Alkaline Battery
An alkaline battery (IEC code: L) is a type of primary battery that provides direct electric current from the electrochemical reaction between zinc and manganese dioxide (MnO2) in the presence of an alkaline electrolyte.
The alkaline battery gets its name because it has an alkaline electrolyte of potassium hydroxide (KOH) instead of the acidic ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) or zinc chloride (ZnCl2) electrolyte of the zinc–carbon batteries. Other battery systems also use alkaline electrolytes, but they use different active materials for the electrodes.
The primary alkaline battery is a widely used product, which is essential for powering many portable devices, such as power tools, radios, toys, and remote controls. The most common size of alkaline battery is the well-known AA battery. Alkaline batteries are most commonly used in portable devices that have low current drains, are used only intermittently, or are used well away from an alternative power source, such as in alarm and communication circuits where other electric power is only intermittently available.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Alkaline Batteries
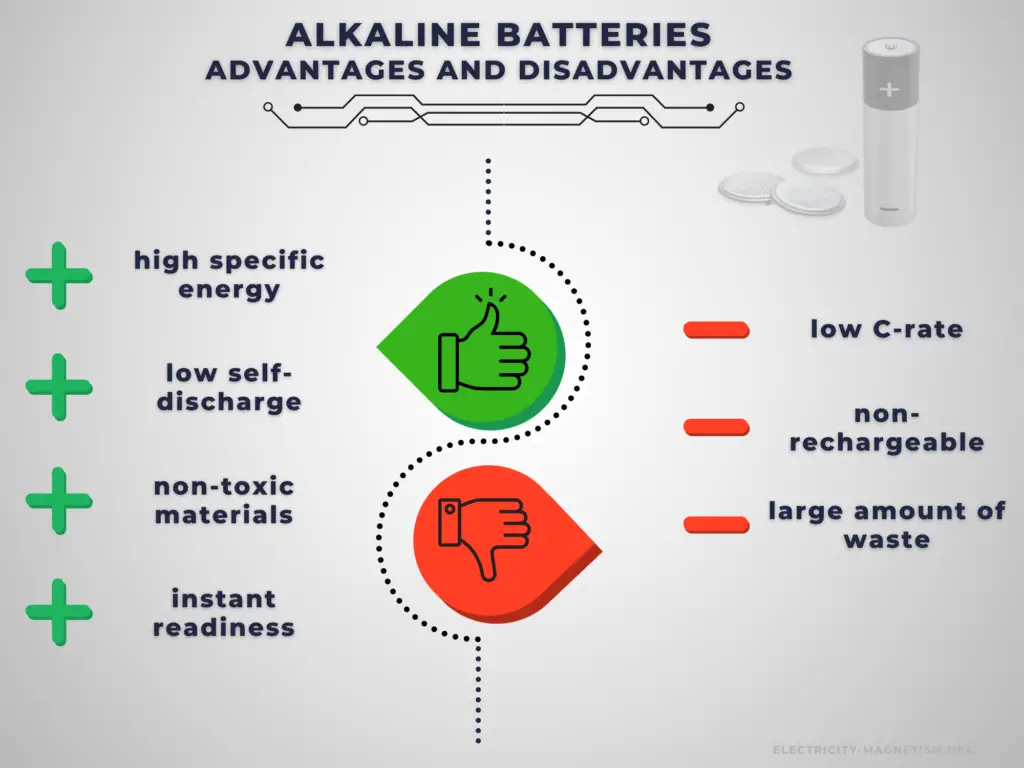
Advantages:
Alkaline batteries have higher energy density than rechargeable secondary cells. High specific energy, long storage times (low self-discharge), and instant readiness give alkaline batteries a unique advantage over other power sources. They are usually the best choice for low-drain applications. They can be carried to remote locations and used instantly, even after long storage; they are also readily available and environmentally friendly when disposed.
Disadvantages:
The main disadvantage of alkaline batteries is that they are non-rechargeable. Another disadvantage is their low C-rate. Even high current types are considered low in comparison to rechargeable batteries. They are also less environment friendly than rechargeable batteries. The application of primary batteries leads to a large amount of waste batteries to be recycled. For large batteries, primary batteries are usually not cost-effective.
Characteristics of Alkaline Batteries
To compare and understand the capability of each battery, some important parameters are characteristic of each battery, also within a type of battery. These parameters are a reference when a battery is needed, and specific qualities are required since batteries are used in all types of devices and for infinite purposes.
Cell Voltage
The voltage of electric batteries is created by the potential difference of the materials that compose the positive and negative electrodes in the electrochemical reaction.
The voltage produced by each lithium-ion cell is about 3.6 volts. This has many advantages. Being higher than that of the standard nickel-cadmium, nickel metal hydride, and even standard alkaline cells at around 1.5 volts.
Cut-off Voltage
The cut-off voltage is the minimum allowable voltage. It is this voltage that generally defines the “empty” state of the battery.
When testing the capacity of a NiMH or NiCd battery, a cut-off voltage of 1.0 V per cell is normally used, whereas 0.9 V is normally used as the cut-off voltage of an alkaline cell.
Capacity
The coulometric capacity is the total Amp-hours available when the battery is discharged at a certain discharge current from 100% SOC to the cut-off voltage.
A typical alkaline or NiMH battery in the standard “AA” size has about 2000 to 3000 mAh (or 2 to 3 Ah).
C-rate of Battery
The cut-off voltage is the minimum allowable voltage. It is this voltage that generally defines the “empty” state of the battery.
To obtain a reasonably good capacity reading, manufacturers commonly rate alkaline and lead acid batteries at a very low 0.05C, or a 20-hour discharge.
Self-discharge
Batteries gradually self-discharge even if not connected and delivering current. This is due to non-current-producing “side” chemical reactions that occur within the cell even when no load is applied.
Alkaline batteries have a very low self-discharge rate, typically stated by manufacturers to be 2–3% per year.






