A diaphragm pressure sensor measures pressure by detecting diaphragm deformation, ensuring accurate readings in various industries.
Diaphragm Pressure Sensor: An Overview
The diaphragm pressure sensor is a crucial component in various industries, including automotive, medical, and process control. These sensors, designed to measure pressure accurately and reliably, are essential for maintaining safety, efficiency, and optimal performance. This article delves into the basics of diaphragm pressure sensors, their working principle, and the different types available in the market.
What is a Diaphragm Pressure Sensor?
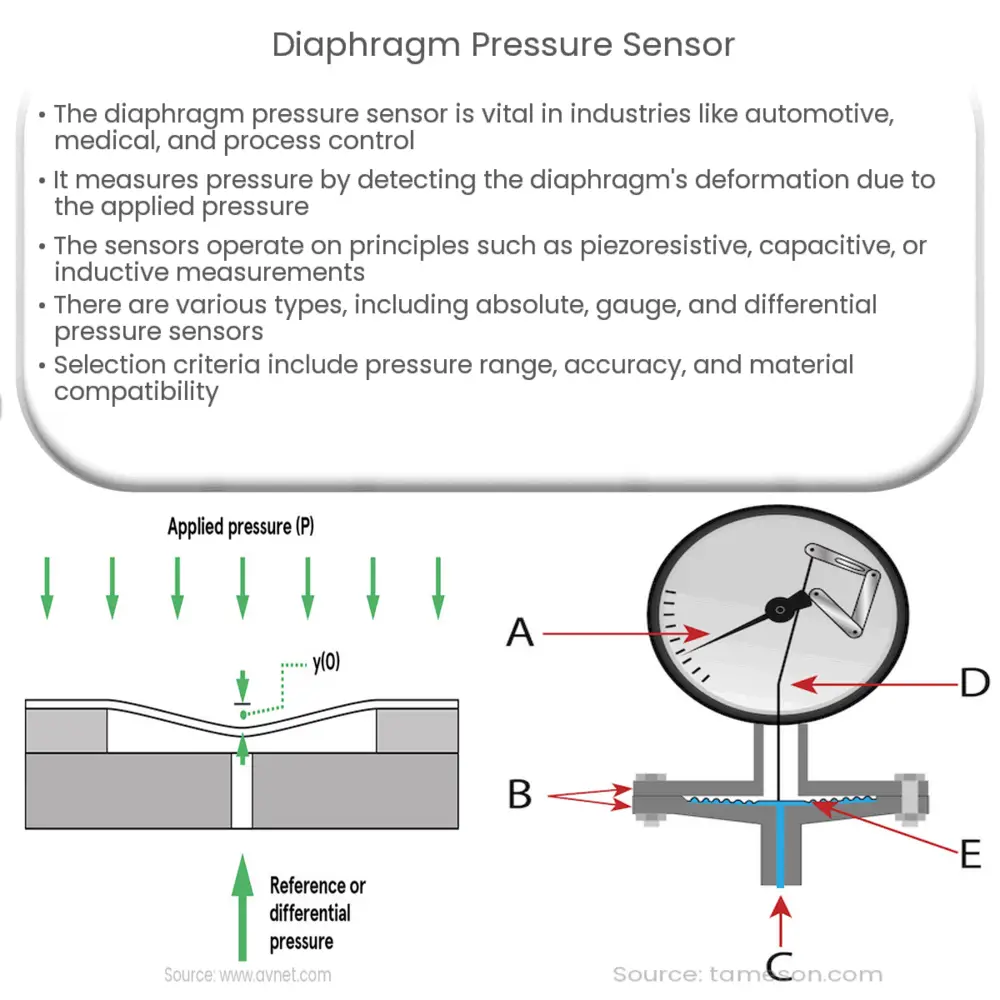
A diaphragm pressure sensor, also known as a diaphragm transducer, is a device used to measure pressure by detecting the deformation of a diaphragm due to applied pressure. The diaphragm, usually made of metal or flexible materials such as elastomers or polymers, serves as the primary sensing element. As pressure is exerted on the diaphragm, it deflects, causing a change in the sensor’s electrical output. This change is then converted into a pressure measurement through calibration.
