Shielded cables reduce EMI/RFI interference, ensuring signal integrity and reliability in various applications like telecom, audio/video, and industrial automation.
Understanding Shielded Cables: An In-Depth Guide
Introduction
Electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI) are two common issues that can significantly impact the performance of electronic devices and systems. One way to mitigate these problems is by using shielded cables. This article aims to provide an in-depth understanding of shielded cables, their types, applications, and benefits.
What are Shielded Cables?
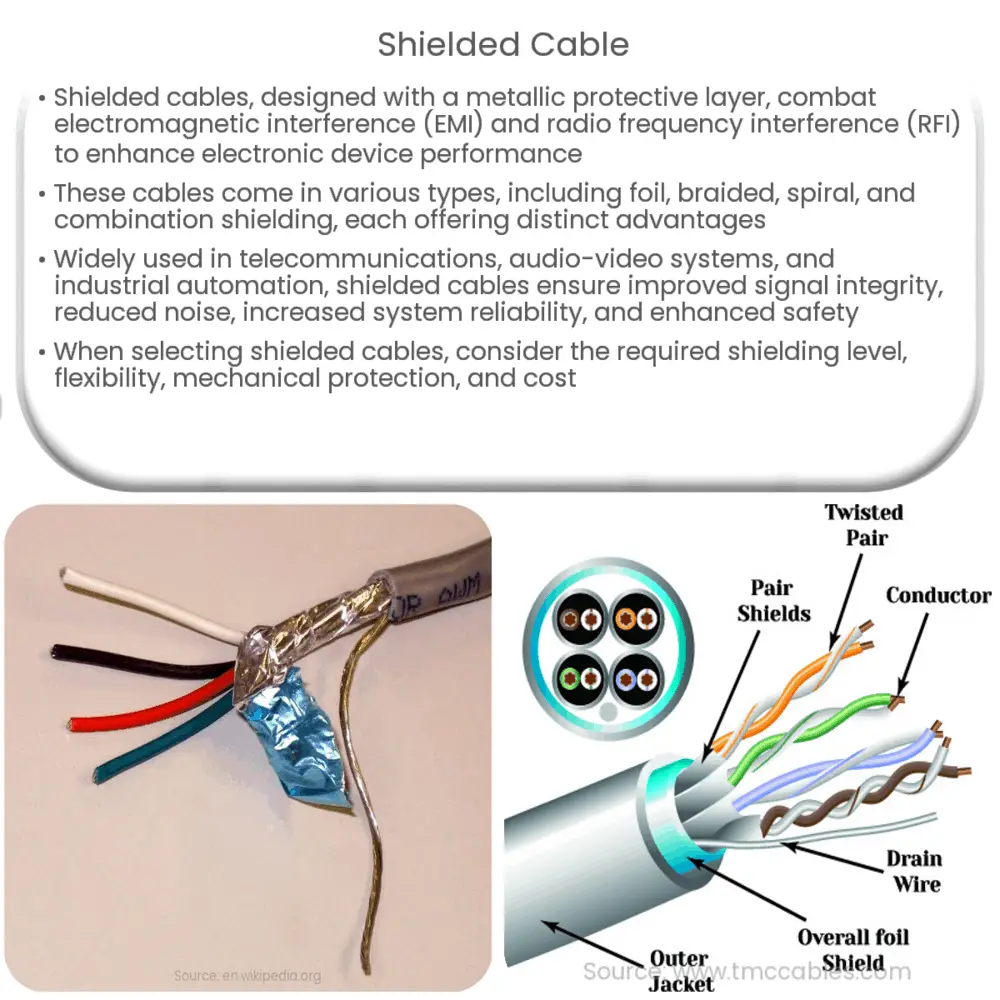
Shielded cables, also known as screened cables, are electrical cables that are designed with a protective outer layer, typically made from a metallic material, such as copper or aluminum. This shielding layer is intended to block or minimize the impact of external electromagnetic fields (EMF) on the conductors within the cable. By reducing EMI and RFI, shielded cables ensure the integrity of the signal being transmitted and improve the overall performance of electronic devices and systems.
Types of Shielded Cables
There are several types of shielded cables, each designed to address specific shielding requirements. These include:
- Foil shielding: Foil shielding involves wrapping the cable’s conductors in a thin layer of aluminum foil. This type of shielding is lightweight, cost-effective, and provides excellent coverage. However, it may not offer the same level of mechanical protection as other shielding types.
- Braided shielding: Braided shielding consists of woven strands of metal (usually copper) that cover the cable’s conductors. This type of shielding offers excellent mechanical protection and flexibility but may not provide complete coverage due to the small gaps between the woven strands.
- Spiral shielding: Spiral shielding uses helically-wrapped metal strands to cover the cable’s conductors. This type of shielding provides good flexibility and coverage but may not offer the same level of mechanical protection as braided shielding.
- Combination shielding: Combination shielding uses multiple layers of shielding, such as foil and braid, to maximize EMI and RFI protection. This type of shielding offers excellent coverage and mechanical protection, but it may be more expensive and less flexible than other options.
Applications of Shielded Cables
Shielded cables are widely used in various industries and applications where EMI and RFI protection is critical. Some of these applications include:
- Telecommunications: Shielded cables are used in telephone and data transmission lines to maintain signal integrity and minimize interference from external sources.
- Audio and video systems: Shielded cables help prevent signal degradation and interference in audio and video equipment, such as home theater systems, professional audio systems, and broadcasting equipment.
- Industrial automation: In manufacturing plants and other industrial settings, shielded cables are essential to protect sensitive equipment and ensure reliable communication between devices and systems.
Benefits of Using Shielded Cables
Using shielded cables in various applications offers numerous benefits, such as:
- Improved signal integrity: Shielded cables help maintain the quality of the signal being transmitted, reducing the risk of signal degradation due to EMI and RFI.
- Reduced noise and interference: Shielding in cables minimizes the impact of external noise sources, ensuring reliable and accurate data transmission.
- Increased system reliability: With reduced interference and improved signal integrity, shielded cables contribute to the overall reliability of electronic devices and systems.
- Enhanced safety: In some applications, shielded cables can help reduce the risk of electrical hazards, such as short circuits and electrical fires, by providing additional insulation and protection.
Considerations When Choosing Shielded Cables
When selecting shielded cables for your application, there are several factors to consider:
- Level of shielding required: Assess the potential EMI and RFI sources in your environment to determine the appropriate shielding type and coverage needed.
- Flexibility: If the cables will be subject to frequent bending or movement, choose a shielding type that offers sufficient flexibility without compromising on EMI and RFI protection.
- Mechanical protection: In environments where cables may be exposed to physical stress or damage, consider shielded cables with robust mechanical protection, such as braided or combination shielding.
- Cost: Compare the costs of different shielded cable types, keeping in mind that a higher initial investment may result in better long-term performance and reliability.
Conclusion
Shielded cables are an essential component in many electronic systems, providing protection against EMI and RFI to ensure reliable signal transmission and overall performance. Understanding the different types of shielded cables, their applications, and benefits can help you make an informed decision when selecting the best cable solution for your specific needs. By carefully considering the level of shielding, flexibility, mechanical protection, and cost, you can choose the right shielded cable to optimize your system’s performance and reliability.

