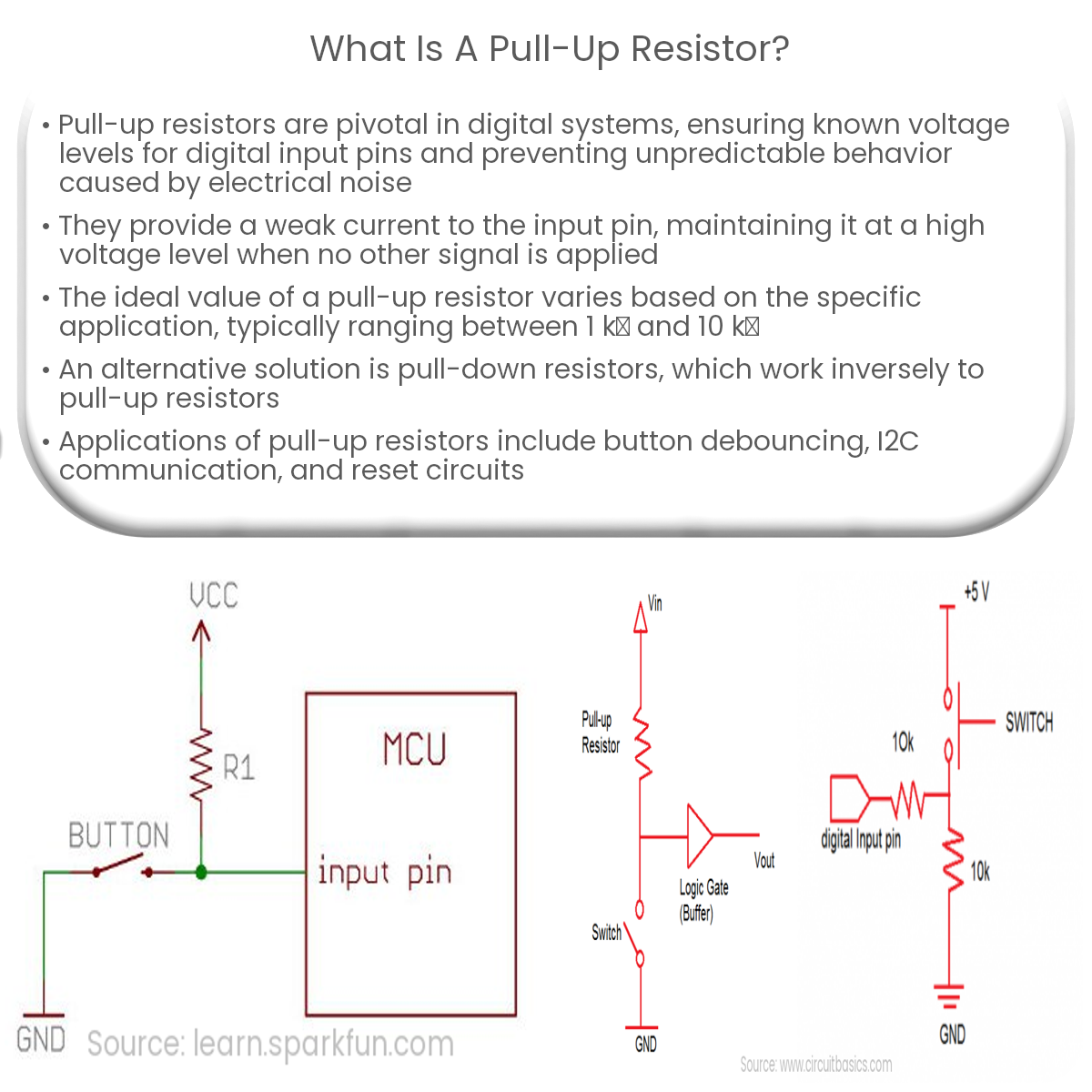
A pull-up resistor is a component in electronic circuits that ensures digital input pins have a defined voltage level, preventing unpredictable behavior.
Understanding Pull-Up Resistors
A pull-up resistor is a crucial component in electronic circuits, which helps establish a known voltage level for digital input pins in microcontrollers and other digital systems. In this article, we will explore the concept of pull-up resistors, their purpose, and how they function in an electronic circuit.
Why Use Pull-Up Resistors?
When digital input pins are left floating, or unconnected, they can be influenced by electrical noise, leading to unpredictable behavior in the system. Pull-up resistors are used to prevent this, by ensuring that input pins are always in a defined state, either high (logic 1) or low (logic 0).
How Pull-Up Resistors Work
A pull-up resistor is connected between the input pin and the positive voltage supply (usually VCC), and its purpose is to provide a weak current to the input pin, keeping it at a high voltage level (logic 1) when no other signal is applied. When an external device, such as a switch, connects the input pin to ground (GND), the voltage at the input pin drops to a low level (logic 0).
Calculating Pull-Up Resistor Values
The value of a pull-up resistor depends on the specific application and the microcontroller being used. Generally, higher resistor values consume less power, while lower values provide a stronger pull-up and faster response times. A typical range for pull-up resistors is between 1 kΩ and 10 kΩ.
Alternative: Pull-Down Resistors
Another method to avoid floating input pins is the use of pull-down resistors. These are connected between the input pin and ground (GND) and work similarly to pull-up resistors, but with an inverted logic. They hold the input pin at a low level (logic 0) when no other signal is applied, and when an external device connects the input pin to a positive voltage supply, the voltage at the input pin rises to a high level (logic 1).
Applications of Pull-Up Resistors
- Button debouncing: Pull-up resistors can help prevent false triggers caused by electrical noise when a button is pressed or released.
- I2C communication: In I2C communication, pull-up resistors are essential to ensure proper functioning of the SDA (serial data) and SCL (serial clock) lines.
- Reset circuits: Pull-up resistors are often used in reset circuits to maintain the microcontroller in a non-reset state when the reset button is not pressed.
In conclusion, pull-up resistors play a vital role in maintaining stability and predictability in digital systems, ensuring that input pins are in a defined state at all times.