Reactance is the opposition to AC current flow presented by inductors and capacitors, and it’s a component of impedance in electrical circuits.
What is Reactance?
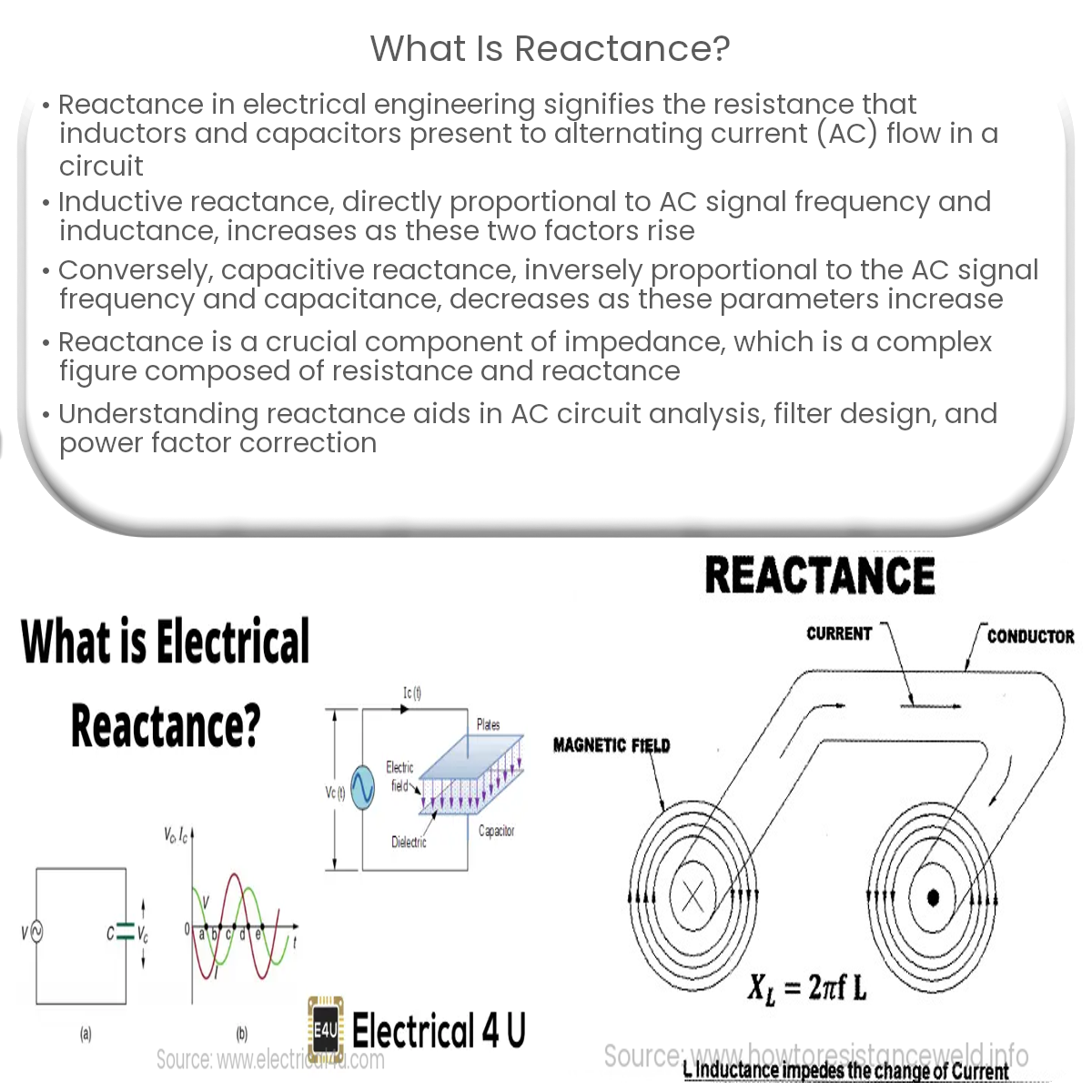
Reactance is a key concept in electrical engineering, representing the opposition that inductors and capacitors offer to the flow of alternating current (AC) in a circuit. Reactance is a component of impedance, a complex quantity that characterizes the total opposition to AC. This article will delve into the two types of reactance, inductive and capacitive, and their roles in electrical circuits.
Inductive Reactance
Inductive reactance (XL) is the opposition to AC current flow presented by an inductor. It is directly proportional to the frequency (f) of the AC signal and the inductor’s inductance (L). The formula for calculating inductive reactance is:
XL = 2πfL
As the frequency or inductance increases, so does the inductive reactance. Inductors store energy in their magnetic fields, which resist changes in the current. Consequently, inductive reactance is higher at higher frequencies, where the rate of change in the current is greater.
Capacitive Reactance
Capacitive reactance (XC) is the opposition to AC current flow presented by a capacitor. It is inversely proportional to the frequency (f) of the AC signal and the capacitor’s capacitance (C). The formula for calculating capacitive reactance is:
XC = 1 / (2πfC)
As the frequency or capacitance increases, capacitive reactance decreases. Capacitors store energy in their electric fields, which oppose changes in voltage. At higher frequencies, the rate of change in voltage is greater, resulting in a lower capacitive reactance.
Reactance in Impedance
Impedance (Z) is a complex quantity comprising resistance (R) and reactance (X). For a circuit containing only inductive or capacitive elements, the impedance is purely imaginary. In a more complex circuit with both resistance and reactance, the impedance is a complex number with real and imaginary components. The impedance formula is:
Z = R + jX
Where j is the imaginary unit, and X is either the inductive or capacitive reactance, depending on the circuit elements.
Applications of Reactance
Reactance plays a vital role in various applications, such as:
- AC circuit analysis: Understanding the behavior of inductors and capacitors in AC circuits.
- Filter design: Creating filters that selectively pass or block specific frequency ranges.
- Power factor correction: Balancing inductive and capacitive reactance to improve power efficiency in AC systems.
Conclusion
Reactance is an essential concept in electrical engineering, determining the behavior of inductors and capacitors in AC circuits. By understanding inductive and capacitive reactance, engineers can analyze, design, and optimize a wide range of electrical systems.