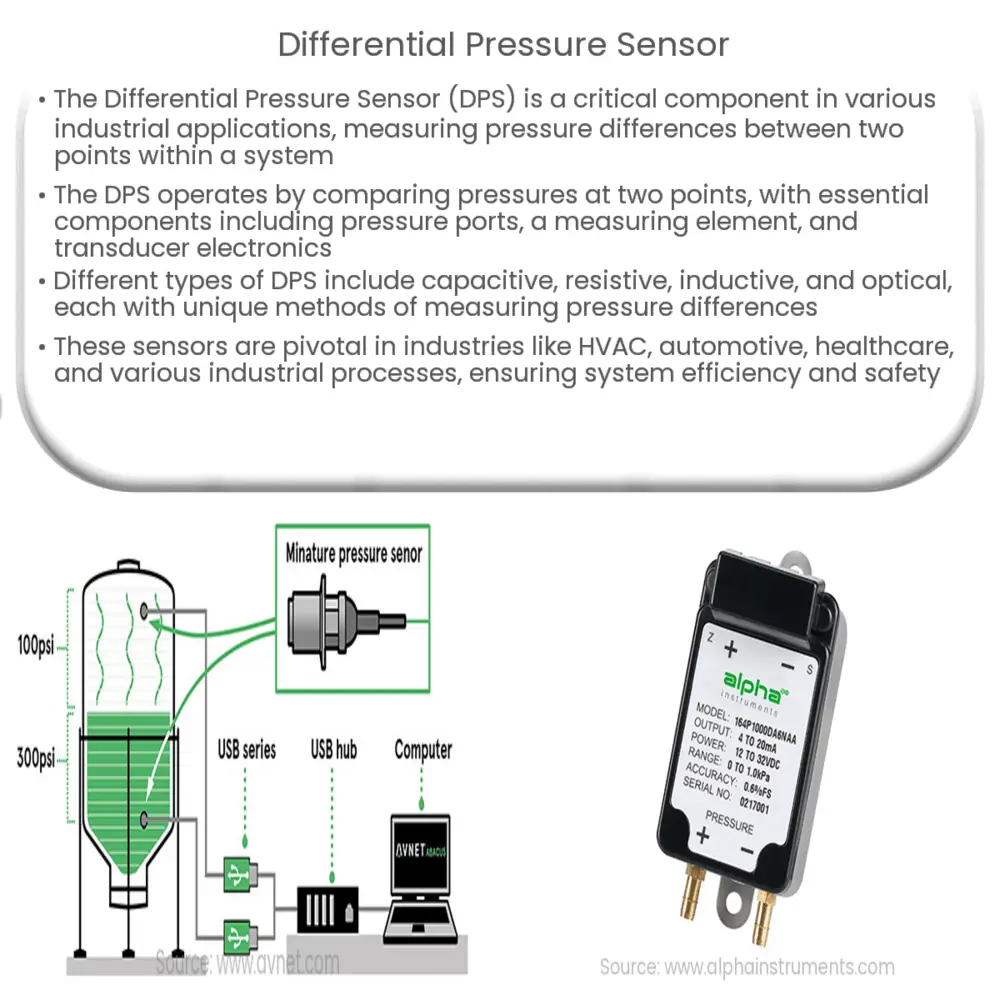
The DPS works by comparing the pressure of two media. In a sealed system, the sensor would measure the pressure at two different points, then calculate the difference. The key components of a DPS include
,
, and
.
The
are the entry points for the pressure media. They are typically marked as high (H) and low (L) to denote the pressure at those points. The
, often a diaphragm or a piston, responds to the pressure difference between these two points. The displacement of this element is then picked up by the
, which convert this mechanical movement into an electrical signal that can be processed and interpreted.
Types of Differential Pressure Sensors
Differential pressure sensors come in different types, each with its unique properties and applications. The most commonly used types include
,
,
, and
DPS.
The
measures pressure differences through the change in capacitance, which occurs due to the displacement of a diaphragm upon pressure changes. The
leverages a change in resistance, often using a strain gauge that alters its resistance as it deforms under the applied pressure.
On the other hand, the
measures the variation in an inductor’s self-inductance or the mutual inductance between two inductors, which changes with the displacement of a ferromagnetic core. Lastly, the
utilizes optical means, such as interferometry or fiber optics, to measure pressure differences.
Applications of Differential Pressure Sensors
Differential pressure sensors play a pivotal role in a variety of industries and applications. Let’s explore some of the key areas where these sensors find their indispensable use.
- HVAC Systems: In Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) systems, DPS are used to ensure optimal air flow and monitor filter status. They help maintain comfortable and healthy indoor air quality by balancing pressure differences.
- Automotive Industry: DPS are used in vehicles to monitor and control the air intake in engines, which is vital for efficient combustion and fuel economy. They also help in monitoring exhaust gas pressure in diesel particulate filters.
- Medical Devices: In the healthcare sector, DPS find use in devices like respirators and ventilators, where they help in regulating and monitoring air pressure delivered to patients. They also play a role in anesthesia machines and blood pressure monitoring devices.
- Industrial Processes: In various industrial applications, DPS are used to monitor fluid levels in tanks, pressure drop across filters, and flow rates in pipes. They help ensure safe and efficient operation of equipment.
Maintaining and Troubleshooting Differential Pressure Sensors
DPS, like all devices, require regular maintenance for optimal performance. This may involve periodic calibration to ensure accurate readings, cleaning of pressure ports to prevent clogging, and routine inspection of the measuring element for any signs of wear or damage.
Problems with DPS can manifest as inaccurate readings, slow response times, or complete failure. Troubleshooting these issues may involve checking the integrity of the sensor’s connections, verifying the condition of the measuring element, or looking for signs of physical damage to the sensor. In many cases, professional service or replacement may be necessary.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Differential Pressure Sensor is an integral component in various applications across multiple industries. Its ability to measure pressure differences with high accuracy enables the safe and efficient operation of many systems. Understanding its working principle, types, and applications aids in not just leveraging its capabilities, but also maintaining and troubleshooting it effectively. While it might be a small component in a complex system, the DPS’ role is undeniably significant, proving that great things often come in small packages.




