Explore the structure, operation, applications, advantages, and limitations of the versatile SEPIC converter in our comprehensive guide.
Understanding the SEPIC Converter
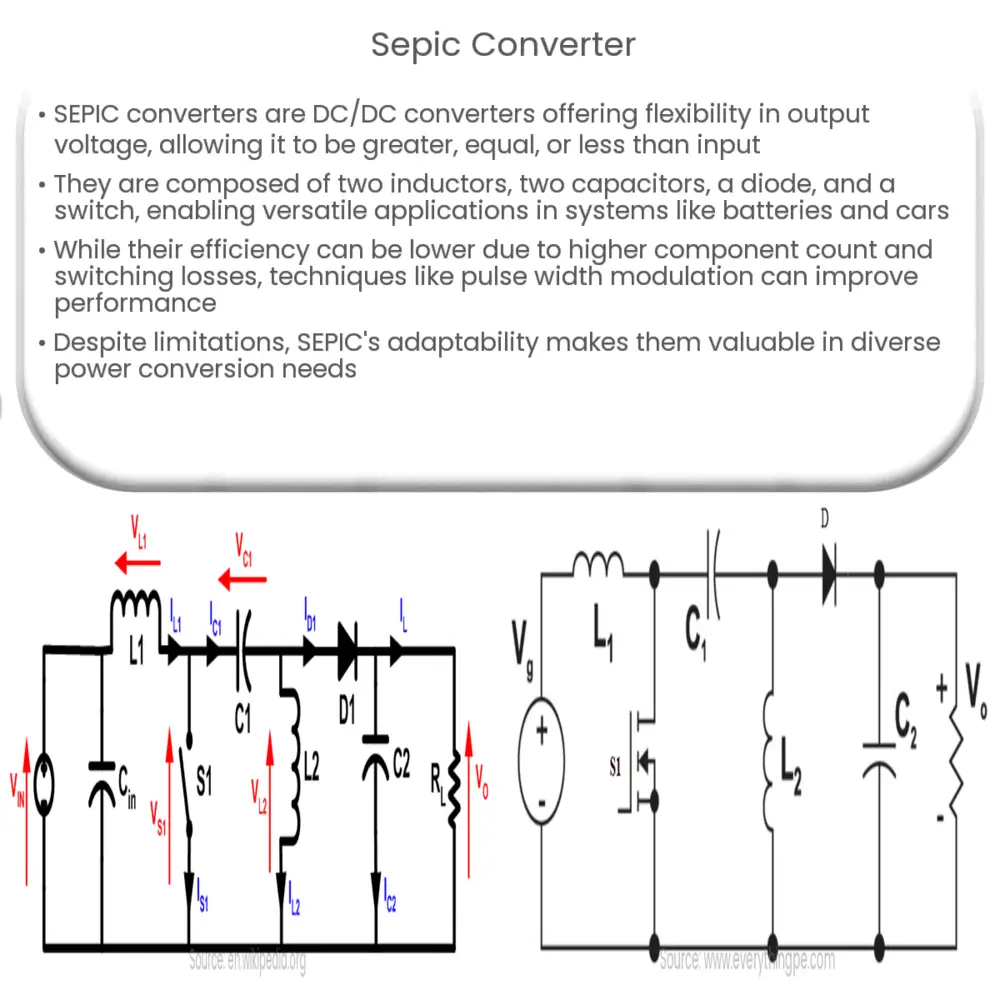
The Single-Ended Primary Inductor Converter (SEPIC) is a type of DC/DC converter that allows the electrical voltage at its output to be greater than, less than, or equal to the input voltage. The flexibility of the SEPIC converter makes it a popular choice in applications where both step-up and step-down conversions are required.
Structure and Operation
The SEPIC converter is built with key components including two inductors, two capacitors, a diode, and a switch, usually a transistor. Its unique configuration allows for the isolated exchange of energy, which differentiates it from other types of converters.
- Inductors: The two inductors in the SEPIC converter can either be separate or a single component with a common core. When the switch is on, the first inductor (L1) stores energy, and the second inductor (L2) discharges, passing its energy to the capacitor C2.
- Capacitors: The input capacitor (C1) is responsible for transferring energy directly from the input to the output, while the output capacitor (C2) helps smooth the output voltage waveform.
- Diode: The diode in the SEPIC converter allows current to flow in one direction, from the inductor L2 to the output load.
- Switch: The switch controls the energy transfer from the inductors to the capacitors. When the switch is turned off, the energy stored in L1 and C1 is transferred to the load.
Applications of SEPIC Converter
SEPIC converters are widely used in various applications due to their versatility. They are a common choice for battery-operated systems, as they can boost a low battery voltage or buck a high battery voltage to a regulated output voltage. Furthermore, SEPIC converters are often used in automotive systems, where input voltage can vary dramatically due to changes in engine speed or battery charge state.
Advantages and Limitations of SEPIC Converter
Like any technology, SEPIC converters have their strengths and limitations. A key advantage is their ability to provide a regulated output voltage that can be either higher or lower than the input voltage. This versatility is not seen in many other types of DC/DC converters. Additionally, SEPIC converters offer continuous input current, which is beneficial in applications such as power factor correction and reduces electromagnetic interference (EMI).
However, SEPIC converters also have some drawbacks. Their efficiency is typically lower than other converter types due to higher component count and more switching losses. Additionally, the design can be more complex due to the need to balance the energy transfer between two inductors.
Improving SEPIC Converter Efficiency
Despite these limitations, several strategies can be used to improve the efficiency of a SEPIC converter. Using high-quality components, optimizing the inductor values, and carefully selecting the switch frequency can all lead to better performance. Moreover, more advanced control techniques such as pulse width modulation (PWM) can be used to increase the efficiency of the energy transfer process.
Conclusion
In conclusion, SEPIC converters are a versatile and valuable tool in the field of electronics, capable of handling a range of input and output voltage requirements. Their ability to function as both a step-up and step-down converter makes them suitable for a variety of applications, from battery-operated systems to automotive electronics. Despite some limitations, with careful design and optimization, SEPIC converters can offer efficient and reliable performance for a wide range of power conversion needs.

