Explore the working principles, types, applications, advantages, and drawbacks of thermal mass flow meters used in various industries.
Understanding Thermal Mass Flow Meters
Thermal mass flow meters are a type of flow meter that measures the flow rate of gases and liquids in a pipe or duct. This is typically achieved by using heat to measure the “mass” flow rate, hence the name. Unlike volumetric flow meters, thermal mass flow meters are not affected by changes in temperature and pressure.
Principles of Operation
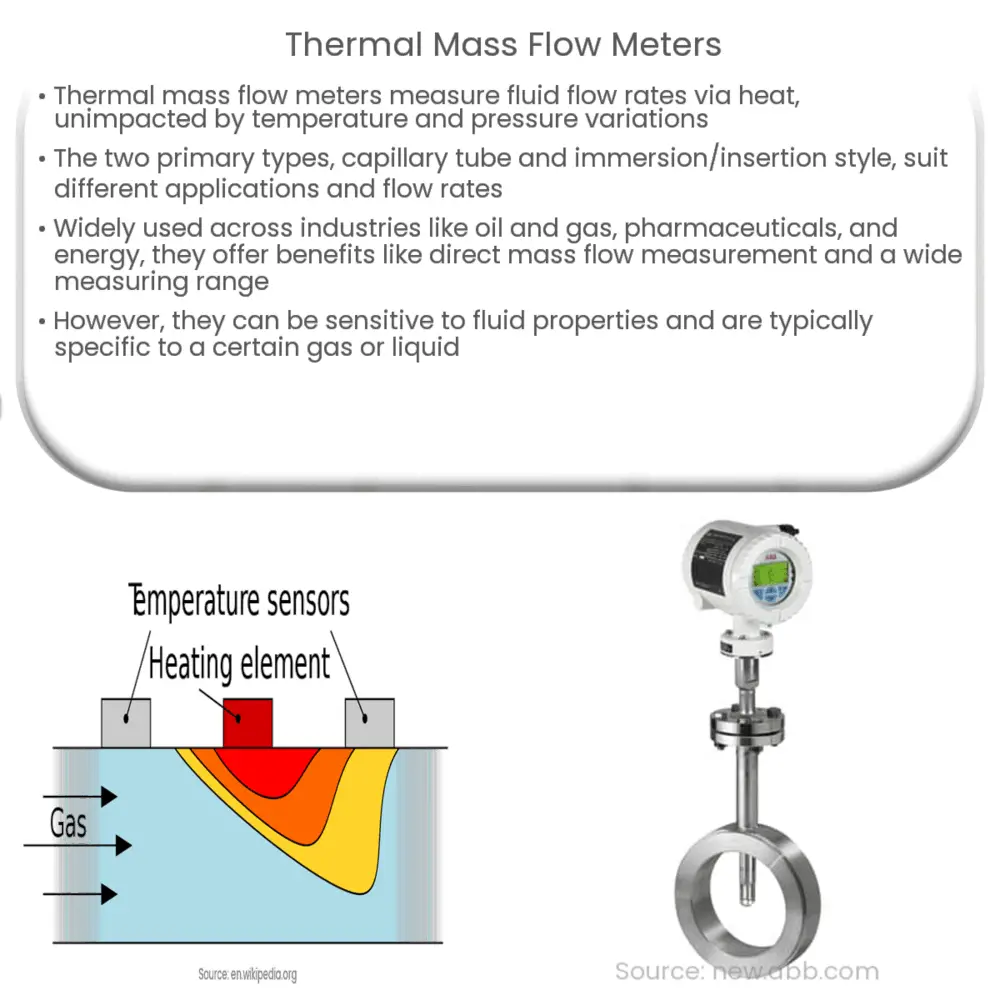
Thermal mass flow meters operate based on the principle of heat transfer. They have two main elements: a heated sensor (or heater) and a temperature sensor. Both are located in the fluid flow path. The heated sensor imparts a specific amount of heat into the fluid, while the temperature sensor measures the temperature of the fluid.
- The heater raises the temperature of the fluid stream.
- As the fluid moves past the heater, it carries away the heat.
- The amount of heat carried away by the fluid correlates directly with its mass flow rate.
Types of Thermal Mass Flow Meters
There are two primary types of thermal mass flow meters: Capillary Tube and Immersion or Insertion style.
- Capillary Tube: These meters use a small, heated capillary tube through which the fluid passes. The temperature differential between two points on the tube indicates the mass flow rate. Capillary tube designs are highly accurate but typically for smaller flow rates.
- Immersion or Insertion Style: This design involves a heated sensor placed directly into the fluid stream. The flow of the fluid across this sensor causes a cooling effect, which correlates with the mass flow rate. This style of meter is commonly used for larger flow rates or ducted air flow applications.
The choice between these types depends on the application, the type of fluid, the flow rate, and the required level of accuracy.
Applications of Thermal Mass Flow Meters
Thermal mass flow meters have a wide range of applications in various industries.
- In the oil and gas industry, they are used for measuring the flow rate of natural gas.
- In pharmaceutical and biotech manufacturing, they are used for controlling the flow rate of gases in processes.
- The food and beverage industry uses these meters for carbonation processes and gas blanketing.
- Thermal mass flow meters are essential in the energy sector, particularly in power plants, where they are used for combustion control and flue gas monitoring.
- In environmental monitoring, they aid in pollution control by measuring the output of greenhouse gases.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Like any other instrument, thermal mass flow meters have their strengths and weaknesses.
Advantages:
- Independence from Physical Properties: Unlike other types of flow meters, thermal mass flow meters do not require temperature or pressure compensation.
- Direct Mass Flow Measurement: They provide direct mass flow measurement without needing any additional equipment or calculations.
- Rangeability: They have a wide measuring range, making them suitable for various applications.
Disadvantages:
- Gas or Liquid Specific: Most thermal mass flow meters are calibrated for a specific gas or liquid, and their performance can degrade when used with other fluids.
- Sensitivity: They can be sensitive to changes in fluid properties like viscosity.
Conclusion
In conclusion, thermal mass flow meters are versatile instruments used for direct mass flow measurement in a variety of industries. They operate on the principle of heat transfer, with two primary types: capillary tube and immersion or insertion style. Despite their sensitivity to fluid properties and specificity to certain gases or liquids, their advantages, such as independence from physical properties, direct mass flow measurement, and rangeability, make them invaluable in applications such as the oil and gas, pharmaceutical, biotech, food and beverage, and energy industries, among others. As technology continues to evolve, improvements to their design and functionality are expected, enhancing their performance and broadening their range of applications.




