Explore the world of touch sensors, their working principles, types, applications, benefits, and future trends in interactive technology.
Introduction to Touch Sensors
One of the most critical components in many electronic devices we use daily is the touch sensor. A touch sensor is a type of equipment that captures and records physical touch or embrace on a device and/or object. It is a crucial part of devices that we have come to rely on, such as smartphones, laptops, and many other interactive devices. The touch sensor technology has rapidly evolved over the years, providing us with the ability to operate our devices with ease and convenience.
Working Principle of Touch Sensors
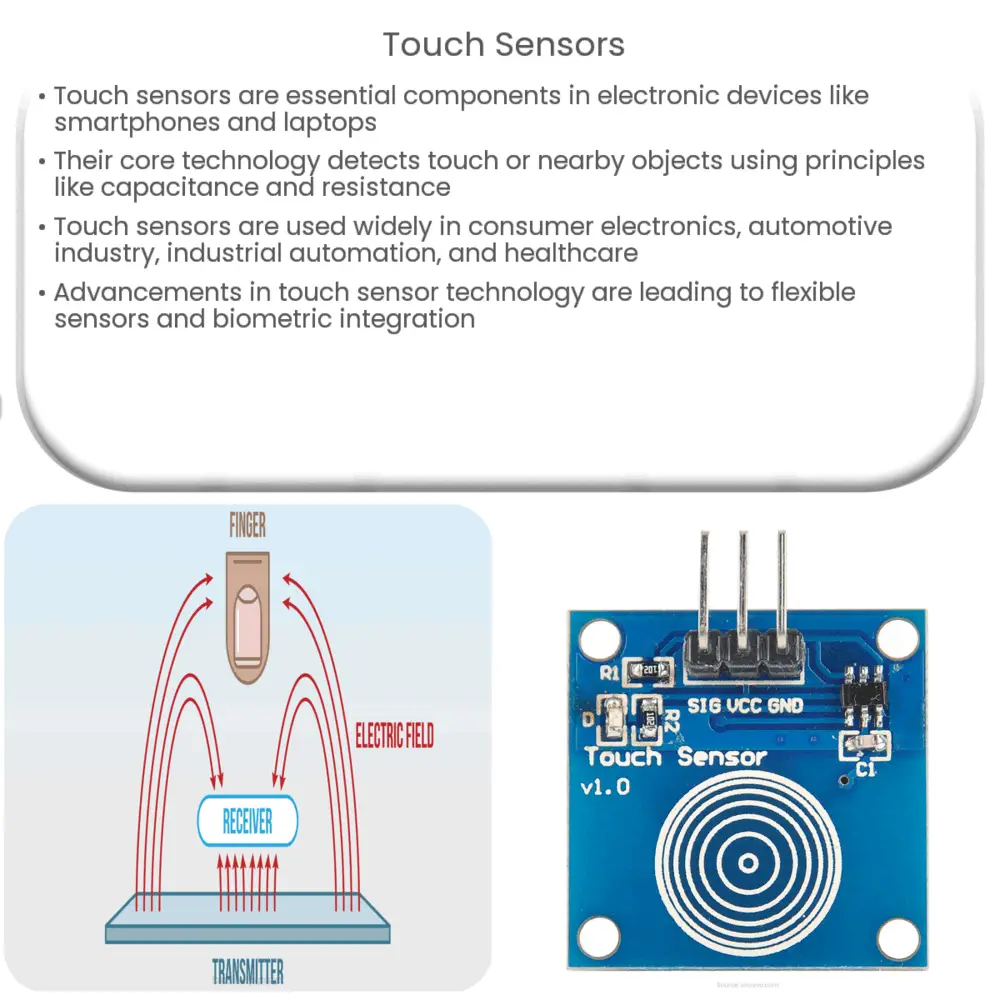
At the core of touch sensor technology is the ability to detect the presence or movement of a touch or nearby object. The sensors work based on various principles, including capacitance, resistance, optical, and acoustic waves.
- Resistive: Resistive touch sensors function by applying pressure on the sensor’s surface, causing a change in resistance that the system then measures. This technology is typically used in applications that require precise and multi-touch functionality.
- Capacitive: Capacitive sensors detect touch by measuring the change in electrical capacitance caused by the presence of a conductive object, like a human finger. These sensors are often used in smartphones and tablets.
- Optical: These sensors detect a change in light intensity. An array of infrared light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and photosensors arranged on the edges of the display can detect any interruption of light when the display is touched.
- Acoustic: Acoustic wave systems use ultrasonic waves that pass over the panel. When the panel is touched, a portion of the wave is absorbed, indicating the touch location to the controller for processing.
Types of Touch Sensors
Touch sensors come in various types and each type has its unique functionality and application. The most common ones are the capacitive touch sensors and resistive touch sensors, but there are also others like infrared touch sensors and surface acoustic wave sensors.
- Capacitive Touch Sensors: These sensors can be either surface capacitive sensors or projected capacitive sensors, with the latter providing multi-touch capabilities.
- Resistive Touch Sensors: Resistive touch sensors consist of a glass panel covered with a conductive and a resistive metallic layer. The two layers are separated by spacers, and a scratch-resistant layer is placed on top.
Touch sensors have drastically transformed the way we interact with electronic devices, making them more intuitive and user-friendly. In the next part of this article, we will delve into more specifics on the applications of touch sensors, their benefits, and future trends in touch sensor technology.
Applications of Touch Sensors
Touch sensors have found widespread application in numerous sectors, thanks to their versatility and efficiency. They have especially revolutionized the way we interact with technology, enhancing our user experience substantially. Here are a few notable applications:
- Consumer Electronics: Touch sensors are commonly used in smartphones, tablets, and laptops. They allow for intuitive control and interaction, enhancing the user experience.
- Automotive Industry: Modern vehicles are increasingly equipped with touch sensors for various controls, including infotainment systems, climate control, and other in-car systems.
- Industrial Automation: In industrial applications, touch sensors are used in machine controls, touch screen kiosks, and in interactive digital signage, among others.
- Healthcare: Touch sensors are used in various medical devices for diagnostics, patient monitoring, and in medical imaging systems.
Advantages of Touch Sensors
The numerous advantages of touch sensors contribute to their widespread adoption. These include:
- User-friendly: Touch sensors provide a natural and intuitive human-machine interface, making devices easier to use.
- Space-saving: Since the touch sensor technology eliminates the need for physical buttons, it saves space in device design.
- Durable: Touch sensors are highly durable and can withstand harsh environments, making them suitable for various applications.
Future Trends in Touch Sensor Technology
With advancements in technology, the applications and capabilities of touch sensors are continuously expanding. Some future trends in this field include:
- Flexible touch sensors: With the rise of flexible electronics, flexible touch sensors have emerged, offering the potential to be integrated into wearable devices or curved surfaces.
- Force sensing: This type of touch sensor can measure the degree of force or pressure applied, adding another dimension to touch interaction.
- Biometric integration: Touch sensors can be combined with biometric technologies such as fingerprint or heart rate detection for enhanced security and personalized user experience.
Conclusion
In conclusion, touch sensors play a crucial role in the world of interactive technology. They have redefined our interaction with electronic devices, making them more intuitive and user-friendly. With continuous advancements in this field, we can anticipate a future where touch sensors become an even more integral part of our daily lives, extending their reach into new and innovative applications. As technology evolves, so too will the capabilities and potential uses of touch sensors, pointing towards an exciting future for this transformative technology.

