Explore the intriguing world of Repulsion Motors, their mechanics, types, applications, challenges, and future in this comprehensive guide.
Introduction to Repulsion Motors
Repulsion motors are unique types of electric motors that exhibit fascinating properties. Known for their impressive starting torque, they are used in applications where a high initial torque is required. These motors utilize the principle of repulsion between similar poles to produce motion. Let’s delve into the intricate details of this subject.
The Mechanics of Repulsion Motors
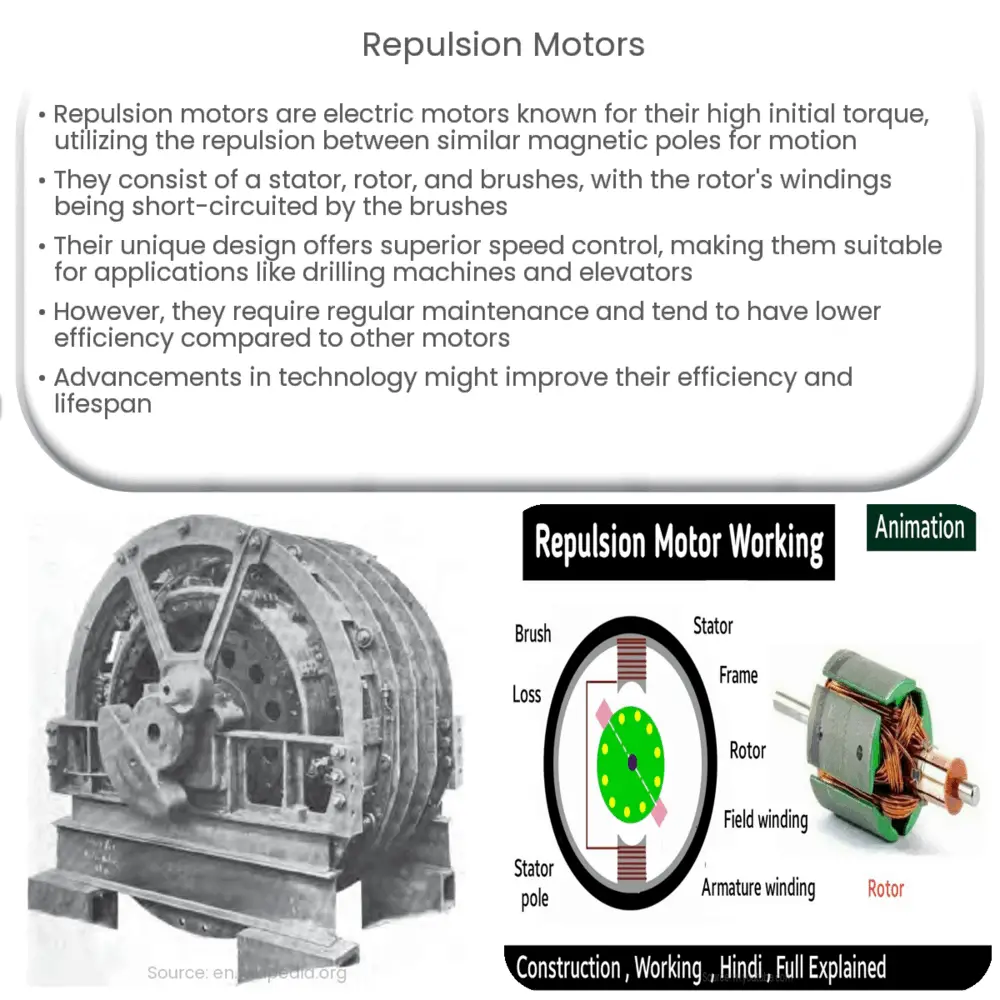
At its core, the construction of a repulsion motor is similar to that of a DC motor. It primarily includes a stator, rotor, and brushes. However, unlike conventional DC motors, the windings of the rotor are short-circuited by the brushes rather than connected to a power source. The stator field creates magnetic poles on the rotor, but the location of these poles is altered by shifting the brushes, creating a force that induces rotation.
- Stator: The stator is the stationary part of the motor, which includes a field winding around the iron core. When a current passes through this winding, it creates a magnetic field.
- Rotor: The rotor, also known as the armature, contains the conductors where the current is induced. It is designed in such a way that it can rotate around the stator.
- Brushes: Brushes in a repulsion motor are used for short-circuiting the rotor conductors rather than supplying current.
The Repulsion Principle
The underlying principle of the repulsion motor is founded on the repulsion that occurs between like magnetic poles. When the stator winding is energized, it creates magnetic poles on the rotor. By adjusting the brushes, we can change the location of these poles, creating a repulsion between the stator and rotor poles. This repulsion force is the driving factor behind the motor’s rotation.
Advantages and Applications of Repulsion Motors
Repulsion motors are known for their high starting torque, making them ideal for applications where this property is required. Additionally, they exhibit a great speed control range. Their inherent design allows for a high degree of regulation in terms of speed, which can be extremely beneficial in certain scenarios. Repulsion motors find widespread use in various fields, such as in drilling machines, printing presses, and elevators, where the high starting torque and speed control are crucial.
Types of Repulsion Motors
Repulsion motors can be categorized into different types based on their design and operation. Each type has its distinct features and suitable applications.
- Repulsion Start Induction Run Motors: These are a hybrid of a repulsion and an induction motor. They start as a repulsion motor to provide high starting torque and then operate as an induction motor for smoother operation.
- Repulsion Induction Motors: These motors have both the repulsion winding and the squirrel cage winding on the rotor. The repulsion winding aids in starting the motor while the squirrel cage provides continuous operation after starting.
- All Repulsion Motors: In these motors, the entire operation, from starting to running, is based on the repulsion principle. They offer excellent speed control but are generally less efficient.
Challenges and Limitations of Repulsion Motors
While repulsion motors offer various advantages, they also come with certain limitations. One significant challenge associated with repulsion motors is that they require regular maintenance due to the mechanical wear and tear of the brushes and commutator. Additionally, their efficiency tends to be lower compared to other types of electric motors.
Future of Repulsion Motors
Despite the challenges, advancements in technology and materials science are paving the way for improving the performance and efficiency of repulsion motors. For instance, the development of brushless designs and the use of superior materials for the brushes and commutator can significantly reduce maintenance requirements and enhance the motor’s lifespan.
Conclusion
Repulsion motors, with their high starting torque and excellent speed control, have carved out a significant niche in many industrial applications. However, they are not without their challenges, particularly in terms of maintenance and efficiency. Looking forward, advancements in technology and materials offer the potential for these motors to become even more effective and efficient, thereby expanding their usability in a wider range of applications.



