Mercury cadmium telluride (MCT) is a type of material that has unique properties that make it highly effective for use in infrared sensors.

Mercury Cadmium Telluride (MCT) Infrared Sensor
Mercury cadmium telluride (MCT) is a type of material that has unique properties that make it highly effective for use in infrared sensors. MCT infrared sensors are capable of detecting the infrared radiation emitted by objects, allowing for a wide range of applications in both military and civilian fields.
What is MCT?
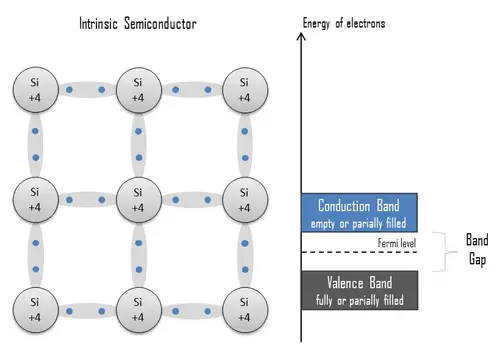
MCT is a semiconductor material that is formed by combining mercury, cadmium, and tellurium. The combination of these elements creates a crystal structure that is able to detect infrared radiation. MCT has several advantages over other infrared materials, including a high sensitivity to infrared radiation and the ability to operate at room temperature.
There are several different types of MCT materials, each with their own unique properties. The most common types of MCT are the ternary alloys HgCdTe and HgZnTe. These materials have a wide range of compositions and bandgaps, allowing for customization to meet the needs of specific applications.
How Do MCT Infrared Sensors Work?
MCT infrared sensors work by detecting the infrared radiation emitted by objects. When infrared radiation hits the surface of an MCT sensor, it creates electron-hole pairs in the material. These electron-hole pairs are then detected and amplified, producing an electrical signal that can be measured and analyzed.
MCT sensors are capable of detecting a wide range of infrared radiation, from short-wavelength radiation (SWIR) to long-wavelength radiation (LWIR). This makes them highly effective for a variety of applications, including night vision, remote sensing, and medical imaging.
Applications of MCT Infrared Sensors
MCT infrared sensors are widely used in both military and civilian applications. In the military, MCT sensors are used for night vision, target tracking, and missile guidance. They are also used in remote sensing applications, such as detecting forest fires or monitoring the Earth’s atmosphere.
In the civilian sector, MCT sensors are used in a variety of applications, including medical imaging, industrial inspection, and remote sensing. They are also used in security applications, such as detecting concealed weapons or monitoring border crossings.
Overall, MCT infrared sensors are a highly effective and versatile technology that has a wide range of applications. With ongoing research and development, it is likely that MCT sensors will continue to be an important technology for many years to come.
Advantages and Disadvantages of MCT Infrared Sensors
MCT infrared sensors have several advantages over other types of infrared sensors. They have a high sensitivity to infrared radiation, which allows them to detect even very low levels of radiation. They also have a high signal-to-noise ratio, which means that they can produce clear images even in low-light conditions. In addition, MCT sensors are capable of operating at room temperature, which eliminates the need for cooling systems and reduces costs.
However, MCT sensors also have some disadvantages. They are expensive to produce, which can limit their use in some applications. They are also sensitive to temperature changes, which can affect their accuracy. Finally, MCT sensors are toxic, as they contain mercury and cadmium. This can make them difficult to dispose of and can pose a risk to human health if not handled properly.
Future of MCT Infrared Sensors
The future of MCT infrared sensors looks promising. Ongoing research and development are focused on improving the performance of MCT sensors, reducing their cost, and addressing their toxicity concerns. One area of research is the development of new MCT materials that are less toxic, such as HgCdTeSe and HgCdTeS. Another area of research is the development of new manufacturing techniques that can reduce costs and improve the quality of MCT sensors.
As technology advances, it is likely that MCT sensors will become even more versatile and effective. They may be used in new applications, such as autonomous vehicles, robotics, and virtual reality. They may also be used in new industries, such as agriculture, where they could be used to monitor crop health and detect pests.
Conclusion
Mercury cadmium telluride (MCT) infrared sensors are a powerful technology that has a wide range of applications in both military and civilian fields. They are capable of detecting the infrared radiation emitted by objects, making them highly effective for night vision, remote sensing, and medical imaging. While they have some disadvantages, ongoing research and development are focused on addressing these concerns and improving the performance and versatility of MCT sensors. As such, MCT sensors are likely to remain an important technology for many years to come.