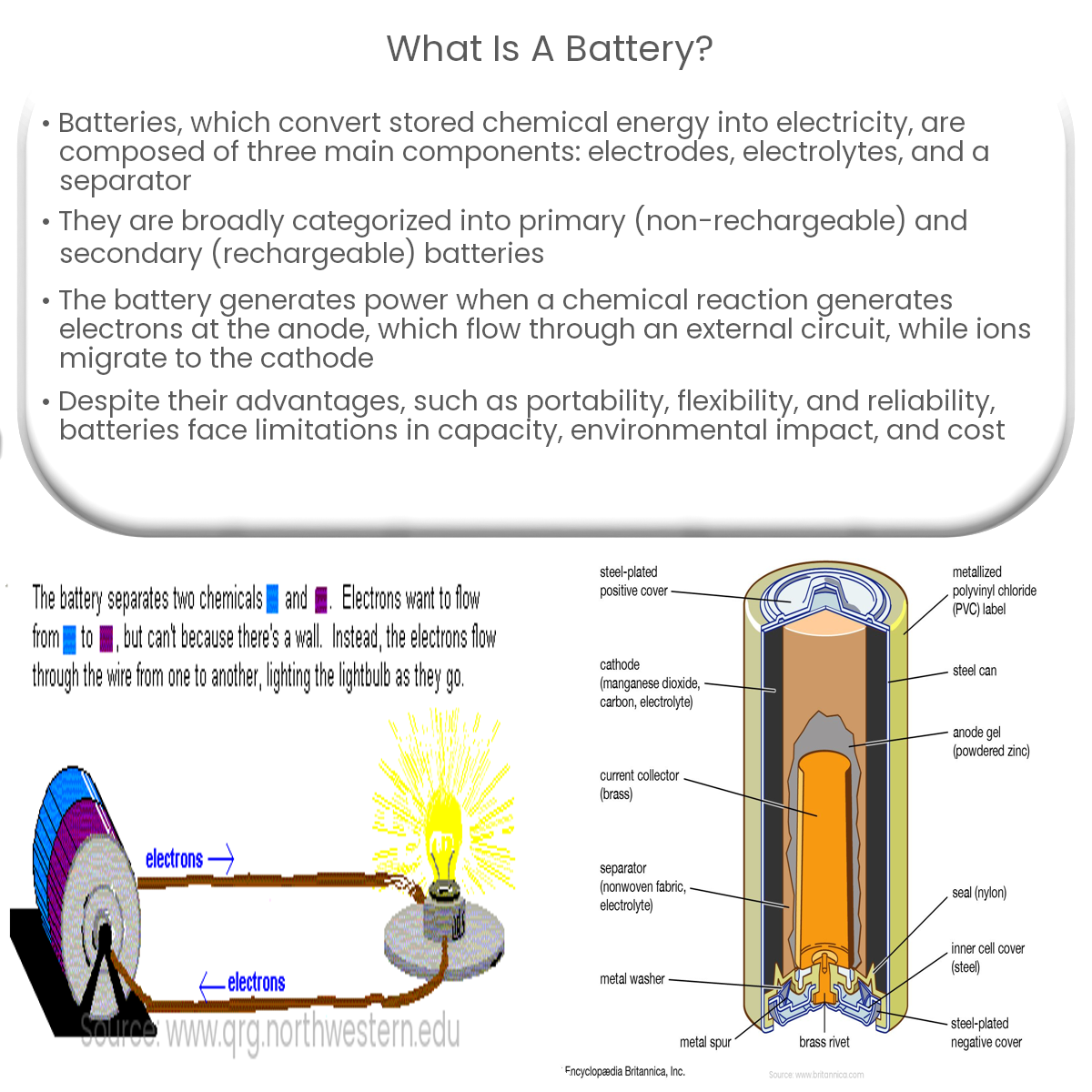
A battery stores electrical energy as chemical energy, which is converted back into electrical energy when needed for various applications.
Introduction to Batteries
A battery is a device that stores electrical energy in the form of chemical energy and converts it into electrical energy when needed. Batteries are widely used in various applications, ranging from powering small electronic devices to electric vehicles and renewable energy systems.
Components of a Battery
A battery typically consists of three main components:
- Electrodes: Two electrodes, the anode (negative) and the cathode (positive), are the current-carrying conductors within the battery.
- Electrolyte: The electrolyte is a medium that allows the flow of ions between the anode and the cathode, facilitating the chemical reactions that produce electricity.
- Separator: A separator is an insulating material that prevents direct contact between the anode and the cathode, preventing short circuits.
Types of Batteries
Batteries can be broadly classified into two types:
- Primary Batteries: These are non-rechargeable batteries that convert stored chemical energy into electrical energy through irreversible electrochemical reactions. Once the chemicals are depleted, the battery is discarded. Examples include alkaline and zinc-carbon batteries.
- Secondary Batteries: Also known as rechargeable batteries, these can be recharged by applying an external voltage to reverse the electrochemical reactions. Examples include lead-acid, nickel-cadmium (NiCd), nickel-metal hydride (NiMH), and lithium-ion batteries.
How Batteries Work
When a battery is connected to a circuit, a chemical reaction occurs at the anode, generating electrons. The electrons flow through the external circuit, providing power to the connected devices. At the same time, ions in the electrolyte migrate to the cathode, where another chemical reaction occurs, consuming the electrons. The battery continues to produce electricity until the chemicals are exhausted or the reactions reach equilibrium.
Advantages and Limitations of Batteries
Batteries offer several advantages:
- Portability: They are compact and can be easily integrated into various devices.
- Flexibility: Batteries are available in different sizes, capacities, and chemistries to suit specific applications.
- Reliability: They provide a stable and continuous power source when needed.
However, batteries also have some limitations:
- Capacity: The energy storage capacity of batteries is limited, requiring frequent recharging or replacement.
- Environmental Impact: The production, disposal, and recycling of batteries can have a negative impact on the environment.
- Cost: High-capacity and advanced batteries can be expensive, impacting the overall cost of devices and systems.