Explore the fascinating world of excimer lasers, their unique properties, applications in medicine, manufacturing, scientific research, and future prospects.
Introduction to Excimer Lasers
Excimer lasers, short for ‘excited dimer’, have revolutionized the fields of manufacturing, medicine, and scientific research with their unique properties and versatile applications. This article delves into the mechanics of excimer lasers, their applications, and their importance in various fields.
Understanding Excimer Lasers
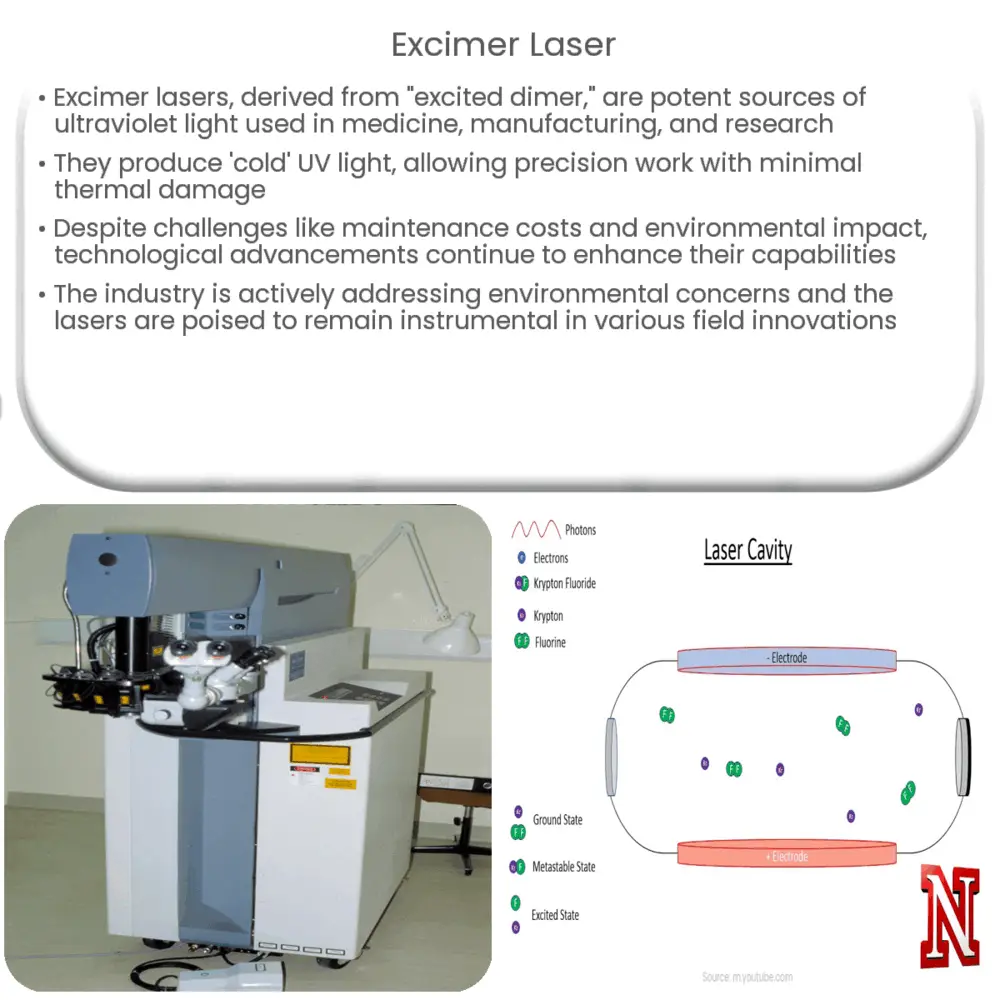
At their core, excimer lasers are powerful and precise sources of ultraviolet light. Their name, “excited dimer,” comes from the way they produce light. The lasers are powered by a gas mixture usually comprising a noble gas like Argon or Krypton, and a halogen like Fluorine or Chlorine. When electrically stimulated, these gases form an excited, or ‘excimer’, state. This excited dimer eventually returns to its ground state, emitting a photon in the process, which is the source of the laser light.
Unique Properties
The light produced by excimer lasers possesses two key properties. First, its wavelength is in the ultraviolet (UV) range. This allows it to be absorbed quickly by most materials, enabling high-precision microfabrication. Second, the light is ‘cold’, or non-thermal, meaning it does not heat the surrounding material as much as other lasers. This minimizes damage to the material being worked on.
Applications
- Medicine: Excimer lasers have revolutionized medical treatments, particularly in ophthalmology. They are used for photorefractive keratectomy (PRK) and laser in-situ keratomileusis (LASIK), which are procedures to correct refractive errors in the eye.
- Manufacturing: In manufacturing, excimer lasers are used for microfabrication. Their ability to make precise, clean cuts without causing thermal damage makes them ideal for producing semiconductors and microelectromechanical systems (MEMS).
- Scientific research: Researchers use excimer lasers for spectroscopy, photochemistry, and in the study of molecular dynamics, among other applications.
The Future of Excimer Lasers
As technology advances, so too does the potential of excimer lasers. Currently, they are at the forefront of research into next-generation lithography techniques for semiconductor manufacturing, aiming to create ever-smaller and more efficient chips.
Advancements in Excimer Laser Technology
The rapid advancement in technology is pushing the boundaries of excimer laser capabilities. A notable development is the creation of high repetition rate lasers, which can pulse hundreds or thousands of times per second. This allows for faster processing times and higher throughput in manufacturing applications. Furthermore, efforts are being made to improve the stability and reliability of excimer lasers, which would further increase their utility and efficiency in various applications.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite their impressive capabilities, excimer lasers do face some challenges. Their complexity and the requirement for precise control of the gas mixture can lead to high maintenance costs. In addition, while the ‘cold’ nature of the laser light is a benefit for precision work, it can be a limitation when heating is required. Finally, safety precautions must be taken due to the ultraviolet light produced, which can be harmful to the eyes and skin.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Excimer lasers use a mixture of gases, some of which are potent greenhouse gases. Hence, there is an environmental impact associated with their use. The laser industry is actively working towards developing more sustainable practices, such as improving gas recycling systems and researching alternative, environmentally-friendly gas mixtures.
Conclusion
In conclusion, excimer lasers are a powerful tool with wide-ranging applications in medicine, manufacturing, and scientific research. Their unique properties, such as the production of ‘cold’ UV light, make them ideal for precision work. While there are challenges associated with their complexity and environmental impact, advancements in technology and ongoing research are continuously enhancing their capabilities and mitigating these issues. As we look to the future, it is clear that excimer lasers will continue to play a pivotal role in driving innovation and development across various fields.

