Optical force sensors measure force using light properties, offering high sensitivity, EMI immunity, and resistance to harsh environments.
Optical Force Sensors: Revolutionizing Force Measurements
Introduction
Optical force sensors are a cutting-edge technology that has rapidly gained popularity in recent years due to their numerous advantages over traditional force sensing methods. These sensors have become an essential tool for a wide range of applications, including robotics, healthcare, aerospace, and manufacturing, among others. This article delves into the fundamentals of optical force sensors, their working principles, and their diverse applications across various industries.
What are Optical Force Sensors?
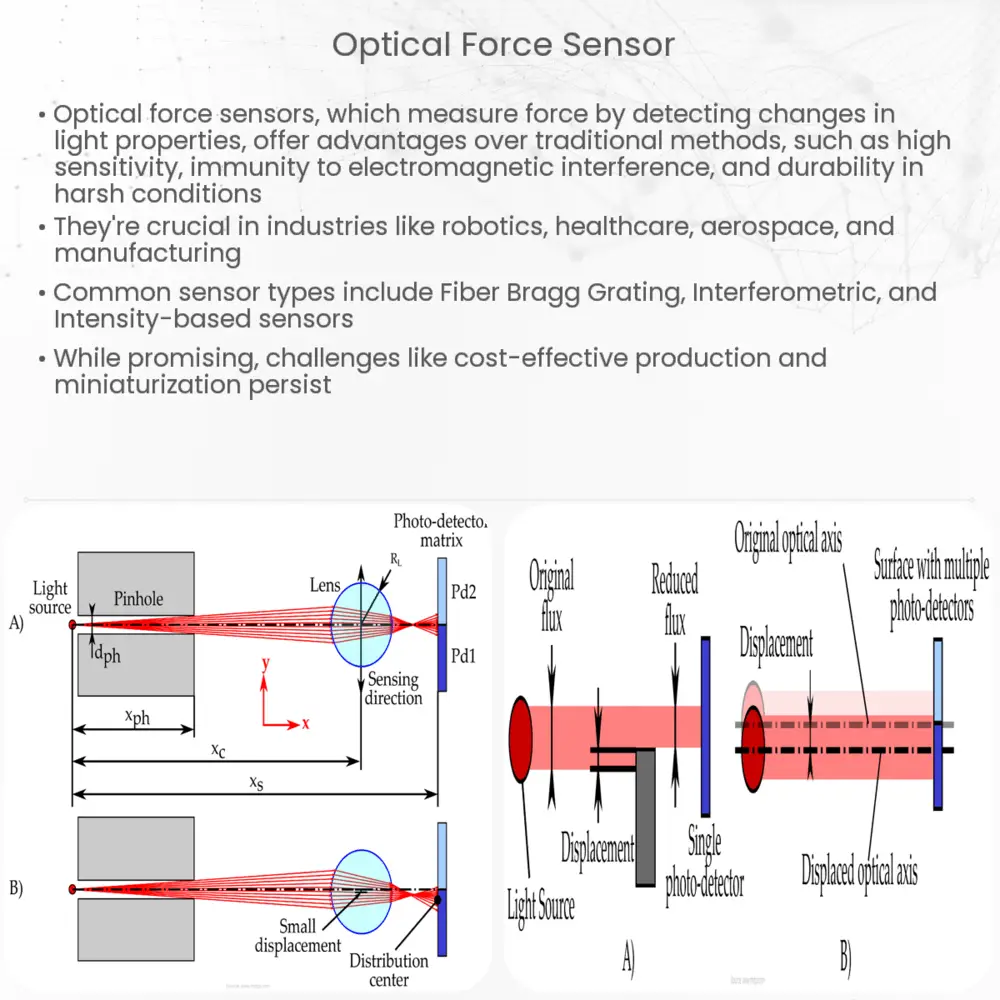
Optical force sensors are devices that measure force by detecting changes in light properties, such as intensity, wavelength, or polarization. Unlike conventional force sensors that rely on mechanical or electrical means to measure force, optical force sensors offer several advantages, including high sensitivity, immunity to electromagnetic interference (EMI), and the ability to operate in harsh environments. These features make optical force sensors suitable for a wide range of applications where traditional sensing methods may not be feasible.
