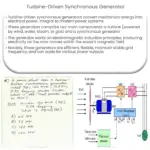
Explore the workings, benefits, and future of Gas-Driven Synchronous Generators, a key component in modern power systems.

Understanding Gas-Driven Synchronous Generators
Gas-Driven Synchronous Generators are a pivotal component in modern power generation systems. These generators are a type of synchronous generator, which means they produce AC power at a constant frequency, synchronized with the grid frequency. The ‘gas-driven’ term refers to the primary source of mechanical energy used to drive the generator – natural gas.
Working Principle
A Gas-Driven Synchronous Generator’s operation can be viewed as a two-stage process. Firstly, the gas turbine converts the energy from the combustion of natural gas into mechanical energy. This mechanical energy is then used to turn the generator’s rotor, which in turn induces an electromagnetic field in the stator, thus producing electrical energy.
Components of a Gas-Driven Synchronous Generator
Benefits of Gas-Driven Synchronous Generators
Gas-Driven Synchronous Generators offer several advantages over other types of generators. The primary advantage is the high efficiency in converting gas to electricity. This is mainly due to the ability of gas turbines to operate at high temperatures, which results in increased thermodynamic efficiency. This high efficiency translates into lower operating costs.
Another significant advantage is their environmental friendliness. Natural gas, as a fossil fuel, burns more cleanly than coal or oil, producing significantly less CO2 and other harmful emissions.
Applications of Gas-Driven Synchronous Generators
These generators are used extensively in power plants for base load and peak load power generation. They are also used in cogeneration plants, where the waste heat from the gas turbine is used to produce steam, which is then used for additional power generation or for industrial processes.
The Future of Gas-Driven Synchronous Generators
The future of Gas-Driven Synchronous Generators is bright, considering the ongoing global efforts to reduce carbon emissions. While renewable energy sources are gaining popularity, gas-driven generators provide a reliable and efficient power generation solution that complements renewable energy sources.
Challenges Faced by Gas-Driven Synchronous Generators
Despite their benefits, Gas-Driven Synchronous Generators also face several challenges. The primary challenge is the fluctuating price of natural gas, which directly impacts the operating cost of these generators. Additionally, these generators also require significant maintenance to keep them operating at peak efficiency.
Technological Advancements
With the advent of new technologies, gas-driven synchronous generators have seen considerable improvements. Modern generators are more efficient, reliable, and require less maintenance than their predecessors. Advanced control systems have also made it easier to synchronize these generators with the grid, improving their overall performance.
Regulations and Policies
Regulations and policies also play a significant role in the adoption of gas-driven synchronous generators. Policies promoting clean energy and imposing restrictions on carbon emissions favor the use of these generators. However, regulations regarding the extraction and use of natural gas can pose challenges.
Integration with Renewable Energy
One of the promising trends in the power generation industry is the integration of gas-driven synchronous generators with renewable energy systems. These hybrid systems use renewable energy sources whenever available, and switch to gas-driven generators during periods of low renewable energy production. This approach ensures a steady supply of power while minimizing environmental impact.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Gas-Driven Synchronous Generators are an essential part of the power generation landscape. Their high efficiency, environmental friendliness, and ability to integrate with renewable energy systems make them an attractive option for power generation. Despite the challenges they face, ongoing technological advancements and supportive regulations promise a bright future for these generators. As we move towards a more sustainable future, the role of gas-driven synchronous generators will become increasingly significant in achieving our energy goals.