Explore the intricacies of turbine flow meters, their components, types, applications, and maintenance for optimized industrial usage.
Introduction to Turbine Flow Meters
Turbine flow meters are an essential instrument in the measurement and control of liquid flow within various industries. These devices translate the mechanical action of the turbine rotating in the liquid flow around an axis into user-readable output.
Operating Principle of Turbine Flow Meters
Turbine flow meters operate on the principle of mechanical motion. The main component of these devices is a multi-bladed rotor, or turbine, which is placed centrally in the flow of the liquid. The flowing liquid engages the turbine, causing it to spin. The speed of rotation is directly proportional to the velocity of the liquid, allowing the flow rate to be determined.
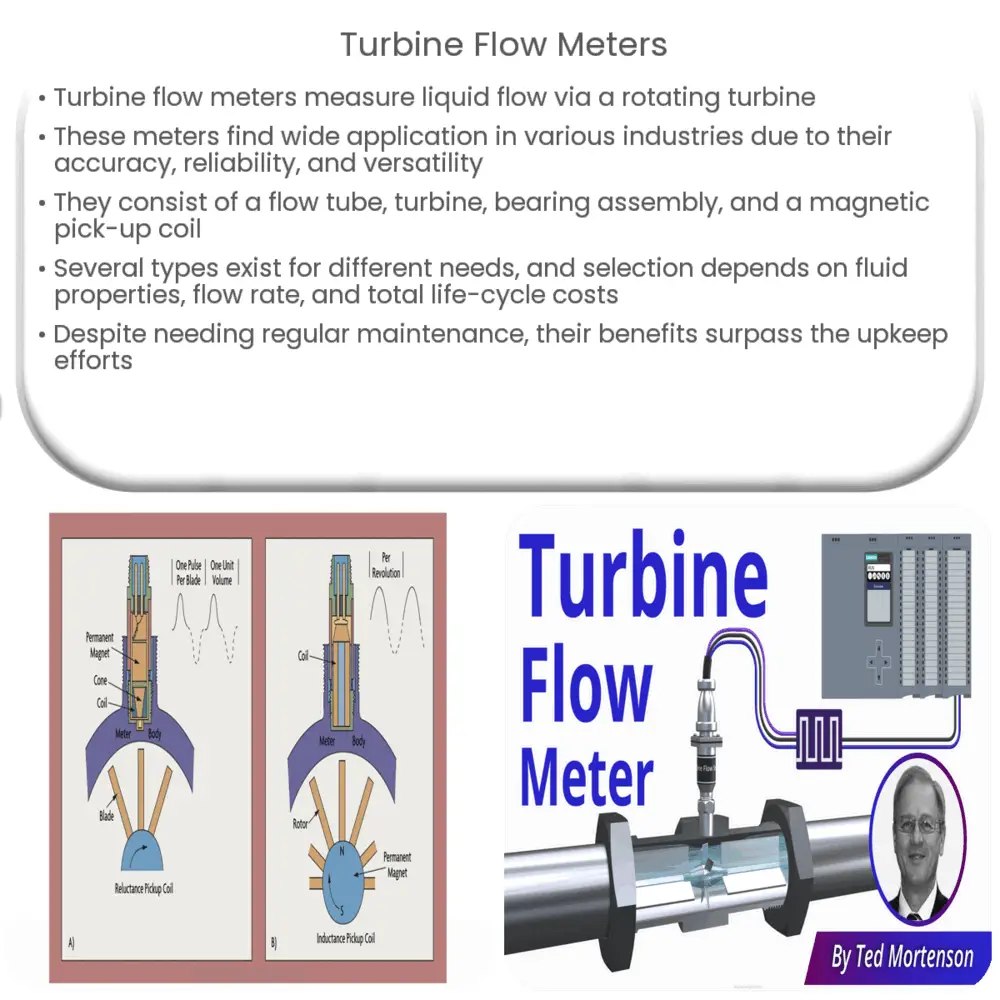
Components of Turbine Flow Meters
- Flow Tube: This is the housing that contains the liquid and the turbine. It’s generally constructed of a robust material like stainless steel to withstand high pressure and corrosive liquids.
- Turbine: As already mentioned, this is the central component of the meter. It rotates when it comes into contact with the flowing liquid.
- Bearing Assembly: The turbine rotates on this assembly. It must be of high quality to ensure minimal friction and long service life.
- Magnetic Pick-up Coil: This component detects and counts the rotations of the turbine.
Applications of Turbine Flow Meters
Turbine flow meters find usage in a wide range of industries due to their accuracy, reliability, and versatility. Some of their prominent applications include:
- Oil and gas industry for hydrocarbon fluid measurements
- Water treatment plants for monitoring water flow
- Food and beverage industry for managing liquid ingredients
- Pharmaceutical industry for controlling the flow of critical fluids
Advantages and Disadvantages
Turbine flow meters offer several advantages, such as high accuracy and repeatability, a wide range of flow rates and fluid compatibility, and availability in a wide variety of sizes. However, they also have a few limitations, including susceptibility to wear and tear due to the mechanical nature of the turbine and sensitivity to flow profile distortions.
Maintenance of Turbine Flow Meters
Like all mechanical devices, turbine flow meters require regular maintenance to perform optimally. Regular inspection and cleaning help prevent the build-up of debris that could potentially obstruct the flow or damage the turbine. The bearing assembly, a critical component, requires special attention due to its constant interaction with the moving parts.
Turbine Flow Meter Types
There are several different types of turbine flow meters designed to meet the varying needs of industries:
- Single Jet Turbine Flow Meters: These have a single jet of fluid engaging the turbine.
- Multiple Jet Turbine Flow Meters: In these meters, multiple jets of fluid impinge on the turbine.
- Insertion Turbine Flow Meters: These are installed into a pipe to measure the flow within and can be removed when not in use.
- Inline Turbine Flow Meters: These are directly installed in the flow path.
Choosing a Turbine Flow Meter
When selecting a turbine flow meter, it’s crucial to consider the fluid’s properties, such as its viscosity and corrosiveness, the required flow rate range, the acceptable pressure drop, and the necessary level of accuracy. One should also consider the total life-cycle costs, including initial purchase, installation, operation, maintenance, and calibration costs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, turbine flow meters are a valuable tool for precise and reliable fluid flow measurement across many industries. Their versatile application, paired with their high degree of accuracy, makes them an essential part of modern industry operations. Though they require regular maintenance due to their mechanical nature, the benefits they offer in terms of cost-effectiveness and adaptability across a range of conditions and liquids far outweigh the upkeep efforts. By understanding their principles, types, advantages, and limitations, users can select the most appropriate turbine flow meter for their specific needs and ensure optimal performance in their respective applications.

