Explore the world of series voltage regulators: their working principle, types, applications, and design considerations in electronics.
Understanding the Concept of a Series Voltage Regulator
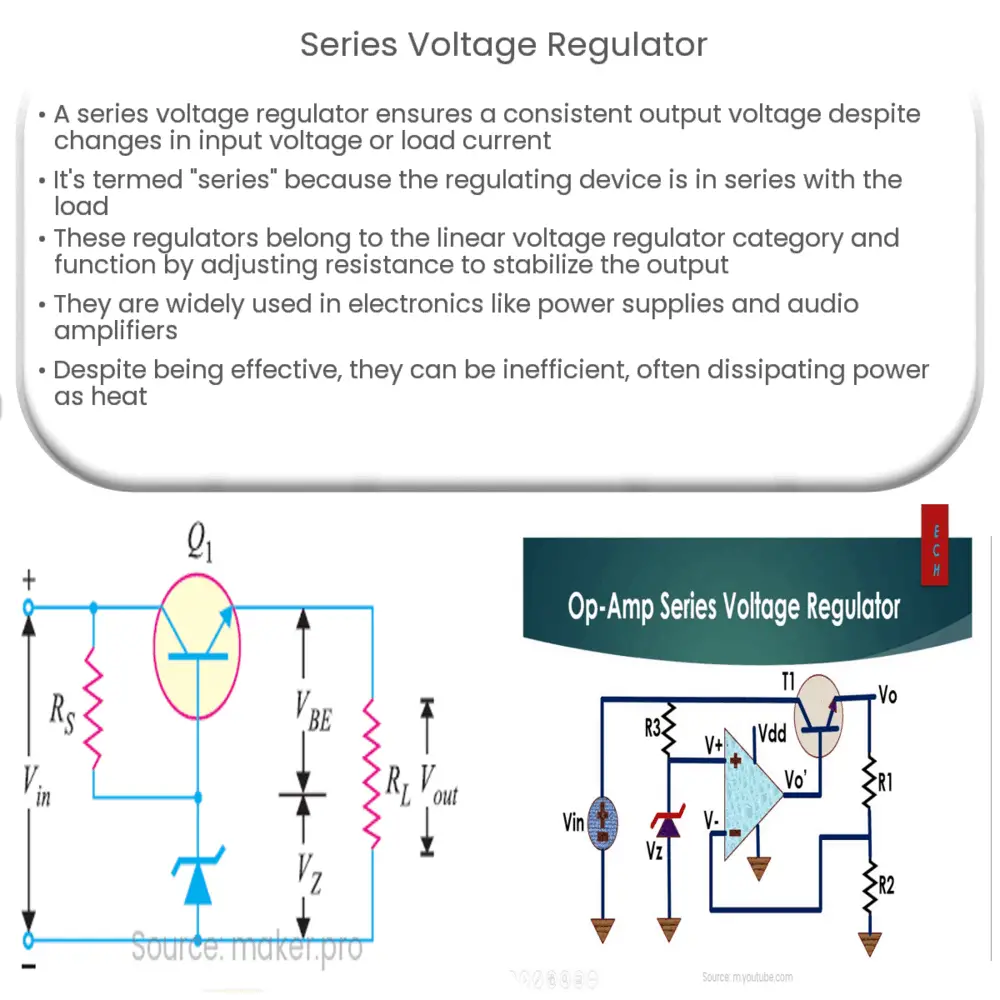
A series voltage regulator is an essential component in electronics that ensures a consistent and regulated output voltage, regardless of changes in the input voltage or the load current. It is called a ‘series’ regulator because the regulating device is in series with the load. The primary aim of this regulator is to maintain a steady output voltage and prevent fluctuations that could potentially damage electrical devices or affect their performance.
There are two primary types of voltage regulators: linear and switching. The series voltage regulator falls under the category of linear voltage regulators. These regulators work by dropping the excess voltage in a series resistive element and are appreciated for their simplicity and low output noise.
The Working Principle of a Series Voltage Regulator
A series voltage regulator operates by using a variable series resistance. The resistance changes in response to fluctuations in input voltage, thereby stabilizing the output voltage. It involves a feedback circuit that adjusts the resistance based on the output voltage. When the input voltage or the load current increases, the resistance increases to maintain a constant output voltage, and vice versa.
- Input Stage: The input stage receives the unregulated input voltage. This voltage can vary widely, which is where the regulator comes into play.
- Error Amplifier: This component compares the reference voltage with the output voltage. If there is a discrepancy between these two voltages, the error amplifier generates a correction signal.
- Series Pass Transistor: This is the crucial component in the regulator. It acts as a variable resistor, adjusting its resistance based on the correction signal from the error amplifier. In this way, it maintains a constant output voltage regardless of changes in the input voltage or load current.
It is important to note that while series voltage regulators are relatively simple and effective, they are not without their drawbacks. One significant disadvantage is their efficiency. They can dissipate a considerable amount of power as heat, especially when there is a large difference between the input and output voltages.
The Application of Series Voltage Regulators
Series voltage regulators find wide application in various fields, including power supplies, computer power systems, and various electronic devices. They are particularly useful in situations where a stable and consistent voltage supply is required. For example, they are often used in audio and radio frequency amplifiers, where a stable power supply is crucial for optimal performance.
Despite their limitations, series voltage regulators offer simplicity, low noise, and a steady output voltage, making them a popular choice in many applications. Understanding their working principle and characteristics can provide a deeper insight into their role in electronic circuits and devices.
Types of Series Voltage Regulators
There are several types of series voltage regulators, each with its unique set of features and applications.
- Fixed Voltage Regulators: As the name suggests, these regulators provide a fixed output voltage. They are often used in applications where the load is relatively constant and does not need frequent adjustments. An example of a fixed voltage regulator is the popular 7805 IC, which provides a fixed 5V output.
- Adjustable Voltage Regulators: These regulators offer a variable output voltage, which can be adjusted as per the requirements of the load. They are more flexible than fixed voltage regulators and find use in a wide variety of applications.
- Switching Regulators: While not a traditional linear series regulator, they are worth mentioning because of their higher efficiency. Instead of dissipating excess voltage as heat, switching regulators convert it into useful power, making them more efficient but also more complex.
Designing a Series Voltage Regulator
Designing a series voltage regulator involves several factors such as load requirements, input voltage range, and desired efficiency. Additionally, considerations such as heat dissipation and component selection also play a significant role. While the design process may seem complex, it is a rewarding experience that provides a practical understanding of the principles of voltage regulation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, series voltage regulators play a crucial role in maintaining the stability and reliability of electronic systems. They ensure that the output voltage remains steady, irrespective of variations in input voltage or load current. Despite their relatively low efficiency and power dissipation as heat, they are appreciated for their simplicity and low output noise. With a sound understanding of their working principle and applications, one can appreciate the significance of series voltage regulators in the world of electronics.
The various types of series voltage regulators, including fixed, adjustable, and switching regulators, offer unique advantages and are suited to different applications. Consequently, choosing the right type of regulator depends on the specific requirements of the electronic system in question. The design of a series voltage regulator is a complex but enriching process that sheds light on the intricacies of voltage regulation and electronic design.

