Explore the world of voltage references, their types, applications, and design considerations in this comprehensive guide.
Understanding Voltage References
A voltage reference is a crucial electronic component that serves as a stable voltage source. It is a standardized and precisely defined voltage, used to calibrate and maintain system accuracy. These are essential in analog-to-digital converters (ADCs), digital-to-analog converters (DACs), and many other applications.
Why Voltage References are Important
Voltage references are essential for a variety of electrical devices. They serve as a central point of stability in circuits where exact voltages are vital. For example, a digital-to-analog converter (DAC) often uses a voltage reference to convert binary numbers into an analog voltage. Without a stable and accurate voltage reference, the resulting signal could vary, leading to inaccurate output.
Types of Voltage References
- Zener Diode Voltage References: This is the simplest form of voltage references. A Zener diode operates in its breakdown region to provide a stable reference voltage. However, it has a relatively high temperature coefficient and noise level.
- Bandgap Voltage References: These types of voltage references use a combination of positive and negative temperature coefficients to create a voltage that remains stable over temperature. This type offers a lower noise level and better stability compared to Zener diode references.
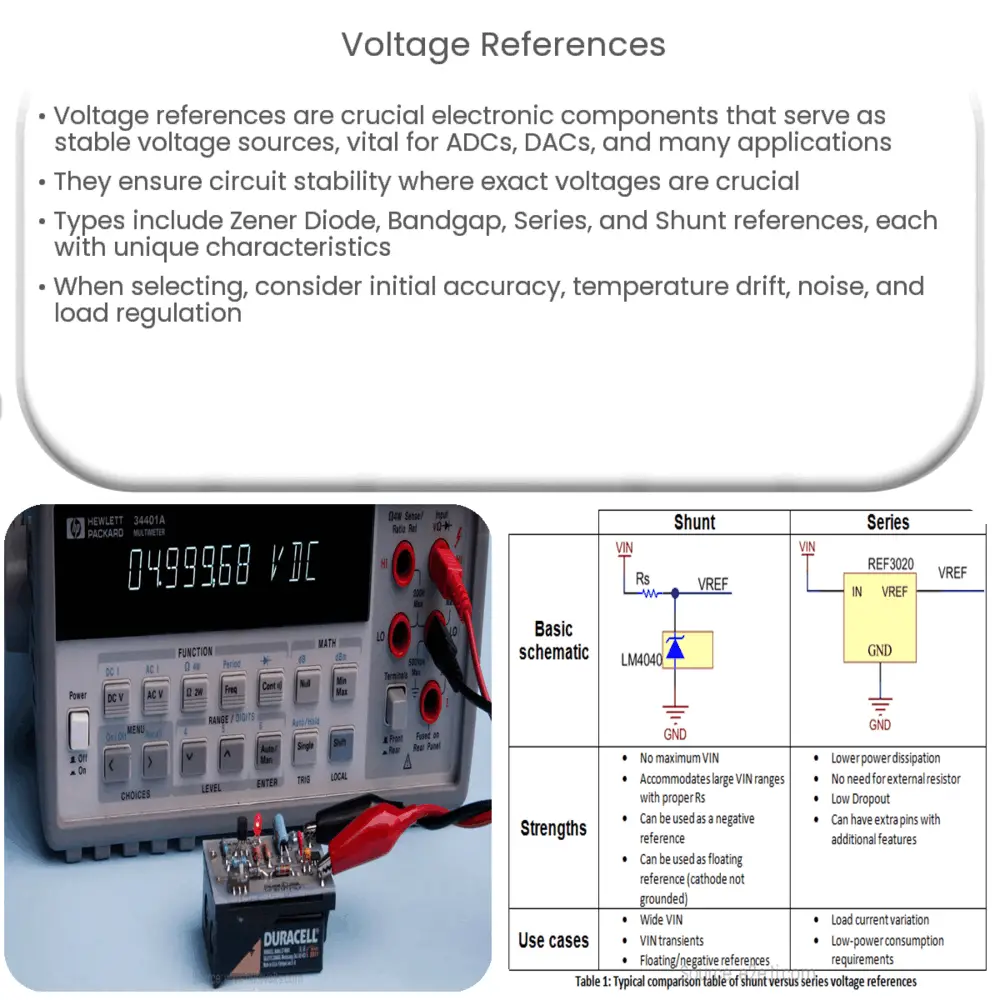
- Series Voltage References: In a series voltage reference, the reference device and error amplifier are connected in series with the load. This results in higher performance and improved noise rejection, albeit at a slightly higher cost.
- Shunt Voltage References: Here, the reference device and error amplifier are in parallel with the load. This configuration offers the advantage of simplicity and low cost.
Parameters to Consider
When choosing a voltage reference, several parameters come into play. These include:
- Initial Accuracy: This refers to the reference’s voltage output at room temperature. It’s usually expressed as a percentage of the output voltage or in millivolts.
- Temperature Drift: This is the change in output voltage due to variations in ambient temperature. It’s typically denoted in ppm/°C (parts per million per degree Celsius).
- Noise: This parameter is an important consideration in precision applications. It represents the high-frequency fluctuations around the nominal output voltage.
- Load Regulation: This refers to the change in output voltage due to changes in load current.
- Line Regulation: This is the change in output voltage due to changes in input voltage.
These are just a few insights into voltage references. Their role in the world of electronics is undeniably critical, enabling consistent and accurate operation across a plethora of applications.
Applications of Voltage References
Voltage references find wide-ranging applications in various electronic and electrical systems. Here are a few of them:
- Analog-to-Digital and Digital-to-Analog Converters: ADCs and DACs use voltage references to ensure accurate conversion processes. These converters are widely used in telecommunications, audio equipment, and many other digital systems.
- Power Supply: Power supplies often use voltage references to stabilize their output and reduce fluctuation.
- Instrumentation: Precision instruments, such as multimeters and oscilloscopes, use voltage references to calibrate their readings and ensure measurement accuracy.
- Battery Chargers: In battery chargers, voltage references are used to regulate the charging process, ensuring the battery is neither undercharged nor overcharged.
Voltage Reference Design Considerations
Designing with voltage references requires a clear understanding of the requirements and constraints of the application at hand. The choice of voltage reference type, initial accuracy, temperature drift, noise, load regulation, and line regulation all must be carefully considered. Additionally, the power supply voltage, load current requirements, thermal considerations, and budget also play a critical role in determining the right voltage reference for the job.
Conclusion
Despite their simplicity, voltage references play a fundamental role in electronic systems. They ensure accuracy, stability, and performance across an array of applications, from basic household devices to sophisticated instrumentation and communication systems. Understanding their functioning, types, parameters, and application areas helps in choosing the right voltage reference for your specific needs, ultimately leading to more reliable and efficient electronic designs.
With the continual evolution of electronics and ever-growing demand for high-precision applications, the significance of voltage references is only poised to increase. So, whether you are an electronics enthusiast, a budding engineer, or a seasoned professional, staying well-versed with voltage references and their nuances can greatly enhance your grasp over electronics design and troubleshooting.

