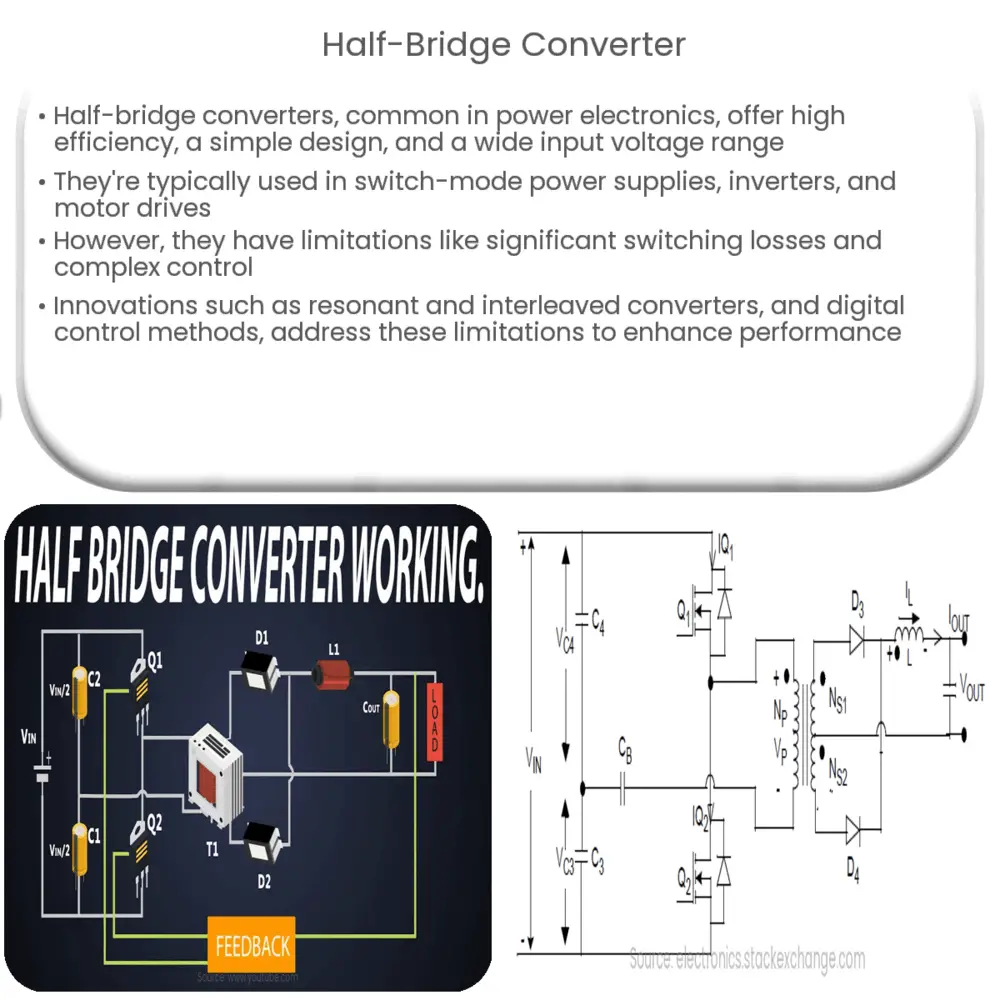
A half-bridge converter is a DC-DC converter with high efficiency, used in power supplies, inverters, and motor drives for voltage or current regulation.
Introduction to Half-Bridge Converters
The half-bridge converter is a widely used topology in power electronics for applications that require voltage or current regulation, such as switch-mode power supplies, inverters, and motor drives. This article will discuss the basic principles, advantages, and limitations of half-bridge converters, as well as some common applications.
Principles of Operation
A half-bridge converter is a type of DC-DC converter that uses two switches to alternately connect a load to a voltage source and a reference (typically ground). The switches are typically transistors, such as metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors (MOSFETs) or insulated-gate bipolar transistors (IGBTs), and they are controlled by a pulse-width modulation (PWM) signal to regulate the output voltage or current.
When one switch is closed (on), the other is open (off), creating a path for current to flow through the load. By controlling the duty cycle of the PWM signal, which determines the ratio of the on-time to the total switching period, the average voltage across the load can be regulated.
In its simplest form, a half-bridge converter consists of two switches, an inductor, and a capacitor. The inductor and capacitor form an LC filter that smooths the output voltage, while the switches are used to alternately connect the load to the voltage source and reference. The output voltage is determined by the duty cycle of the PWM signal and the input voltage.
Advantages of Half-Bridge Converters
Half-bridge converters offer several advantages compared to other converter topologies:
- High Efficiency: The efficiency of a half-bridge converter is typically higher than that of other topologies, such as flyback or forward converters, due to the lower conduction losses in the switches and reduced voltage stress on the output capacitor.
- Simple Design: The basic half-bridge converter requires only two switches and an LC filter, making it a relatively simple and compact design. This can lead to reduced component count and lower manufacturing costs.
- Wide Input Voltage Range: Half-bridge converters can accommodate a wide range of input voltages, making them suitable for various applications, including battery-powered devices and systems with varying input voltages.
Limitations of Half-Bridge Converters
Despite their advantages, half-bridge converters also have some limitations:
- Switching Losses: The switching losses in half-bridge converters can be significant, particularly at higher switching frequencies. This can result in increased heat dissipation, reducing the overall efficiency of the converter.
- Complex Control: Controlling the PWM signal to regulate the output voltage or current can be complex, particularly when the converter is subjected to varying input voltages or load conditions.
Applications of Half-Bridge Converters
Half-bridge converters are used in a variety of applications due to their high efficiency, simple design, and wide input voltage range. Some common applications include:
- Switch-Mode Power Supplies: Half-bridge converters are commonly used in switch-mode power supplies (SMPS) for devices such as computers, televisions, and other consumer electronics. They provide efficient voltage regulation and can accommodate a wide range of input voltages, making them suitable for various power supply requirements.
- Inverters: Inverters, which convert DC voltage to AC voltage, often utilize half-bridge converters. They are used in applications like solar power systems, uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), and electric vehicles, where efficient voltage conversion is crucial.
- Motor Drives: Half-bridge converters can be found in motor drives for applications like electric vehicles, robotics, and industrial automation. They are used to regulate the voltage and current supplied to the motor, enabling precise control of motor speed and torque.
Improvements and Variations of Half-Bridge Converters
Over the years, several improvements and variations of the basic half-bridge converter have been developed to address the limitations and enhance the performance of the topology:
- Resonant Converters: Resonant converters are a variation of the half-bridge converter that use a resonant circuit to reduce switching losses and improve efficiency. By carefully selecting the resonant frequency, the converter can operate with zero-voltage or zero-current switching, which minimizes the switching losses and reduces the heat dissipation.
- Interleaved Converters: Interleaved converters use multiple parallel-connected half-bridge converters to reduce the input and output current ripple, resulting in lower electromagnetic interference (EMI) and improved efficiency. Interleaving also allows for the reduction of the filter components’ size, leading to a more compact and cost-effective design.
- Digital Control: Implementing digital control techniques in half-bridge converters can simplify the control complexity and improve the performance under varying input voltages or load conditions. Digital control allows for more precise regulation and advanced control algorithms, leading to improved efficiency and dynamic response.
Conclusion
Half-bridge converters are a versatile and efficient solution for a wide range of applications in power electronics. Their simple design, high efficiency, and wide input voltage range make them suitable for various voltage or current regulation tasks, such as in switch-mode power supplies, inverters, and motor drives. Despite their limitations, ongoing research and development continue to improve the performance of half-bridge converters, making them an attractive choice for power conversion applications.