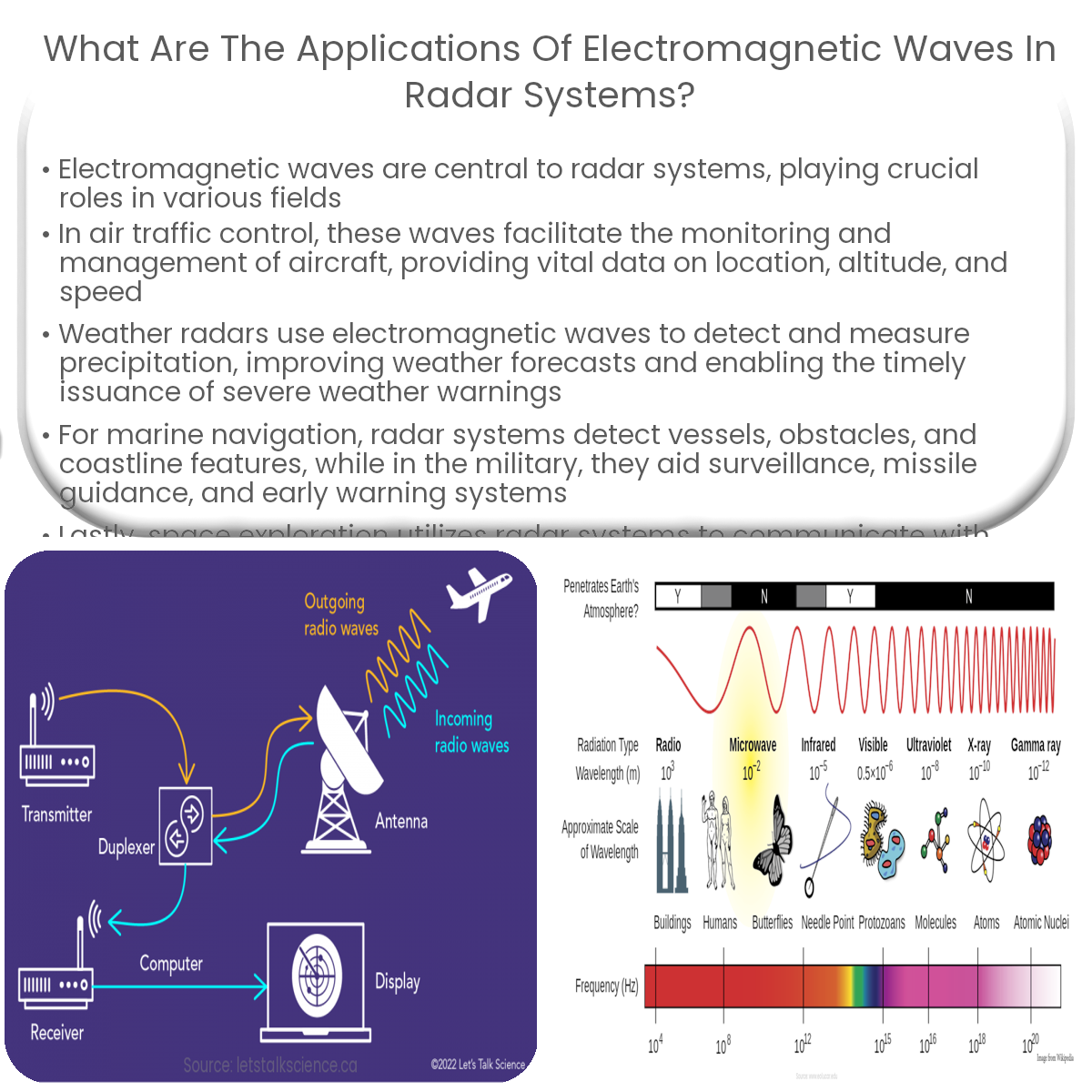
Electromagnetic waves in radar systems are used for air traffic control, meteorology, marine navigation, military applications, and space exploration.
Applications of Electromagnetic Waves in Radar Systems
Radar systems play a vital role in various industries, from aviation to meteorology. Central to their functionality is the use of electromagnetic waves to detect and locate objects. In this article, we will explore the key applications of electromagnetic waves in radar systems.
1. Air Traffic Control
-
Air traffic control relies on radar systems to monitor and manage aircraft during takeoff, landing, and while en route. Primary radar systems emit electromagnetic waves that bounce off aircraft, providing controllers with information about an aircraft’s location, altitude, and speed.
-
Secondary surveillance radar (SSR) further enhances this process by communicating with transponders on board the aircraft, allowing for more accurate and reliable data transmission.
2. Meteorology
-
Weather radars utilize electromagnetic waves to detect and measure precipitation, such as rain, snow, and hail. The data gathered helps meteorologists predict and track storms, improving the accuracy of weather forecasts and enabling the timely issuance of severe weather warnings.
-
Doppler radar systems measure the frequency shift of the returned electromagnetic waves, allowing meteorologists to estimate wind speed and direction. This information is crucial for identifying and monitoring the development of severe weather events like tornadoes and hurricanes.
3. Marine Navigation
Marine radar systems are essential for ship navigation, particularly in low-visibility conditions. By emitting electromagnetic waves and interpreting the returned signals, radar systems can detect the presence of other vessels, obstacles, and coastline features, ensuring safe navigation and collision avoidance.
4. Military Applications
-
Surveillance and reconnaissance: Military radar systems are employed to monitor and track the movements of enemy aircraft, ships, and ground vehicles. This information is critical for planning and executing strategic operations.
-
Missile guidance: Radar-guided missiles rely on electromagnetic waves to track and engage targets, ensuring precision and accuracy in both offensive and defensive operations.
-
Early warning systems: Radar installations are used to detect incoming missiles or hostile aircraft, providing early warning and allowing for appropriate defensive measures to be taken.
5. Space Exploration
Ground-based radar systems are utilized to track and communicate with satellites, space probes, and other orbiting objects. Additionally, radar systems on space missions, such as lunar or planetary landers, use electromagnetic waves to map and analyze the surface of celestial bodies, providing valuable data for scientific research and exploration.