Explore the world of wirewound resistors: their construction, types, advantages, limitations, and applications in diverse industries.
Introduction to Wirewound Resistors
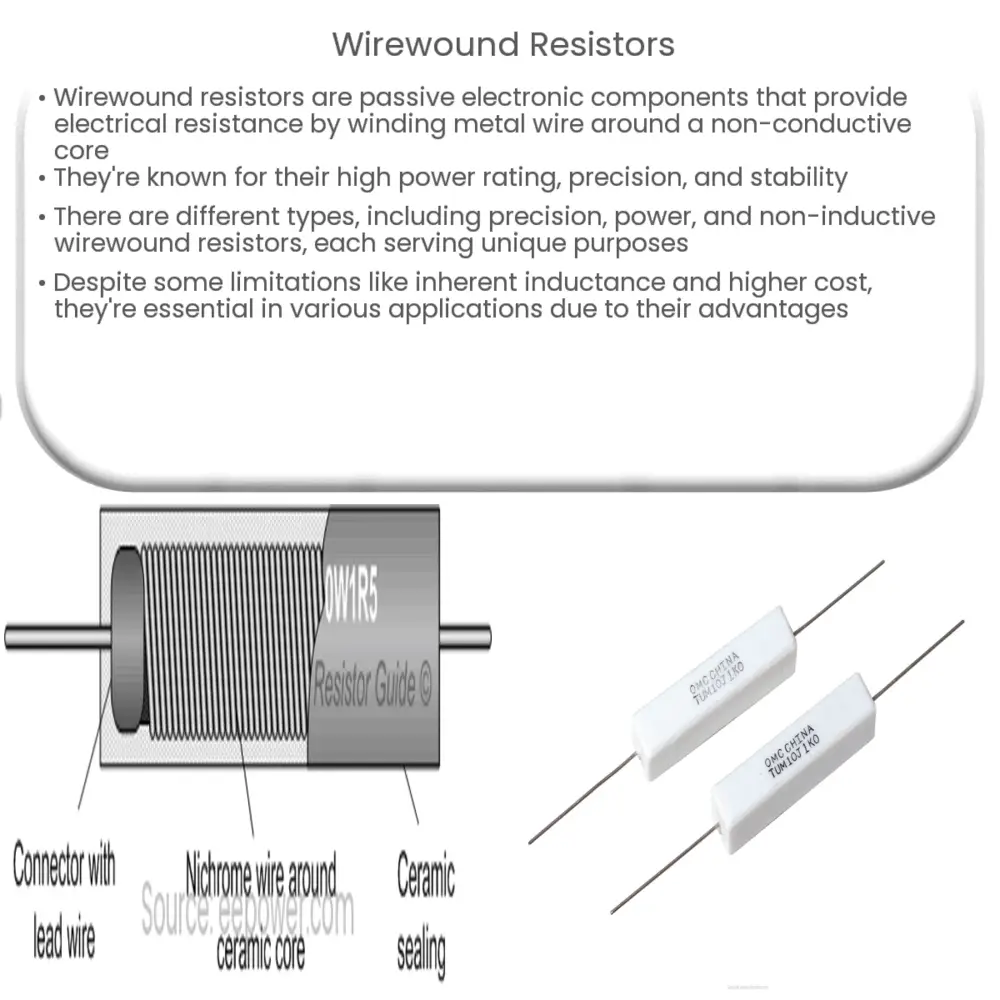
A wirewound resistor is a type of passive component in electronics that provides electrical resistance. The unique characteristic of these resistors is their construction: they are made by winding a metal wire, usually an alloy such as nickel-chromium, around a non-conductive core, which is typically made of ceramic, plastic, or fiberglass.
The objective of a resistor in any electronic circuit is to regulate the amount of current flowing through it. Wirewound resistors distinguish themselves by their high power rating, precision, and stability, which makes them ideal for applications where these attributes are essential.
The Construction of Wirewound Resistors
Wirewound resistors are constructed by tightly wrapping a high-resistivity wire around a non-conductive core. The wire’s diameter and the number of windings dictate the resistance value, with a thinner wire or more turns resulting in higher resistance.
The wire is usually made from a conductive metal alloy like nickel-chromium, manganese-copper, or nickel-copper, chosen for its suitable temperature coefficient of resistance (TCR). The core material is often ceramic, offering excellent thermal conductivity and stability.
Types of Wirewound Resistors
- Precision Wirewound Resistors: These resistors are known for their high accuracy and stability. They are primarily used in measuring instruments and precision electronics equipment.
- Power Wirewound Resistors: As the name suggests, power wirewound resistors are used in high power applications. These resistors are capable of dissipating large amounts of heat, making them suitable for power supplies and motor drives.
- Non-Inductive Wirewound Resistors: These resistors are designed to minimize inductive effects by winding the wire in such a way that the magnetic fields created by the windings cancel each other out. They are mainly used in high-frequency applications.
Each type of wirewound resistor serves a unique purpose, catering to different needs in the electronic industry. The choice of a specific resistor is primarily dictated by the demands of the application it is to be used in.
The Advantages of Wirewound Resistors
Wirewound resistors offer several advantages over other resistor types. Primarily, they exhibit high power dissipation capacity, which means they can handle large amounts of current without overheating. Additionally, they have high precision and stability, especially in high-temperature environments. Their inductance can be minimized when manufactured in a non-inductive style, making them suitable for high-frequency applications.
Limitations of Wirewound Resistors
Despite their advantages, wirewound resistors are not without limitations. First, due to their construction, these resistors typically exhibit some level of inductance and capacitance, which can affect their performance in high-frequency circuits. However, this can be mitigated by adopting a bifilar or Ayrton-Perry winding technique, resulting in non-inductive wirewound resistors.
Secondly, wirewound resistors tend to be more expensive compared to other types of resistors, owing to their complex manufacturing process. Finally, they are generally larger in size, which may be a consideration in space-constrained applications.
Applications of Wirewound Resistors
- Industrial Applications: Due to their high power handling capability, wirewound resistors are extensively used in industrial power electronics, such as motor controllers and power conversion systems.
- Audio Equipment: Their precision and low noise characteristics make wirewound resistors a favorite choice in high-end audio amplifiers.
- Measurement Devices: Precision wirewound resistors are used in measurement and calibration equipment due to their excellent stability and accuracy.
- Automotive Electronics: Wirewound resistors’ ability to operate at high temperatures without degrading makes them ideal for use in the harsh environments typical of automotive electronics.
Conclusion
In summary, wirewound resistors, with their high power dissipation capability, precision, and stability, have a significant role in various electronics applications. Although they have limitations, including a certain degree of inherent inductance and capacitance, a higher cost, and larger physical size compared to other resistor types, their advantages often outweigh these drawbacks in many application scenarios. By understanding the unique characteristics of wirewound resistors, engineers can make informed decisions about when to use them to achieve optimal circuit performance.


