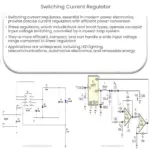
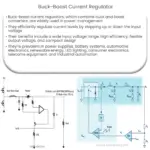
Boost Current Regulators efficiently step up input voltage while maintaining constant output current, enhancing device performance and energy use.

Boost Current Regulator: Enhancing Efficiency and Performance
The demand for power-efficient electronic devices has led to the development of various technologies that aim to optimize energy consumption. One such advancement is the Boost Current Regulator (BCR), a vital component in power electronics. In this article, we will explore the concept, operation, and benefits of the Boost Current Regulator, as well as its applications in various industries.
What is a Boost Current Regulator?
A Boost Current Regulator is a type of DC-DC converter that increases the output voltage while maintaining a constant output current. It is also known as a step-up converter, as it steps up the input voltage to a higher level. BCRs are designed to provide a stable and precise output voltage, ensuring efficient and reliable performance in various applications. These regulators are essential for devices that require a higher voltage output than the input source can provide.
How does a Boost Current Regulator work?
The operation of a Boost Current Regulator is based on the principle of inductor energy storage and release. The basic components of a BCR include an inductor, a switch (usually a MOSFET), a diode, and a capacitor. The input voltage is applied to the inductor, and the switch is used to control the current flow through the inductor. When the switch is closed, the current flows through the inductor, storing energy in its magnetic field. When the switch is opened, the energy stored in the inductor is released, causing the diode to conduct and charge the capacitor to a higher voltage than the input source.
This process of energy storage and release repeats continuously, stepping up the input voltage to the desired output level. The output voltage can be controlled by adjusting the duty cycle of the switch, which determines the proportion of time the switch is closed in each cycle. A higher duty cycle results in a higher output voltage, while a lower duty cycle yields a lower output voltage.
Benefits of Boost Current Regulators
Boost Current Regulators offer several advantages over other types of DC-DC converters, including:
- Efficiency: BCRs are highly efficient, as they only require a single switch and minimal passive components, resulting in reduced power losses and improved overall efficiency.
- Compact size: Due to their simple design and small number of components, Boost Current Regulators are compact and can be easily integrated into various electronic devices.
- Wide input voltage range: BCRs can accommodate a wide range of input voltages, making them suitable for applications with varying power requirements.
- Constant output current: BCRs maintain a constant output current, ensuring stable and reliable performance across various operating conditions.
Applications of Boost Current Regulators
Boost Current Regulators are utilized in a wide range of applications across various industries, including:
- Consumer Electronics: BCRs are used in devices such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops to efficiently manage power and ensure stable performance, even when the battery voltage decreases.
- Automotive: In electric vehicles and hybrid systems, Boost Current Regulators play a crucial role in managing power conversion between the battery and the vehicle’s electrical systems, ensuring optimal energy efficiency and performance.
- Renewable Energy: BCRs are commonly used in solar power systems to step up the voltage generated by photovoltaic panels, enabling efficient energy conversion and storage.
- LED Lighting: Boost Current Regulators are employed in LED lighting systems to maintain a constant current, ensuring consistent brightness and long life for the LED components.
- Industrial Automation: BCRs are used in various industrial applications, such as motor control and power supply systems, to maintain stable voltage levels and ensure reliable operation of equipment.
Choosing the Right Boost Current Regulator
Selecting the appropriate Boost Current Regulator for a specific application involves considering several factors, including:
- Input Voltage Range: Ensure that the BCR can accommodate the input voltage range required for your application.
- Output Voltage and Current: Choose a BCR that can provide the desired output voltage and current levels for your application.
- Efficiency: Select a BCR with a high efficiency rating to minimize power losses and optimize energy consumption.
- Size Constraints: Consider the size of the BCR and its compatibility with the space available in your device or system.
- Thermal Performance: Evaluate the BCR’s thermal performance and ensure that it can operate effectively within the temperature range of your application.
Conclusion
Boost Current Regulators are essential components in modern electronics, providing efficient and stable voltage conversion in a compact package. Their ability to step up input voltage while maintaining constant output current makes them invaluable in a variety of applications, from consumer electronics to renewable energy systems. By understanding the principles, benefits, and applications of Boost Current Regulators, engineers and designers can optimize energy efficiency and performance in their devices and systems, contributing to a more sustainable and energy-efficient future.