How Do Optical Force Sensors Work?
Optical force sensors operate based on various principles, depending on the type of sensor and the application. Some of the most common working principles include:
Fiber Bragg Grating (FBG) Sensors
Fiber Bragg Grating (FBG) sensors consist of a fiber optic cable with periodic variations in its refractive index, which cause certain wavelengths of light to be reflected while others pass through. When a force is applied to the fiber, the Bragg wavelength shifts, providing an accurate measure of the force. FBG sensors are renowned for their high sensitivity, compact size, and immunity to EMI, making them ideal for use in various applications.
Interferometric Sensors
Interferometric sensors use the interference of light waves to measure force. When a force is applied to the sensing element, it causes a change in the optical path length, leading to a change in the interference pattern. By measuring this change, the applied force can be accurately determined. Interferometric sensors are highly sensitive and can measure very small forces with great precision.
Intensity-based Sensors
Intensity-based optical force sensors rely on changes in light intensity to measure force. As the force is applied to the sensing element, it causes a change in the light intensity, which is then detected and converted into an electrical signal proportional to the force. These sensors are relatively simple, cost-effective, and can operate over a wide range of forces.
Advantages of Optical Force Sensors
Optical force sensors offer several benefits over traditional force sensing methods, making them highly attractive for various applications. Some of these advantages include:
- High sensitivity: Optical force sensors can measure very small forces with high precision, making them suitable for applications that require accurate force measurements.
- Immunity to EMI: Since optical force sensors do not rely on electrical signals, they are immune to electromagnetic interference, making them ideal for use in environments with high levels of EMI.
- Resistance to harsh environments: Optical force sensors can operate in extreme temperatures, corrosive environments, and high-pressure conditions, making them suitable for applications in industries such as aerospace, oil and gas, and automotive.
- Remote sensing capabilities: Optical force sensors can be used for remote sensing applications, allowing for real-time monitoring of force measurements over long distances.
Applications of Optical Force Sensors
Thanks to their numerous advantages, optical force sensors have found applications in a wide range of industries and sectors. Some of the most prominent applications include:
Robotics and Automation
Optical force sensors are increasingly being used in robotics and automation for tasks such as gripping, assembly, and manipulation. Their high sensitivity and immunity to EMI enable accurate force feedback and control, leading to enhanced performance and efficiency in robotic systems.
Healthcare and Biomedical
In the healthcare and biomedical sectors, optical force sensors are used for applications such as surgical instruments, diagnostic tools, and rehabilitation devices. Their ability to operate in harsh environments and provide accurate force measurements make them well-suited for these applications.
Aerospace and Defense
Optical force sensors are employed in various aerospace and defense applications, including structural health monitoring, vibration analysis, and load monitoring. Their resistance to extreme temperatures, corrosive environments, and high pressures make them ideal for the demanding conditions found in these industries.
Manufacturing and Industrial
Optical force sensors play a crucial role in manufacturing and industrial applications, such as quality control, material testing, and process monitoring. Their high sensitivity, immunity to EMI, and remote sensing capabilities enable precise and reliable force measurements in a variety of industrial settings.
Future Outlook and Challenges
As technology advances, optical force sensors are expected to become even more sophisticated and widely adopted across various industries. Researchers are continuously working to develop new sensing techniques, materials, and designs to improve the performance, sensitivity, and durability of optical force sensors.
Despite their numerous advantages, some challenges still need to be addressed to further expand the use of optical force sensors. These challenges include the development of cost-effective manufacturing techniques, miniaturization of the sensors for specific applications, and improving the sensors’ long-term stability and reliability.
Conclusion
Optical force sensors have emerged as a promising alternative to traditional force sensing methods, offering numerous advantages such as high sensitivity, immunity to EMI, and resistance to harsh environments. With their diverse applications in industries like robotics, healthcare, aerospace, and manufacturing, optical force sensors are poised to play a significant role in revolutionizing force measurement technologies. As research and development in this field continue to advance, it is anticipated that optical force sensors will overcome existing challenges and become even more prevalent in the years to come.