Explore the workings, benefits, drawbacks, and mitigation strategies of Diesel-Driven Synchronous Generators in our comprehensive guide.
Understanding Diesel-Driven Synchronous Generators
A Diesel-Driven Synchronous Generator is a significant piece of equipment in the power generation sector. These generators are widely used in industries, commercial establishments, and homes for emergency power supply, and in remote locations where grid supply is unavailable or unreliable.
Components and Functioning
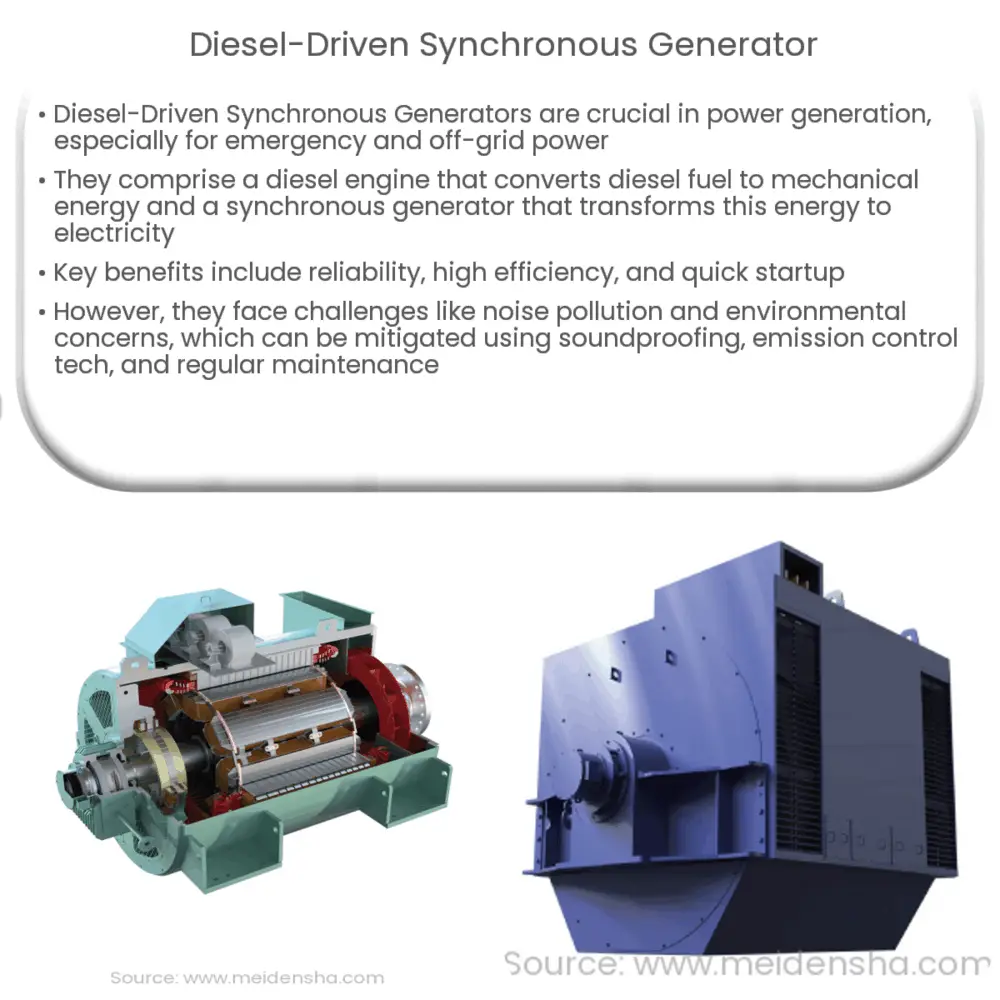
The main components of a diesel-driven synchronous generator are the diesel engine and the synchronous generator. The diesel engine, powered by diesel fuel, acts as the prime mover that drives the synchronous generator. This arrangement can be described as follows:
- Diesel Engine: This is the heart of the generator. It converts the chemical energy stored in diesel fuel into mechanical energy through the process of combustion. The engine’s rotating crankshaft, connected to the rotor of the generator, provides the required rotational motion.
- Synchronous Generator: The mechanical energy from the engine is transferred to the synchronous generator, which transforms this mechanical energy into electrical energy based on Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction. As the rotor spins, it induces a magnetic field in the stator, causing the generation of alternating current (AC).
Benefits of Diesel-Driven Synchronous Generators
There are several key benefits associated with the use of diesel-driven synchronous generators, which include:
- Reliability: Diesel generators are known for their durability and reliability. They can operate for long periods without significant maintenance, making them ideal for continuous power supply needs.
- Efficiency: Diesel engines have high thermal efficiency, meaning they can convert a higher percentage of fuel into useful work. This makes diesel-driven synchronous generators a cost-effective choice for power generation.
- Quick Startup: Another notable feature of these generators is their rapid startup and load acceptance capabilities, making them ideal for emergency power supply applications.
- Noise Pollution: Diesel engines can be quite noisy during operation, which may cause disturbances in residential areas or workplaces. However, this problem can be mitigated using soundproof enclosures or installing the generator set at a sufficient distance.
- Environmental Impact: Diesel engines emit harmful substances such as particulate matter and nitrogen oxides, which contribute to air pollution. They also produce carbon dioxide, a major greenhouse gas. Increasing environmental concerns have led to stringent emission standards, pushing manufacturers to develop cleaner and more efficient engines.
- Fuel Dependence: Diesel generators depend on the availability of diesel fuel, which may be a challenge in remote areas or during natural disasters.
- Soundproofing: Encasing generators in soundproof materials or structures can reduce noise pollution significantly.
- Emission Controls: Utilizing advanced emission control technologies, such as Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) and Diesel Particulate Filters (DPF), can help reduce harmful emissions.
- Regular Maintenance: Regular servicing and maintenance can ensure optimal performance and longevity of the generator, reducing the overall environmental impact.
Despite these benefits, it is essential to remember that diesel-driven synchronous generators also have a few drawbacks. These include the high noise levels they produce during operation and their environmental impact due to the emission of greenhouse gases.
Drawbacks of Diesel-Driven Synchronous Generators
As with any technology, diesel-driven synchronous generators have their disadvantages. These include:
Mitigating the Drawbacks
Despite these drawbacks, several measures can be implemented to mitigate the impact of diesel-driven synchronous generators:
Conclusion
In conclusion, Diesel-Driven Synchronous Generators are a vital component in the power generation sector, offering reliable and efficient power supply, especially in locations without grid access or during power outages. Despite some drawbacks such as noise pollution and environmental concerns, these challenges can be effectively mitigated through soundproofing measures, emission control technologies, and regular maintenance. As energy needs continue to grow, diesel-driven synchronous generators will remain a critical part of the energy landscape, particularly for emergency power supply and off-grid applications.




