The electric field points in the direction of the steepest decrease in electric potential, and they are related through the gradient operation.
Relationship Between Electric Field and Electric Potential
The electric field and electric potential are two fundamental concepts in electromagnetism, both describing different aspects of the interaction between charged particles. The electric field (E) represents the force experienced by a unit charge placed in a region around charged particles, while the electric potential (V) quantifies the potential energy per unit charge in that region. To understand their relationship, we need to explore their definitions and how they connect mathematically.
Electric Field
The electric field is a vector quantity that describes the force exerted on a test charge (q) due to other charges in its vicinity. It is given by the formula:
E = F/q
where F is the electric force experienced by the test charge.
The direction of the electric field is the same as the direction of the force acting on a positive test charge placed in that field.
Electric Potential
Electric potential, on the other hand, is a scalar quantity that describes the potential energy per unit charge at a point in space. It is given by the formula:
V = W/q
where W is the work done to move the test charge from infinity to that point in the electric field. Electric potential is often expressed in volts (V).
Connecting Electric Field and Electric Potential
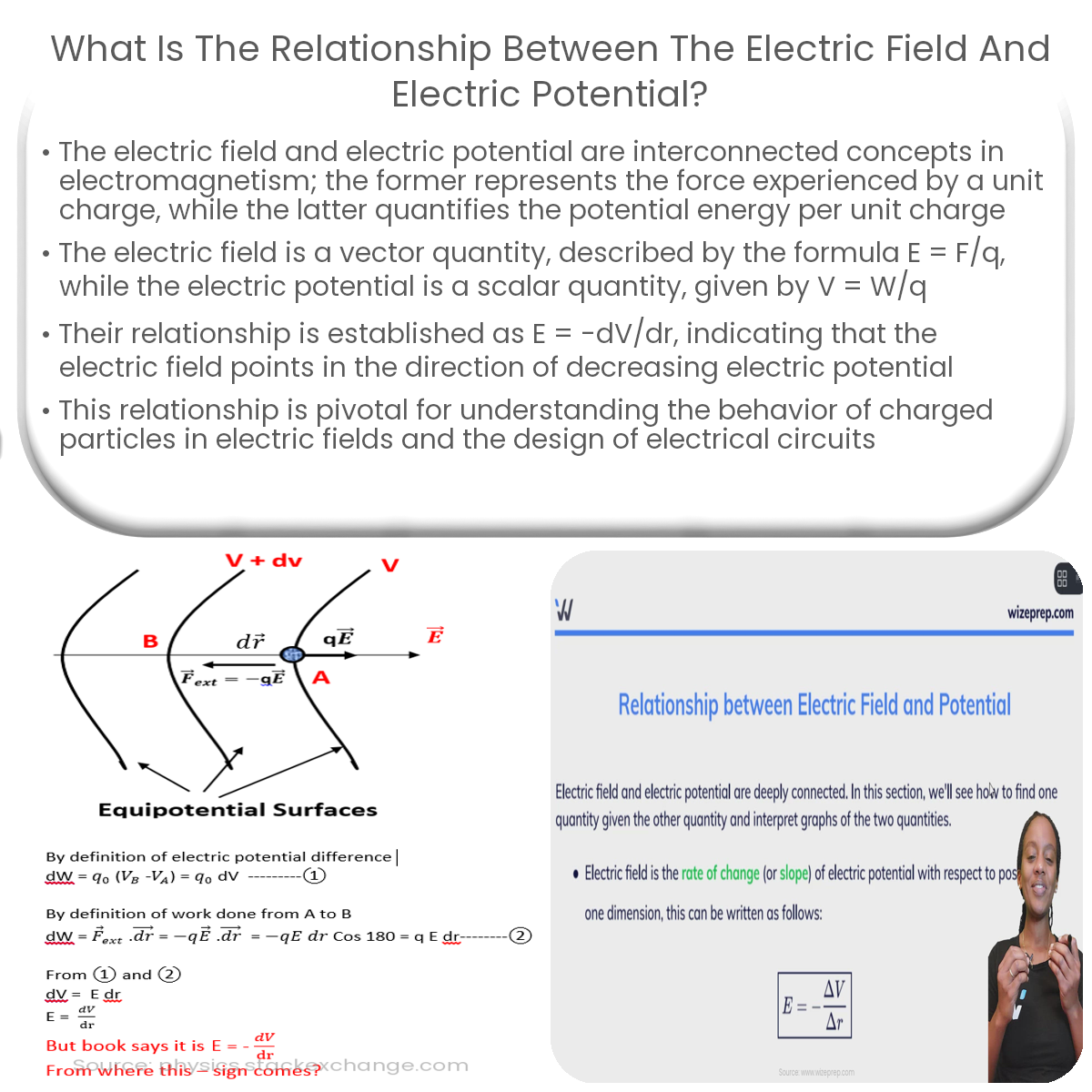
The relationship between the electric field and electric potential can be established by considering the work done on a test charge moving in the electric field. This relationship is given by:
E = -dV/dr
where dV is the change in electric potential, dr is the displacement in the direction of the field, and the negative sign indicates that the electric field points in the direction of decreasing electric potential.
Implications of the Relationship
The relationship between the electric field and electric potential highlights several important points:
- The electric field points in the direction of the steepest decrease in electric potential.
- Since the electric field is a vector and electric potential is a scalar, they are related through a gradient operation.
- The relationship is valid for both static and time-varying electric fields, making it a powerful tool in the analysis of electric fields and circuits.
In summary, the electric field and electric potential are interrelated, with the electric field describing the force on a test charge, while the electric potential provides information about the potential energy associated with the charge. The relationship between the two quantities helps in understanding the behavior of charged particles in electric fields and the design of electrical circuits.