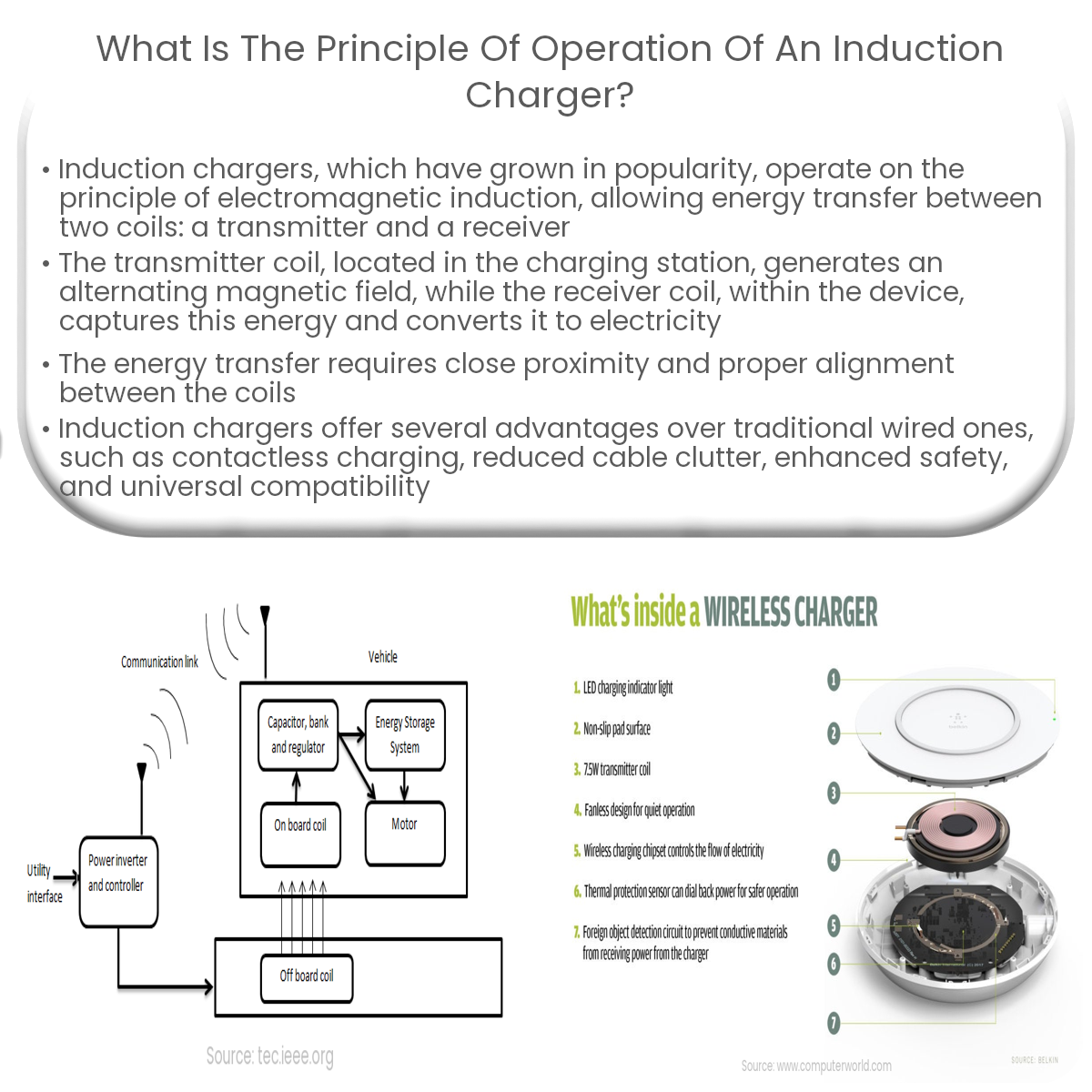
An induction charger uses electromagnetic induction to transfer energy between a transmitter coil and a receiver coil, enabling contactless charging.
Induction Chargers: Principle of Operation
Induction chargers have become increasingly popular in recent years, providing a convenient and efficient way to charge electronic devices without the need for physical connectors. The primary principle behind induction chargers is electromagnetic induction, which enables the transfer of energy between two coils. In this article, we will discuss the principle of operation of an induction charger, exploring its components, the process of energy transfer, and its advantages.
1. Components of an Induction Charger
An induction charger consists of two main components:
- Transmitter Coil: This coil is housed within the charging station or pad and is responsible for generating an alternating magnetic field when an alternating current is applied.
- Receiver Coil: Located within the device being charged, this coil captures the energy from the transmitter coil’s magnetic field and converts it into electrical energy for charging the device’s battery.
2. Process of Energy Transfer
The process of energy transfer in an induction charger involves the following steps:
- An alternating current flows through the transmitter coil, generating an alternating magnetic field around it.
- The alternating magnetic field induces an alternating voltage in the receiver coil, which is in close proximity to the transmitter coil.
- The induced alternating voltage is rectified by a rectifier circuit within the receiving device, converting it into direct current (DC).
- The DC current charges the device’s battery, providing power for its operation.
It is essential to maintain close proximity and proper alignment between the transmitter and receiver coils for efficient energy transfer.
3. Advantages of Induction Chargers
Induction chargers offer several benefits compared to traditional wired chargers:
- Contactless Charging: The absence of physical connectors reduces wear and tear, increasing the charger’s lifespan and reliability.
- Reduced Cable Clutter: Induction chargers eliminate the need for multiple charging cables, simplifying the charging process and reducing clutter.
- Enhanced Safety: With no exposed electrical contacts, induction chargers reduce the risk of electric shock and damage from water or other liquids.
- Universal Compatibility: Many induction chargers adhere to standard specifications, allowing compatibility with multiple devices and brands.
In conclusion, the principle of operation of an induction charger revolves around electromagnetic induction, which enables contactless and efficient energy transfer between two coils. This technology offers several advantages over traditional wired chargers, making it a popular choice for charging a wide range of electronic devices.