A series current regulator maintains a stable current flow in circuits, protecting components and ensuring efficiency, despite input voltage variations.
Series Current Regulator: An Overview
Introduction
A series current regulator is an essential component in many electronic circuits that ensures a stable and constant current flow irrespective of variations in input voltage or load resistance. This device offers a range of benefits, including protection from overcurrent and thermal issues, improved efficiency, and reduced noise in sensitive applications. In this article, we’ll explore the fundamentals of series current regulators, their applications, and how they work.
What is a Series Current Regulator?
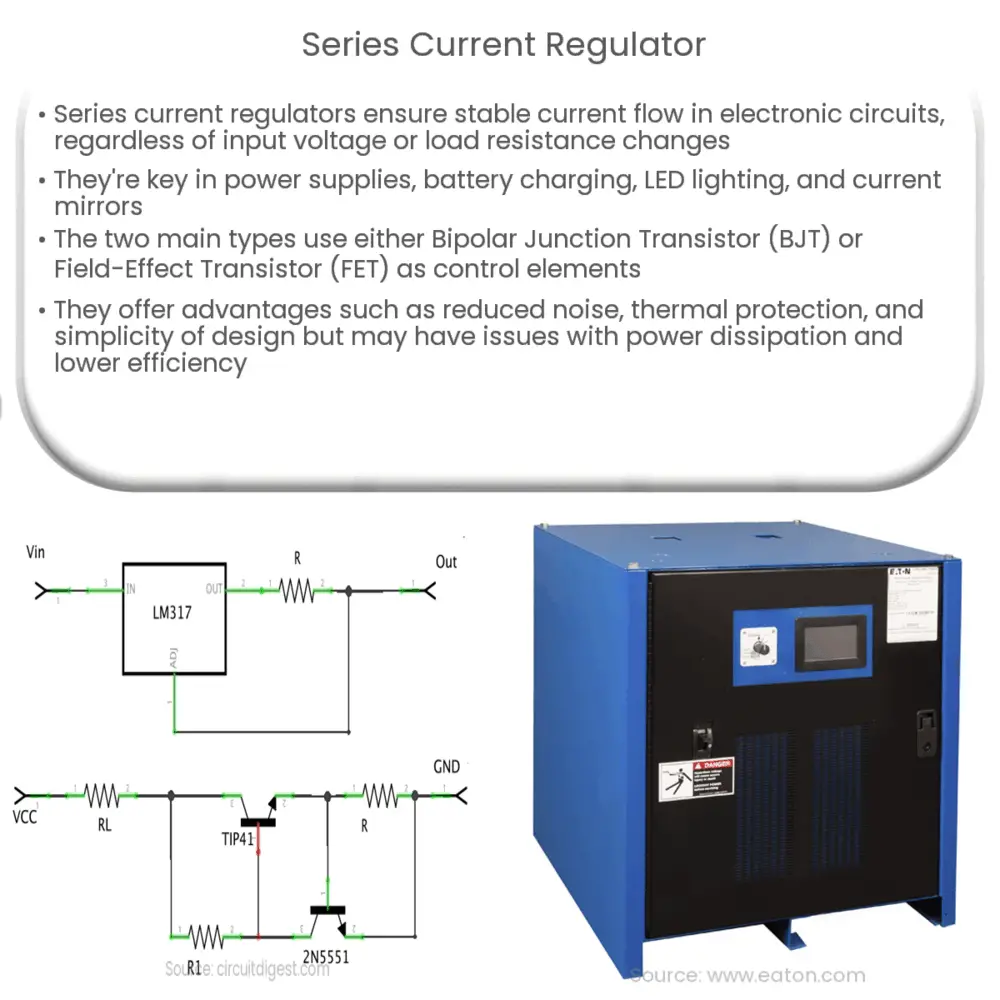
A series current regulator, also known as a series pass regulator, is a type of linear voltage regulator that controls the current flow in a circuit by adjusting its output voltage. The regulator is placed in series with the load, and it ensures that a constant current is maintained even if the input voltage or load resistance changes. This is achieved by continuously adjusting the output voltage to maintain the desired current level, hence the name ‘series’ regulator.
Applications of Series Current Regulators
Series current regulators find their application in various electronic devices and systems, such as:
- Power supplies: They are used in power supplies to maintain a stable output current, preventing damage to components and ensuring efficient operation.
- Battery charging: In battery charging circuits, series current regulators help control the charging current, ensuring safe and efficient charging of the battery.
- LED lighting: Constant current regulators are essential in LED lighting circuits, as they prevent LED damage due to fluctuations in input voltage or load resistance.
- Current mirrors: They are used to create a current mirror, a circuit that generates a constant current output proportional to an input current.
How Series Current Regulators Work
The primary function of a series current regulator is to maintain a constant current flow through a load, regardless of changes in input voltage or load resistance. To achieve this, the regulator uses a control element, such as a transistor or a field-effect transistor (FET), to adjust its output voltage.
When the input voltage increases, the control element reduces its resistance, lowering the output voltage to maintain a constant current flow. Conversely, when the input voltage decreases, the control element increases its resistance, raising the output voltage and ensuring a stable current. Similarly, if the load resistance changes, the series current regulator adjusts its output voltage to maintain the desired current level.
Types of Series Current Regulators
There are two primary types of series current regulators based on their control elements:
- Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) based regulators: These regulators use a bipolar transistor as the control element. They are known for their low output impedance and high current gain, which contribute to better regulation performance. However, they have a higher base current requirement and generate more heat compared to FET-based regulators.
- Field-Effect Transistor (FET) based regulators: FET-based regulators use a field-effect transistor as the control element. These regulators exhibit lower input current requirements and generate less heat than BJT-based regulators. However, their output impedance and current gain are typically lower, which may result in reduced regulation performance.
Advantages of Series Current Regulators
Series current regulators offer several benefits that make them a popular choice for various applications:
- Stable current output: They maintain a constant current flow, ensuring consistent performance and protecting sensitive components from damage due to current fluctuations.
- Reduced noise: The linear regulation technique used in series current regulators effectively filters out noise from the input voltage, providing a clean and stable current output.
- Thermal protection: By controlling the current flow, series current regulators help prevent overheating and damage to components caused by excessive current.
- Simple design: Series current regulators have a relatively simple circuit design, making them easier to implement and maintain compared to more complex regulation techniques.
Disadvantages of Series Current Regulators
Despite their numerous advantages, series current regulators also have some drawbacks:
- Power dissipation: Due to their linear operation, series current regulators can generate significant heat, leading to power loss and decreased efficiency, especially when the difference between the input and output voltage is large.
- Size and weight: Linear regulators may require larger heatsinks to dissipate heat, increasing the overall size and weight of the circuit.
- Lower efficiency: The linear nature of series current regulators results in lower efficiency compared to alternative solutions, such as switching regulators.
Conclusion
Series current regulators play a crucial role in ensuring stable current flow in various electronic applications, including power supplies, battery charging circuits, LED lighting, and current mirrors. By understanding their working principles, advantages, and disadvantages, designers can make informed decisions on the most suitable current regulation solution for their specific needs. Despite their drawbacks, series current regulators remain a popular choice due to their stable output, reduced noise, thermal protection, and simplicity of design.