Radar, an acronym for “radio detection and ranging,” is a sophisticated technology that utilizes radio waves to detect and locate objects. This article explains the fundamental principles of radar systems and the underlying operation of their components.
Understanding the Principle of Operation of a Radar System
Radar, an acronym for “radio detection and ranging,” is a sophisticated technology that utilizes radio waves to detect and locate objects. This article explains the fundamental principles of radar systems and the underlying operation of their components.
Key Components of a Radar System
- Transmitter
- Antenna
- Receiver
- Signal Processor
Basic Principle of Operation
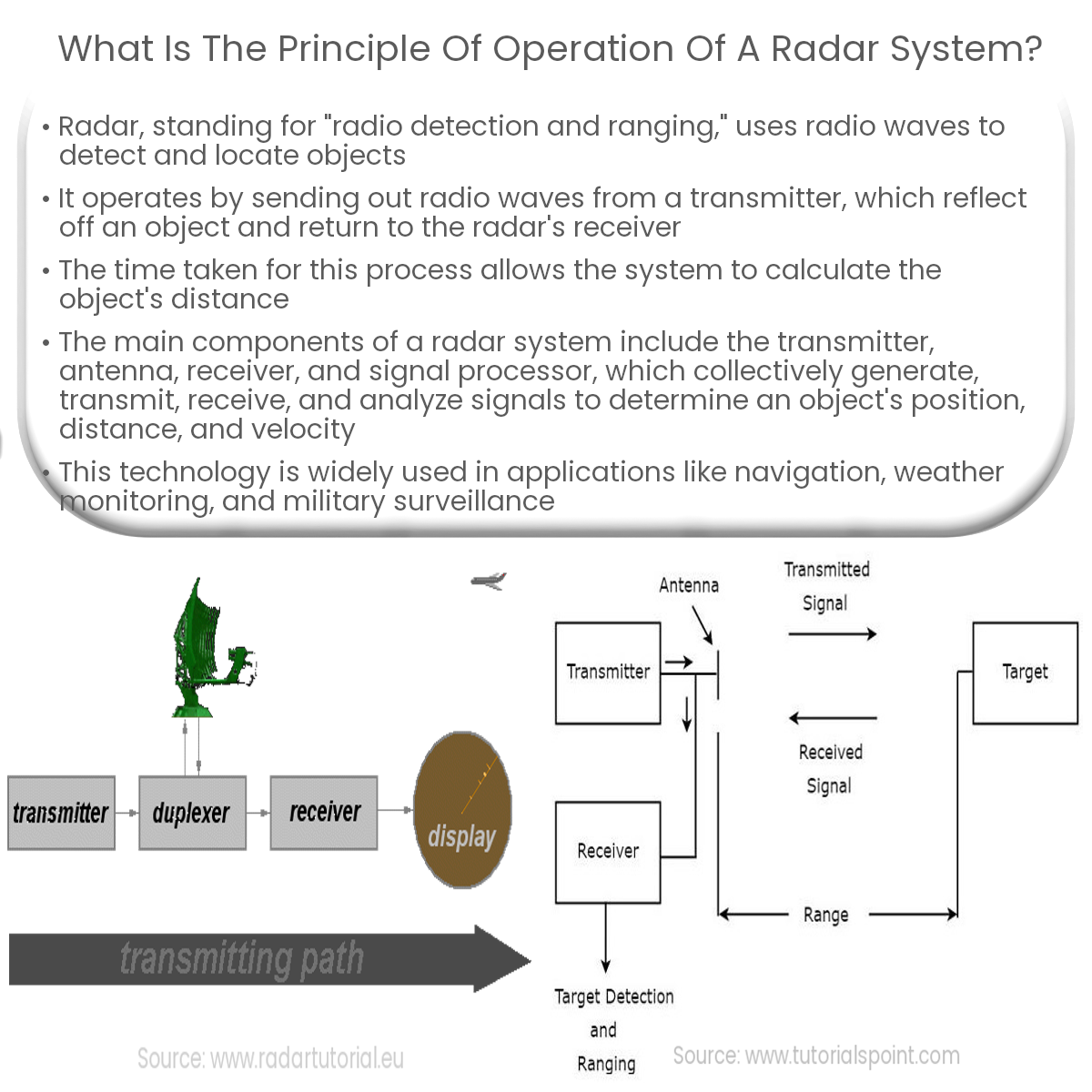
The radar system operates by emitting radio waves from its transmitter, which then bounce off an object and return to the radar’s receiver. The time it takes for the radio waves to travel to the object and back allows the system to determine the object’s distance. The direction of the received signal provides information about the object’s position.
Detailed Process
- Transmitter: The radar system’s transmitter generates a high-frequency radio signal, typically in the microwave range. This signal is amplified and modulated according to the desired characteristics, such as frequency, pulse width, and repetition rate.
- Antenna: The antenna is responsible for broadcasting the radio waves into the environment and receiving the reflected signals. It can be designed to focus the energy in a specific direction or to have a wide beamwidth for broader coverage.
- Propagation and Reflection: As the radio waves propagate through the environment, they interact with objects in their path. When they encounter a target, the waves reflect off its surface and return to the radar system. The strength and delay of the reflected signal depend on the object’s size, shape, and composition, as well as the distance between the radar and the target.
- Receiver: The radar’s receiver detects the reflected signals and amplifies them. It also filters out noise and processes the received information to extract the relevant data.
- Signal Processor: The signal processor performs various algorithms to determine the object’s range, velocity, and angle. It calculates the range by measuring the time delay between the transmitted and received signals, while the Doppler effect is used to estimate the object’s velocity. Angle estimation is achieved by analyzing the direction of the received signal.
In conclusion, a radar system operates by emitting radio waves that interact with objects in their path and then processing the reflected signals to determine the object’s position, distance, and velocity. This technology has a wide range of applications, including navigation, weather monitoring, and military surveillance.