To calculate impedance in a circuit, add individual impedances in series, use the reciprocal formula for parallel, and apply complex arithmetic.
Calculating Impedance in a Circuit
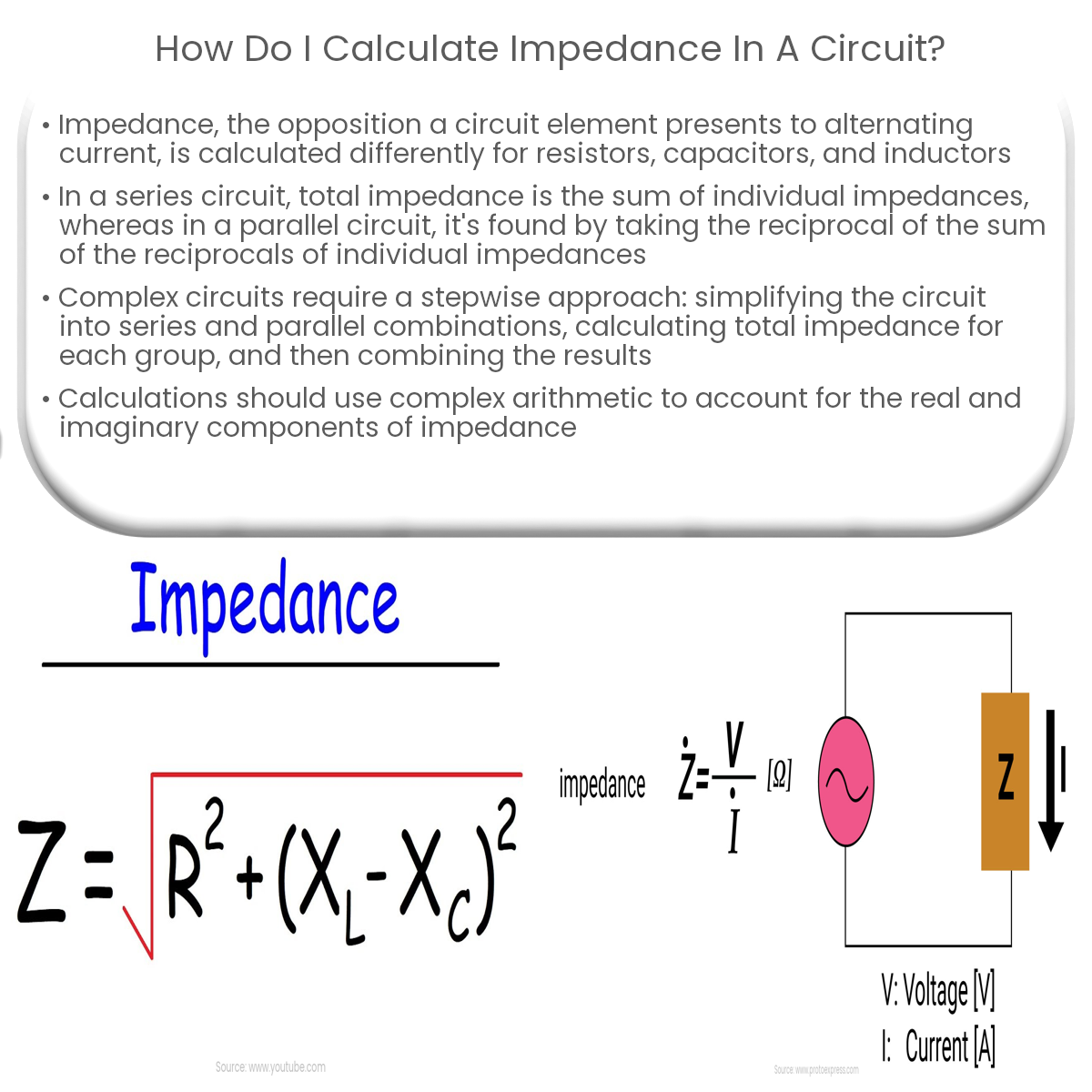
Impedance is a crucial concept in electrical engineering, as it represents the opposition a circuit element presents to alternating current (AC) or complex voltage. In this article, we’ll explore how to calculate impedance in various circuit configurations.
Impedance of Basic Circuit Elements
The impedance of resistors, capacitors, and inductors can be calculated using the following formulas:
- Resistors: Impedance (Z) equals resistance (R) itself, i.e., Z = R.
- Capacitors: Impedance is inversely proportional to the capacitance (C) and frequency (f) of the AC signal, i.e., Z = 1 / (jωC), where ω = 2πf.
- Inductors: Impedance is directly proportional to the inductance (L) and frequency (f) of the AC signal, i.e., Z = jωL, where ω = 2πf.
Impedance in Series Circuits
In a series circuit, the total impedance is the sum of the individual impedances. To calculate the total impedance (ZT), simply add the impedances of all the elements:
ZT = Z1 + Z2 + … + Zn
Impedance in Parallel Circuits
In a parallel circuit, the total impedance is found by taking the reciprocal of the sum of the reciprocals of the individual impedances. To calculate the total impedance (ZT), use the following formula:
1 / ZT = 1 / Z1 + 1 / Z2 + … + 1 / Zn
Impedance in Complex Circuits
For complex circuits with series and parallel combinations, follow these steps:
- Break down the complex circuit into simpler series and parallel combinations.
- Calculate the total impedance for each series or parallel group.
- Combine the resulting impedances using the rules for series and parallel circuits, working your way back to the original circuit.
Using Complex Numbers
When calculating impedance, it’s important to use complex numbers. Impedance is a complex value, with real and imaginary components representing resistance and reactance, respectively. Make sure to perform calculations using complex arithmetic to obtain accurate results.
Conclusion
Calculating impedance in a circuit is essential for understanding circuit behavior and optimizing performance. By breaking down complex circuits into simpler series and parallel combinations and using complex arithmetic, you can accurately determine the impedance of any circuit configuration.