Explore the world of Transient Voltage Suppressors (TVS), their types, applications, selection, and importance in protecting electronic circuits.
Introduction to Transient Voltage Suppressors (TVS)
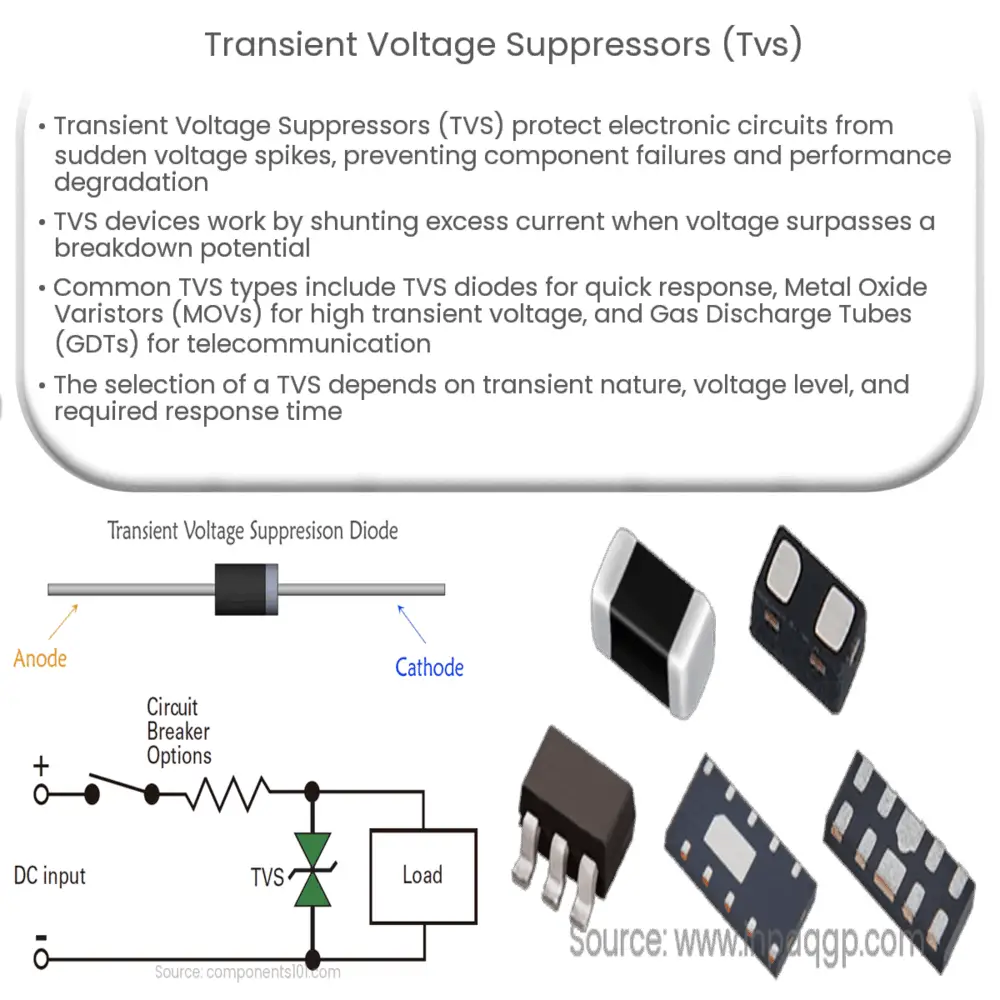
A Transient Voltage Suppressor (TVS)
is a general classification of an array of devices designed to protect electronic circuits against sudden voltage spikes caused by environmental conditions or internal changes. These voltage surges can lead to catastrophic failure of the components or severe degradation of their performance. Hence, TVS devices are crucial for improving the robustness and reliability of electronics.
Working Principle of a TVS Device
A TVS device works by shunting the excess current when the induced voltage exceeds the avalanche breakdown potential. This voltage is a precise and inherent property of the semiconductor materials that constitute the TVS device. This characteristic behavior of a TVS device makes it an ideal solution for transient voltage suppression applications.
Types of Transient Voltage Suppressors
- TVS Diodes: These are the most common types of transient voltage suppressors. They can react quickly to a surge voltage, providing protection in nanoseconds. TVS diodes are typically used in low-voltage and sensitive electronics systems to protect against electrostatic discharges, inductive load switching, and other forms of transients.
- Metal Oxide Varistors (MOVs): MOVs are voltage-dependent, nonlinear devices that provide excellent transient voltage suppression. When exposed to high transient voltage, MOVs exhibit a low electrical resistance. They are frequently employed in power supply circuits and are known for their ability to handle high transient current.
- Gas Discharge Tubes (GDTs): GDTs use an inert gas trapped in a ceramic tube to suppress high voltage transients. When a specific breakdown voltage is reached, the gas ionizes and becomes a short circuit to shunt the excess current, thereby protecting the circuit. GDTs are typically used in telecommunication applications.
Applications of TVS Devices
TVS devices find their uses in a broad spectrum of applications due to their transient protection capabilities. They are typically found in communication systems, microprocessors, power supplies, and industrial equipment, among others. However, the choice of a particular type of TVS depends on the nature of the transient, the voltage level, and the required response time.
Selecting the Right TVS
While choosing a TVS for a specific application, it is essential to consider several factors such as the working voltage, clamping voltage, peak pulse current, and response time. The working voltage should be higher than the maximum system operating voltage. The clamping voltage is the voltage the TVS will limit to during a transient event and should be as low as possible to prevent damage to downstream components.
The peak pulse current is the maximum current that the TVS can safely dissipate without failure. This should be equal to or higher than the maximum expected surge current. The response time is a measure of how quickly the TVS can react to a surge event. In general, a lower response time translates to better protection.
Installation of TVS
When installing a TVS, it is crucial to position it as close as possible to the point of transient entry to minimize the length of the path between the TVS and the transient source. This would help to reduce the parasitic inductance and resistance that can limit the effectiveness of the TVS.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Transient Voltage Suppressors are vital components in today’s electronic systems for managing voltage transients and enhancing system robustness. With a plethora of choices like TVS diodes, MOVs, and GDTs, it is possible to find a TVS to suit nearly any application. However, it is crucial to carefully select the right TVS based on its working voltage, clamping voltage, peak pulse current, and response time, among other parameters.
By choosing the right TVS device and installing it correctly, electronics manufacturers and designers can significantly improve the resilience and lifespan of their products. As we move towards an increasingly connected world with electronics at its core, the role of TVS devices in safeguarding our devices from transient voltages becomes ever more critical.

