A ferroelectric capacitor uses a ferroelectric material as a dielectric, offering unique properties for applications like tunable devices, memory, and sensors.
Introduction to Ferroelectric Capacitors
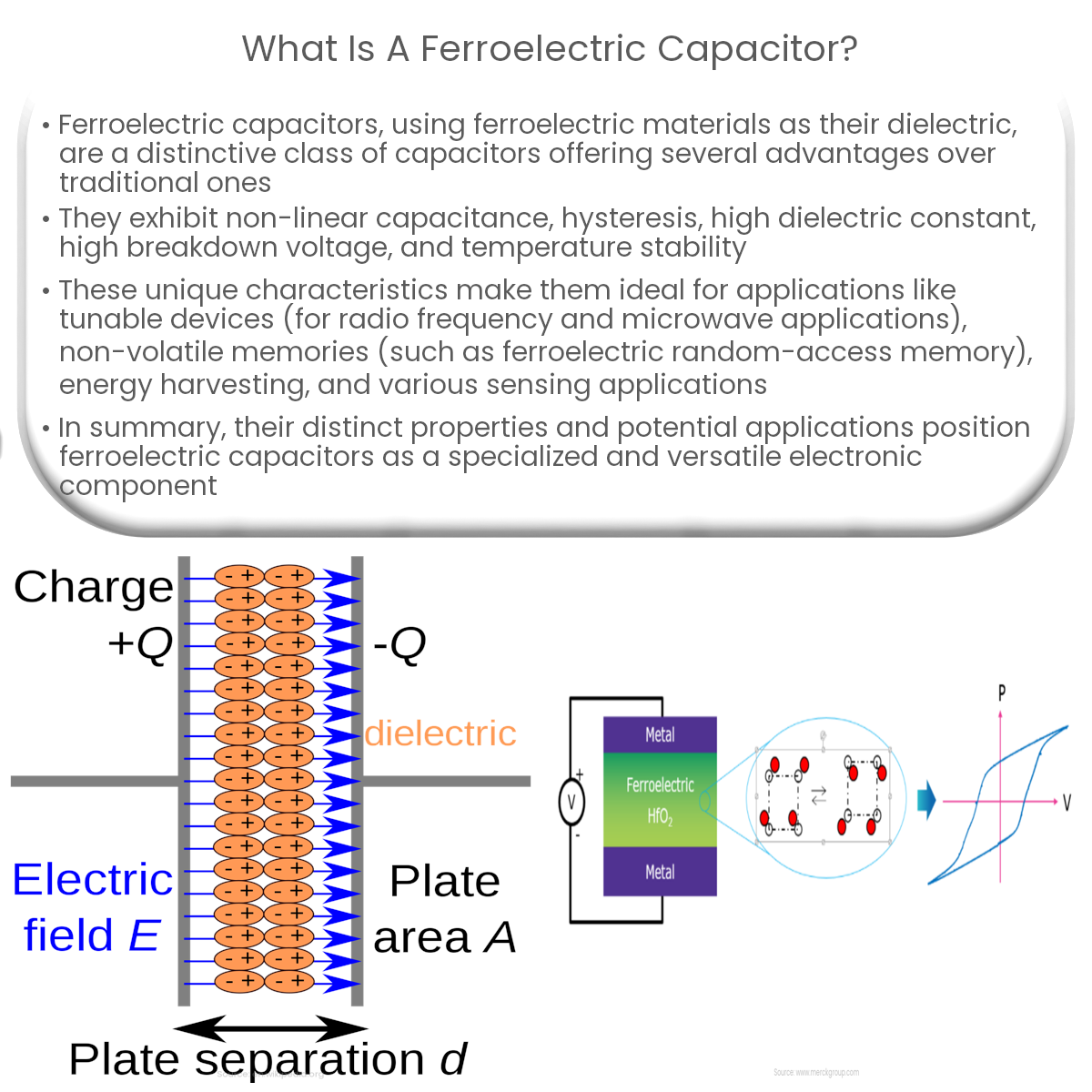
Ferroelectric capacitors are a unique class of capacitors that use ferroelectric materials as their dielectric, providing distinct advantages over traditional capacitors. This article discusses the fundamentals of ferroelectric capacitors, their key properties, and potential applications.
What is a Ferroelectric Capacitor?
A ferroelectric capacitor is an electronic component that stores and releases electrical energy using a ferroelectric material as the dielectric between its conductive plates. Ferroelectric materials exhibit spontaneous polarization, meaning they possess a permanent electric dipole moment that can be reversed by applying an external electric field. This property allows ferroelectric capacitors to exhibit non-linear capacitance and a hysteresis loop in their voltage-capacitance relationship, making them suitable for specialized applications.
Key Properties of Ferroelectric Capacitors
Ferroelectric capacitors possess several unique properties that differentiate them from traditional capacitors:
Applications of Ferroelectric Capacitors
Thanks to their unique properties, ferroelectric capacitors find use in a variety of specialized applications:
In conclusion, ferroelectric capacitors are specialized capacitors that utilize ferroelectric materials as dielectrics, offering unique properties and advantages over conventional capacitors. Their non-linear capacitance, hysteresis behavior, and high dielectric constant make them suitable for applications in tunable devices, non-volatile memories, energy harvesting, and sensors, among others.