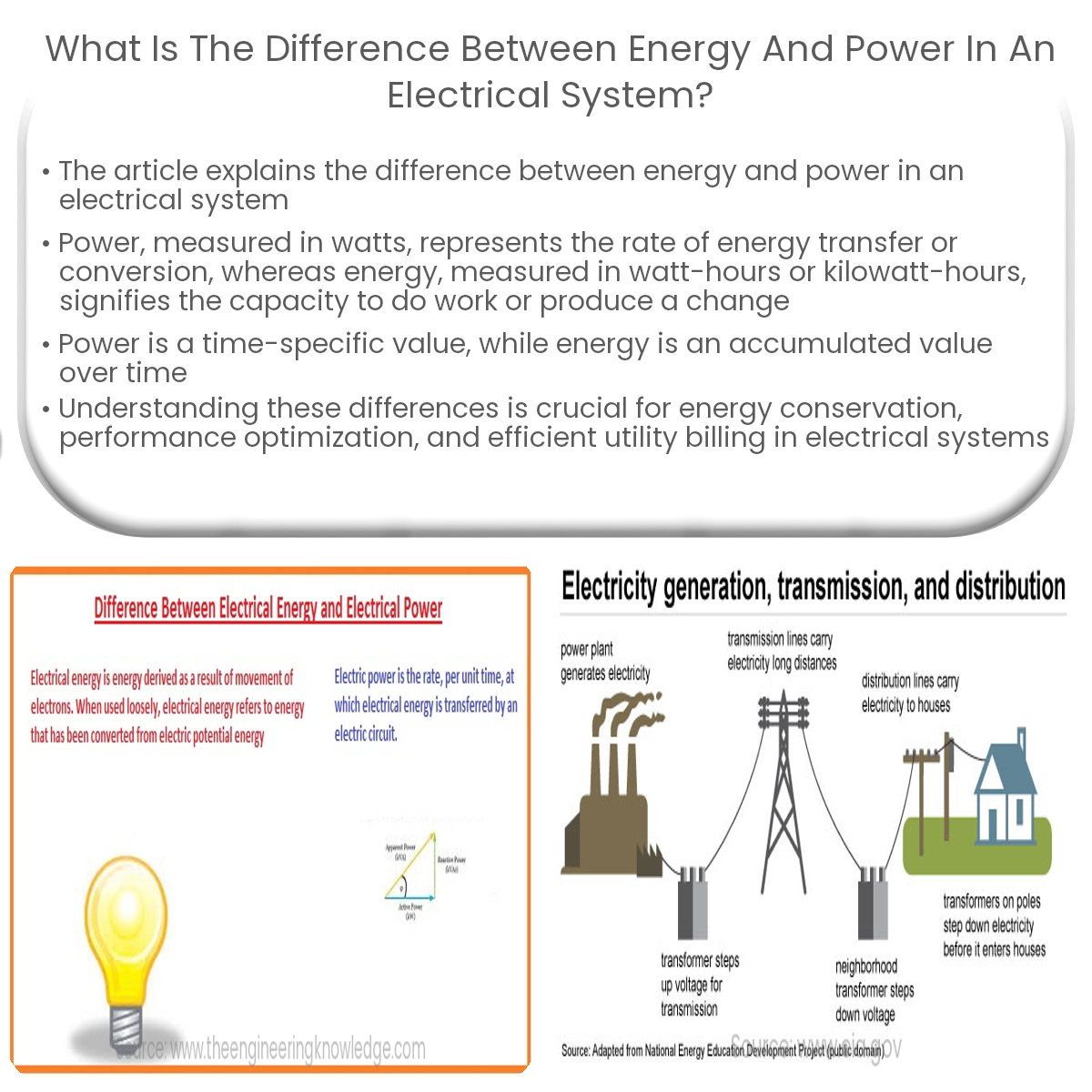
Power is the rate of energy transfer, measured in watts, while energy is the capacity to do work, measured in watt-hours or kilowatt-hours.
Difference Between Energy and Power in an Electrical System
Energy and power are fundamental concepts in the study of electrical systems. They are used to describe the behavior, efficiency, and performance of various devices and components. This article will discuss the differences between energy and power in an electrical system and provide examples of their applications.
Defining Power
Power refers to the rate at which work is done or energy is transferred in a system. In electrical systems, power is measured in watts (W) and is calculated as the product of voltage (V) and current (I):
P = V × I
Power can also be related to resistance (R) in a circuit using Ohm’s Law:
P = I2 × R
In essence, power describes how quickly energy is converted or utilized within an electrical system.
Defining Energy
Energy is the capacity to do work or the ability of a system to produce a change. It can be stored in various forms, such as kinetic, potential, thermal, or electrical energy. In electrical systems, energy is typically measured in watt-hours (Wh) or kilowatt-hours (kWh), where one kWh is equivalent to 1,000 Wh. The amount of electrical energy consumed over time is the product of power and time:
E = P × t
Key Differences Between Energy and Power
Energy and power, while related, represent distinct concepts in an electrical system:
- Rate vs. capacity: Power represents the rate at which energy is transferred or converted, whereas energy represents the capacity to do work or produce a change.
- Units of measurement: Power is measured in watts (W), while energy is measured in watt-hours (Wh) or kilowatt-hours (kWh).
- Time dependency: Power is an instantaneous value that describes the rate of energy transfer at a specific moment in time, whereas energy is an accumulated value that represents the total amount of energy transferred or consumed over a period of time.
Applications of Power and Energy
Understanding the differences between power and energy is crucial for various applications in electrical systems, such as:
- Energy conservation: Comparing the power consumption of different devices helps identify more energy-efficient alternatives, leading to reduced energy consumption and costs.
- Performance analysis: Assessing power and energy consumption can help engineers and technicians optimize the performance of electrical systems and select appropriate components.
- Utility billing: Electricity providers typically bill customers based on energy consumption (kWh), making it essential to understand the relationship between power and energy for cost management.
Conclusion
In an electrical system, power represents the rate of energy transfer, while energy represents the capacity to do work. By understanding the differences between these two concepts, individuals and organizations can better manage energy consumption, optimize system performance, and make informed decisions about energy efficiency.