A photovoltaic infrared sensor is a device that detects infrared radiation and converts it into an electrical signal. It is a self-contained, low-power device used in security, environmental monitoring, medical equipment, and industrial applications.
Photovoltaic Infrared Sensor: Understanding its Function and Applications
A photovoltaic infrared sensor is a device that can detect the presence of infrared radiation and convert it into an electrical signal. This sensor is commonly used in a wide range of applications, including security systems, environmental monitoring, and medical equipment. In this article, we will explore the function of a photovoltaic infrared sensor and its various applications.
How Does a Photovoltaic Infrared Sensor Work?
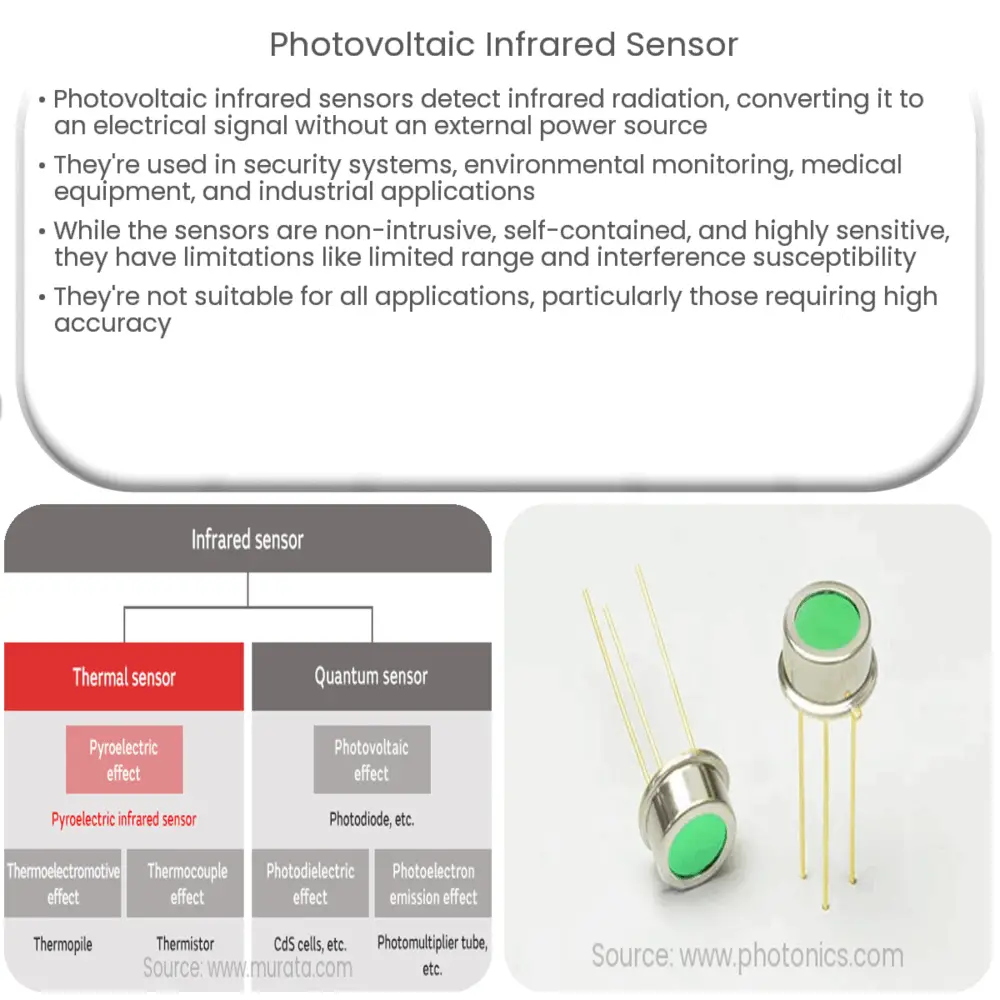
A photovoltaic infrared sensor consists of a material that can absorb infrared radiation and convert it into an electrical signal. This material is usually made of a semiconductor material, such as silicon or germanium, which can absorb photons of infrared radiation and release electrons.
When infrared radiation enters the sensor, it is absorbed by the semiconductor material, creating a flow of electrons that generates an electrical current. This current is then amplified and measured by the sensor’s electronic circuitry, which can then determine the presence and intensity of the infrared radiation.
One of the advantages of a photovoltaic infrared sensor is its ability to detect infrared radiation without the need for an external power source. The sensor can generate its own electrical signal from the absorbed radiation, making it a self-contained and low-power device.
Applications of Photovoltaic Infrared Sensors
Photovoltaic infrared sensors are used in a wide range of applications, including:
Security Systems
Photovoltaic infrared sensors are commonly used in security systems to detect the presence of intruders. The sensors can detect the heat emitted by a person’s body, even in complete darkness, making them an effective tool for detecting unwanted visitors.
Environmental Monitoring
Photovoltaic infrared sensors can be used to monitor environmental conditions, such as temperature and humidity. The sensors can detect the infrared radiation emitted by objects in the environment, providing a non-intrusive way to monitor conditions without disturbing the environment.
Medical Equipment
Photovoltaic infrared sensors are used in medical equipment, such as blood glucose monitors, to detect the presence of glucose in a patient’s blood. The sensors can detect the infrared radiation emitted by glucose molecules, providing a non-invasive and painless way to monitor blood glucose levels.
Industrial Applications
Photovoltaic infrared sensors are also used in industrial applications, such as detecting leaks in pipelines and monitoring the temperature of machinery. The sensors can detect the infrared radiation emitted by leaking gases or overheating machinery, providing an early warning of potential problems.
Conclusion
Photovoltaic infrared sensors are versatile and useful devices that can detect the presence of infrared radiation and convert it into an electrical signal. These sensors are used in a wide range of applications, including security systems, environmental monitoring, and medical equipment. Their ability to detect infrared radiation without an external power source makes them a self-contained and low-power device, making them an attractive option for many applications.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Photovoltaic Infrared Sensors
Like any technology, photovoltaic infrared sensors have their advantages and disadvantages. Here are some of the pros and cons of using these sensors:
Advantages:
- Non-intrusive: Photovoltaic infrared sensors can detect infrared radiation without the need for physical contact with the object or environment being monitored.
- Self-contained: These sensors generate their own electrical signal from the absorbed radiation, making them a self-contained and low-power device.
- High sensitivity: Photovoltaic infrared sensors are highly sensitive and can detect even small amounts of infrared radiation.
- Wide range of applications: These sensors are used in a wide range of applications, from security systems to medical equipment, making them a versatile technology.
Disadvantages:
- Limited range: Photovoltaic infrared sensors have a limited range and can only detect infrared radiation within a certain distance from the sensor.
- Not suitable for all applications: These sensors are not suitable for applications where high accuracy is required, such as temperature measurement in industrial processes.
- Interference: Photovoltaic infrared sensors can be affected by interference from other sources of infrared radiation, such as sunlight or other heat sources.
Conclusion
Photovoltaic infrared sensors are a useful and versatile technology that can detect the presence of infrared radiation and convert it into an electrical signal. These sensors are commonly used in security systems, environmental monitoring, and medical equipment, among other applications. While they have their limitations, such as a limited range and susceptibility to interference, photovoltaic infrared sensors offer many advantages, such as being non-intrusive, self-contained, and highly sensitive.



