Explore the world of voltage regulators, their functions, types, applications, and recent innovations in this comprehensive guide.

Understanding Voltage Regulators
Voltage regulators are integral components in the design of numerous electrical and electronic systems. They serve a critical role in maintaining a constant voltage level, enabling devices to operate smoothly under varying power conditions. In this article, we’ll dive into the world of voltage regulators, looking at their function, types, and uses.
Function of Voltage Regulators
Voltage regulators are devices designed to automatically maintain a constant voltage level. They might be a simple feed-forward design or incorporate negative feedback control loops. It may use an electromechanical mechanism, or electronic components.
They function as an intermediary between the power source and the device, ensuring that the voltage supplied to the device remains stable and within its operational limits, even when there are fluctuations in the input voltage or changes in the load.
Types of Voltage Regulators
There are broadly two types of voltage regulators – linear voltage regulators and switching voltage regulators. Each has its own strengths and limitations, making them suitable for different applications.
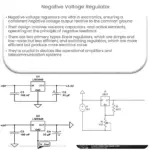
- Linear Voltage Regulators: These are simple and inexpensive voltage regulators that operate by using a voltage-controlled device to drop the input voltage to a desired level. The primary disadvantage of linear regulators is their inefficiency, especially at higher voltage differences between input and output, as the excess power is dissipated as heat.
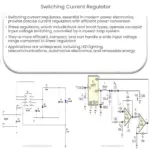
- Switching Voltage Regulators: More efficient than linear regulators, these use a high-frequency switching element like a transistor to convert the input voltage. They can step-up, step-down or invert the input voltage, making them versatile. However, they are more complex and can generate more electrical noise due to the switching action.
In addition, there are also specialized variants like the Low-Dropout (LDO) regulators and the voltage regulator modules (VRM).
Applications of Voltage Regulators
Voltage regulators find application in a wide array of electronic devices. They are critical in maintaining the health of batteries in renewable energy systems, protecting them from overcharging. In computer systems, voltage regulators ensure the microprocessor receives a stable and correct voltage.
The role of voltage regulators extends to automotive systems too, where they maintain the voltage to the vehicle’s electrical systems within acceptable limits, ensuring optimal performance and longevity of the vehicle’s electrical components.
The Working Principle of Voltage Regulators
Regardless of the type, the fundamental principle of a voltage regulator revolves around the concept of feedback. The regulator measures the output voltage, compares it with the reference voltage, and adjusts the pass element to maintain a constant output voltage. This feedback control mechanism ensures a stable voltage, even under varying load and input voltage conditions.
Factors Influencing the Choice of Voltage Regulators
Choosing the right voltage regulator for a specific application requires considering several factors. Among them, the input and output voltage requirements, the maximum load current, power dissipation, efficiency, transient response time, and physical size are crucial.
Moreover, if the application involves sensitive analog circuits or RF circuits, the amount of electrical noise generated by the voltage regulator becomes a deciding factor. In such cases, despite their inefficiency, linear regulators may be preferred due to their low-noise characteristics.
Challenges and Innovations in Voltage Regulators
Despite their advantages, voltage regulators face challenges, primarily related to efficiency, size, and heat dissipation. To overcome these, there have been significant innovations in the field.
- Digital Voltage Regulators: These utilize digital technology to provide higher precision and programmability. They’re typically used in complex applications where tight voltage regulation and communication with a microcontroller are needed.
- Integrated Voltage Regulators: Also known as power management ICs (PMICs), these combine multiple regulators and power management features on a single chip, reducing board space and enabling more efficient power management.
Conclusion
In conclusion, voltage regulators are critical components that ensure the smooth operation of various electrical and electronic systems by maintaining a steady output voltage. Whether it’s a simple linear regulator for low-noise applications or an advanced digital regulator for complex systems, the key to optimal system performance lies in choosing the right voltage regulator based on the application’s specific requirements.
The challenges that voltage regulators face are driving innovation, resulting in more efficient, compact, and sophisticated solutions. As our reliance on electronic devices grows, so will the importance of voltage regulators in our lives.