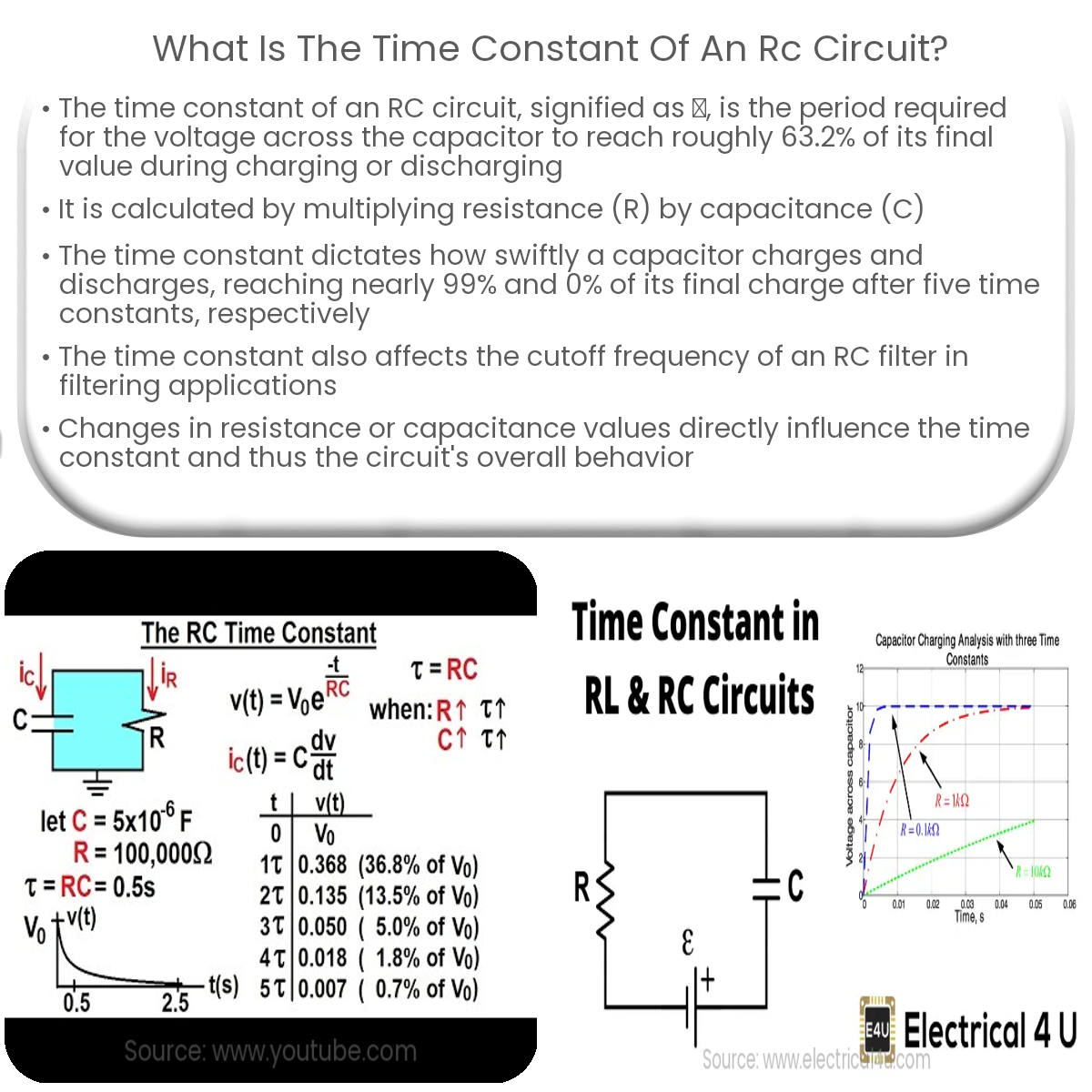
The time constant of an RC circuit (τ) represents the time for the capacitor to charge or discharge to ~63.2% of its maximum value (τ = R * C).
Introduction
The time constant of an RC circuit is an essential parameter that characterizes the response of the circuit to changes in voltage. This article will explore the concept of the time constant in RC circuits, how it is calculated, and its significance in electronic systems.
Time Constant in RC Circuits
In an RC circuit, which consists of a resistor (R) and a capacitor (C), the time constant (τ) represents the time it takes for the capacitor to charge or discharge to approximately 63.2% of its maximum value. The time constant governs the rate at which the voltage across the capacitor changes in response to a step input or when the circuit is connected to or disconnected from a voltage source.
Calculating the Time Constant
The time constant of an RC circuit can be calculated using the following formula:
τ = R * C
Where:
- τ is the time constant (in seconds)
- R is the resistance of the resistor (in ohms)
- C is the capacitance of the capacitor (in farads)
This simple formula illustrates that the time constant is directly proportional to both the resistance and capacitance values of the circuit.
Significance of the Time Constant
The time constant of an RC circuit has several implications in various electronic applications:
- Filtering: In low-pass and high-pass filters, the time constant determines the cutoff frequency, which is the point where the filter attenuates the input signal by 3 decibels (dB).
- Timing: In timing circuits, the time constant governs the duration of output pulses or the time it takes for a signal to reach a specific amplitude.
- Transient response: In control systems and other applications, the time constant affects the transient response of the circuit, dictating how quickly the circuit reacts to changes in input voltage.
Conclusion
The time constant of an RC circuit is a crucial parameter that determines the response of the circuit to changes in voltage. It is calculated by multiplying the resistance and capacitance values of the circuit. Understanding the time constant and its implications is vital for designing and analyzing electronic systems that incorporate RC circuits for filtering, timing, or transient response applications.