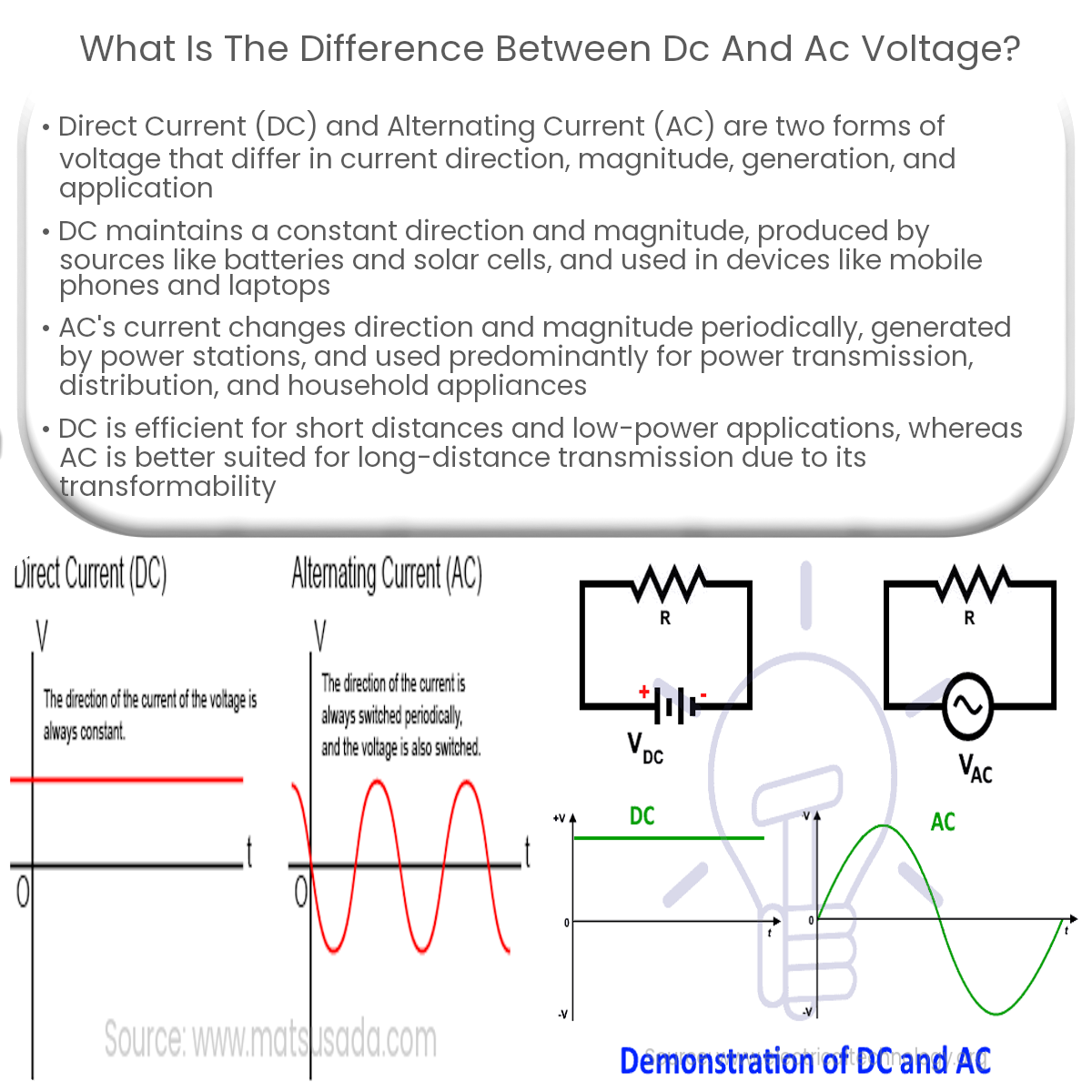
DC voltage has constant direction and magnitude, while AC voltage periodically changes direction and magnitude, affecting their applications.
Difference between DC and AC Voltage
Direct Current (DC) and Alternating Current (AC) are two types of voltage that are used to transmit electrical energy. Although both serve a similar purpose, they differ in how they deliver power and their applications. This article will explore the key differences between DC and AC voltage.
Direct Current (DC) Voltage
DC voltage is a constant voltage that flows in one direction. In DC circuits, the electrical current always flows from the positive terminal to the negative terminal, with a steady magnitude. DC voltage sources include batteries, fuel cells, and solar cells. Common applications for DC voltage are electronic devices such as mobile phones, laptops, and LED lights.
Alternating Current (AC) Voltage
AC voltage, on the other hand, is a type of voltage where the direction and magnitude of the current periodically change. The electrical current in AC circuits alternates between flowing forward and backward, following a sinusoidal waveform. AC voltage is generated by power stations and is the most common form of voltage used for power transmission and distribution. It is also used to power household appliances and industrial machinery.
Key Differences
- Direction of Current: DC voltage maintains a constant direction of current flow, while AC voltage changes direction periodically.
- Magnitude: The magnitude of DC voltage remains constant, whereas the magnitude of AC voltage varies sinusoidally over time.
- Generation: DC voltage is generated by sources such as batteries and solar cells, while AC voltage is produced by power stations using generators.
- Applications: DC voltage is commonly used for electronic devices, while AC voltage is primarily used for power transmission, distribution, and household appliances.
- Efficiency: DC voltage is more efficient for short distances and low-power applications, while AC voltage is more efficient for long-distance power transmission due to its ability to be transformed to higher or lower voltages easily.
In conclusion, DC and AC voltage differ in the direction and magnitude of the current they produce, as well as their generation sources and applications. Understanding the differences between these two types of voltage is essential when designing and operating electrical systems.