Explore the workings, applications, advantages, and challenges of Nd:YAG lasers, a versatile tool revolutionizing various industries.

Introduction to Nd:YAG Laser
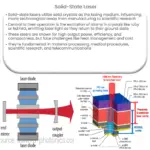
The Nd:YAG (Neodymium-doped Yttrium Aluminum Garnet) laser is a solid-state laser that has found widespread use in various industries due to its versatility and efficiency. Its operational wavelength is 1064 nm, in the infrared range of the light spectrum.
Components of an Nd:YAG Laser
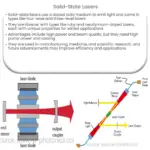
An Nd:YAG laser consists of three main components: the laser medium, pump source, and the resonator. The laser medium is the Nd:YAG crystal itself, which is responsible for producing the laser light. The pump source, usually a flashlamp or a diode laser, provides the energy needed to stimulate the laser medium, while the resonator, made up of two mirrors, amplifies the light produced by the medium.
Working Principle of Nd:YAG Laser
The working principle of an Nd:YAG laser is based on the process of stimulated emission. When the laser medium is excited by the pump source, it elevates the neodymium ions to a higher energy level. Once these ions return to their original state, they emit photons, creating a coherent beam of light.
- Pump Source: The pump source injects energy into the laser medium, exciting the neodymium ions.
- Stimulated Emission: As the excited neodymium ions return to their ground state, they emit photons. This process is known as stimulated emission.
- Amplification: The photons are reflected back and forth between the mirrors of the resonator, stimulating more emissions and amplifying the light beam.
- Laser Emission: Once the beam is sufficiently amplified, it passes through one of the mirrors (which is partially reflective), creating a powerful, coherent laser beam.
Applications of Nd:YAG Lasers
Nd:YAG lasers have a wide range of applications due to their power, efficiency, and versatility. They are used in many industries, including medicine, manufacturing, and telecommunications. For instance, in the medical field, Nd:YAG lasers are used for various surgical procedures such as laser eye surgery and laser hair removal. In manufacturing, they are used for cutting, welding, and engraving.
In the telecommunications industry, Nd:YAG lasers are used in fiber optic communication systems, where they serve as a light source for transmitting data over long distances.
Advantages of Nd:YAG Lasers
Nd:YAG lasers offer several advantages which contribute to their widespread use. These lasers have a high power output, making them suitable for applications that require intense light, such as industrial cutting and welding. Moreover, the infrared wavelength of Nd:YAG lasers can easily be focused and directed, giving users a high degree of control.
- High Power: Nd:YAG lasers can produce a high power output, which makes them useful in industrial applications.
- Control: The light from an Nd:YAG laser can be accurately focused and directed, providing a high degree of precision.
- Efficiency: These lasers are highly efficient, converting a large proportion of the input power into laser light.
- Versatility: Nd:YAG lasers can be used in a wide range of applications, from medicine to manufacturing to telecommunications.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite their advantages, Nd:YAG lasers also come with a few challenges and limitations. For one, they require a significant amount of power to operate. Additionally, due to their high power output, they can generate substantial heat, necessitating efficient cooling systems. Lastly, while the infrared wavelength of the Nd:YAG laser has many benefits, it is also invisible to the human eye, which can pose safety risks if not properly managed.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Nd:YAG laser is a versatile and powerful tool that has revolutionized various industries. Its high power output, precision, and efficiency have made it indispensable in applications ranging from medicine to manufacturing and telecommunications. While it does present certain challenges, such as the need for significant power input and heat management, these can be effectively mitigated with the right infrastructure. As technology continues to evolve, the Nd:YAG laser will undoubtedly remain a key player in the world of lasers, continuing to drive innovation and progress in numerous fields.