Explore the world of two-axis gyroscopes, their mechanics, applications in tech, limitations, and the future prospects in this comprehensive guide.

Introduction to Two-Axis Gyroscope
The two-axis gyroscope is a vital instrument in numerous technological devices. It serves a significant purpose in guiding, controlling, and measuring the orientation, angular velocity, and attitude of a range of equipment, including unmanned aircraft, guided missiles, and robotics. The term “two-axis” refers to the device’s ability to detect or measure rotational motion about two perpendicular axes.
Understanding the Mechanics of a Two-Axis Gyroscope
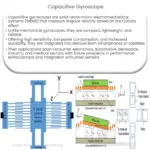
Gyroscopes, in general, operate based on the principles of conservation of angular momentum. A gyroscope comprises a rotor or a spinning wheel, which maintains its orientation due to the conservation law. However, a two-axis gyroscope takes this a notch higher. It can measure or maintain orientation along two different axes, offering greater versatility and control.
Structure and Working Principle
- Structure: At the heart of a two-axis gyroscope is a spinning disc mounted in a frame or a set of gimbals that allows it to pivot in two directions. This structure provides the device with the freedom to rotate or reorient itself about two distinct axes.
- Working Principle: The two-axis gyroscope operates by leveraging the principle of angular momentum conservation. When a torque is applied, the gyroscope experiences a phenomenon known as precession. This results in a movement that is perpendicular to the direction of the applied torque. The gyroscope detects this movement and uses it to provide real-time feedback on the object’s orientation and rotation rate.
Application of Two-Axis Gyroscopes
The utility of two-axis gyroscopes is expansive. They find applications in various technological devices where precise orientation and movement tracking are essential. Some of the most common uses include:
- Aviation: Two-axis gyroscopes are vital for aircraft navigation systems. They help pilots determine their aircraft’s attitude, direction, and rate of turn.
- Space Exploration: Two-axis gyroscopes play a crucial role in maintaining the attitude and direction of spacecraft. They are indispensable in long space voyages where precise orientation is paramount.
While the applications and significance of two-axis gyroscopes are diverse and widespread, it’s important to consider some of its potential limitations. Let’s dive deeper into this in the next section.
Limitations of Two-Axis Gyroscopes
Despite their numerous applications and importance, two-axis gyroscopes are not without limitations. Some of these limitations include:
- Gyroscopic Drift: This refers to the slow and steady change in the output of the gyroscope over time when there’s no rotation. It’s caused by factors like temperature changes, mechanical stress, and electronic noise.
- Physical Constraints: Two-axis gyroscopes cannot measure rotation around the axis perpendicular to the two measurement axes, often referred to as the ‘blind’ axis. To measure rotation around all three axes, a three-axis gyroscope is required.
Advancements and Future Prospects
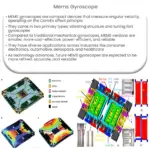
Given these challenges, continuous advancements are being made in the field of two-axis gyroscopes. The advent of micro-electro-mechanical systems (MEMS) has resulted in the miniaturization of these devices, leading to their widespread use in consumer electronics like smartphones and gaming devices.
Furthermore, the future holds great promise for the development of more accurate, reliable, and miniature two-axis gyroscopes. Continued research and development in this field are expected to push the boundaries of what is possible, heralding new and innovative applications across various sectors.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the two-axis gyroscope is an invaluable tool in the technology and engineering sectors. It offers significant advantages in navigation, control, and measurement of orientation and angular velocity, particularly in aviation and space exploration. Despite some limitations, the scope and potential of two-axis gyroscopes are ever-expanding with ongoing advancements and research. As we continue to innovate and push the boundaries of technology, it’s clear that these devices will continue to play a pivotal role in many areas of our lives.