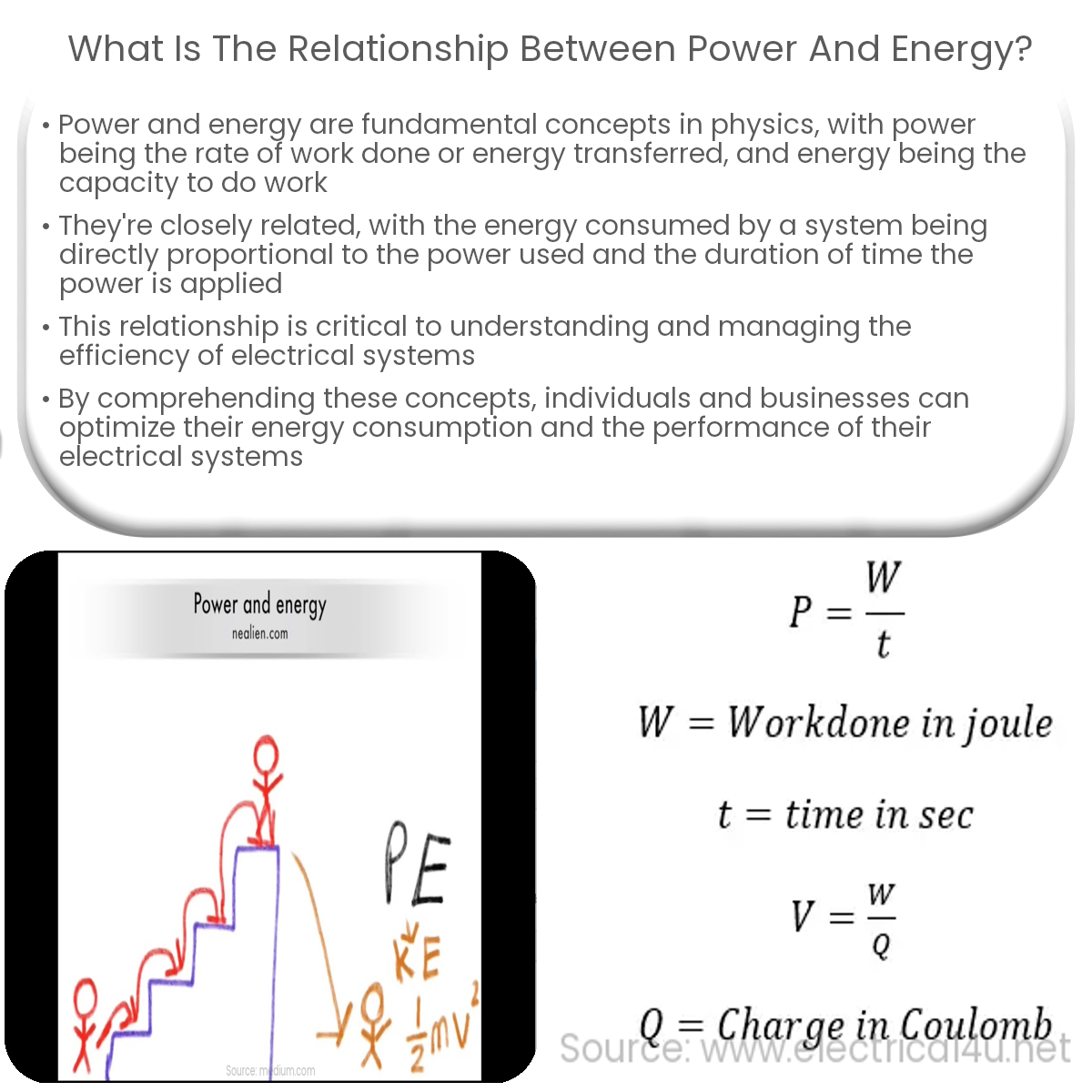
Power is the rate of energy transfer, while energy represents the total work done. They’re related by the formula: Energy = Power × Time.
The Relationship Between Power and Energy
Power and energy are two fundamental concepts in the field of electrical engineering. While they are often used interchangeably, they are distinct from one another. This article aims to explore the relationship between power and energy, highlighting their differences and how they work together.
Understanding Power
Power, measured in watts (W), is the rate at which energy is transferred or converted per unit of time. In electrical systems, power is calculated by multiplying voltage (V) by current (I). This relationship can be expressed as:
P = VI
Power can also be calculated using Ohm’s Law, which states that voltage equals current multiplied by resistance (V = IR). By substituting Ohm’s Law into the power formula, we get:
P = I2R or P = V2/R
Understanding Energy
Energy, measured in joules (J) or more commonly in kilowatt-hours (kWh) for practical purposes, represents the capacity to do work. Electrical energy is the work done when an electrical charge moves through a potential difference (voltage). The amount of electrical energy transferred or consumed can be determined by multiplying power by the time for which it is consumed:
E = Pt
The Relationship Between Power and Energy
Power and energy are intimately related, with power representing the rate at which energy is transferred, and energy representing the total work done. The formula E = Pt demonstrates this relationship, showing that energy can be determined by multiplying the power of an electrical device by the time it operates.
In essence, the higher the power rating of a device, the more energy it will consume over a given period. Conversely, a lower-power device will consume less energy during the same time.
When comparing electrical devices or systems, it is crucial to consider both power and energy consumption. For example, energy-efficient devices typically consume less power, leading to lower energy usage over time. This not only saves money on electricity bills but also helps reduce the environmental impact of energy consumption.
In summary, power and energy are interconnected concepts that describe the behavior of electrical systems. While power represents the rate of energy transfer or conversion, energy represents the total work done. Understanding the relationship between power and energy is essential for optimizing the efficiency and performance of electrical devices and systems.