Working Principle of Diaphragm Pressure Sensors
The working principle of diaphragm pressure sensors is based on the relationship between the applied pressure and the resulting deflection of the diaphragm. As pressure is applied, the diaphragm deforms, causing a change in its dimensions. This deformation is detected by a sensing element, which can be piezoresistive, capacitive, or inductive in nature. The sensing element generates an electrical signal proportional to the diaphragm’s deflection, which is then processed and converted into a pressure reading.
In a piezoresistive diaphragm sensor, a thin film of piezoresistive material is deposited on the diaphragm surface. As pressure is applied and the diaphragm deforms, the piezoresistive material’s resistance changes, resulting in a measurable electrical signal.
In a capacitive diaphragm sensor, the diaphragm is sandwiched between two electrodes, forming a variable capacitor. As pressure is applied, the diaphragm deflects, changing the distance between the electrodes and thus altering the capacitance. This change in capacitance is measured and converted into a pressure reading.
In an inductive diaphragm sensor, the diaphragm is placed between two coils that form an inductive circuit. The diaphragm’s deflection changes the inductance of the circuit, which is then measured and related to the applied pressure.
Types of Diaphragm Pressure Sensors
Diaphragm pressure sensors are available in various types, each with its own unique features and applications. Some common types include:
- Absolute pressure sensors: These sensors measure the pressure relative to a perfect vacuum. They are commonly used in barometric pressure measurement, vacuum monitoring, and leak detection.
- Gauge pressure sensors: Gauge pressure sensors measure the pressure relative to the ambient atmospheric pressure. They are commonly used in industrial applications, such as hydraulic and pneumatic systems.
- Differential pressure sensors: Differential pressure sensors measure the difference in pressure between two points in a system. They are often used in flow measurement, filter monitoring, and level sensing.
In conclusion, diaphragm pressure sensors are versatile and reliable devices employed in various industries to ensure safety and efficiency. Their ability to accurately measure pressure under varying conditions makes them an indispensable tool in numerous applications.
Selecting the Right Diaphragm Pressure Sensor
Choosing the appropriate diaphragm pressure sensor for a specific application involves considering several factors. Some key considerations include:
- Pressure range: Ensure the sensor can measure the required pressure range for the intended application.
- Accuracy: Determine the level of accuracy needed and select a sensor with suitable performance specifications.
- Temperature range: Choose a sensor that can withstand the temperature extremes of the operating environment.
- Material compatibility: Ensure the diaphragm material is compatible with the process media to avoid corrosion or damage to the sensor.
- Size and form factor: Select a sensor with dimensions that fit the available space and suit the intended installation.
- Electrical output: Match the sensor’s electrical output with the input requirements of the connected monitoring or control system.
Common Applications of Diaphragm Pressure Sensors
Diaphragm pressure sensors are employed across various industries due to their versatility and reliability. Some common applications include:
- Automotive: In vehicles, diaphragm pressure sensors help monitor fuel pressure, oil pressure, and tire pressure to ensure optimal performance and safety.
- Medical: Diaphragm pressure sensors are used in medical devices, such as ventilators, blood pressure monitors, and infusion pumps, to ensure accurate pressure control and patient safety.
- Process control: In industrial process control systems, diaphragm pressure sensors monitor and control pressure in pipelines, vessels, and tanks to ensure safe and efficient operation.
- Environmental monitoring: Diaphragm pressure sensors are employed in weather stations to measure barometric pressure, which is essential for accurate weather forecasting.
- Aerospace: In aerospace applications, diaphragm pressure sensors measure cabin pressure, hydraulic system pressure, and engine pressure to maintain safety and performance.
Maintenance and Calibration of Diaphragm Pressure Sensors
To ensure accurate and reliable operation, diaphragm pressure sensors require periodic maintenance and calibration. Some essential maintenance steps include:
- Visual inspection: Regularly examine the sensor for signs of physical damage, corrosion, or leakage.
- Cleaning: Keep the sensor and its surroundings clean to avoid contamination that may affect performance.
- Calibration: Periodically calibrate the sensor to maintain its accuracy and performance. Calibration intervals depend on the sensor’s specifications, application, and operating conditions.
- Replacement: If the sensor is damaged or its performance has significantly degraded, replace it with a new one to ensure accurate pressure measurements.
In summary, diaphragm pressure sensors are critical components in various industries, providing accurate and reliable pressure measurements. Understanding their working principles, types, and applications can help users select the right sensor for their needs and ensure optimal performance and safety in their systems.

