Explore the world of radial flux motors – their design, advantages, applications, and future prospects in the electric motor industry.
Introduction to Radial Flux Motors
The technology of electric motors has been experiencing significant transformations in recent years. One of the most promising types of electric motors emerging from this innovation surge is the Radial Flux Motor. To understand its relevance, let’s first clarify the basics of electric motor technology.
Understanding Electric Motors
Electric motors play a crucial role in a wide variety of applications, from electric vehicles to industrial machinery and home appliances. They function based on the interaction between magnetic fields and electric current. The core principle is that an electric current flowing through a wire generates a magnetic field. If this magnetic field is within another magnetic field, the interaction between the two will create a force, driving motion.
The Axial Flux vs Radial Flux Debate
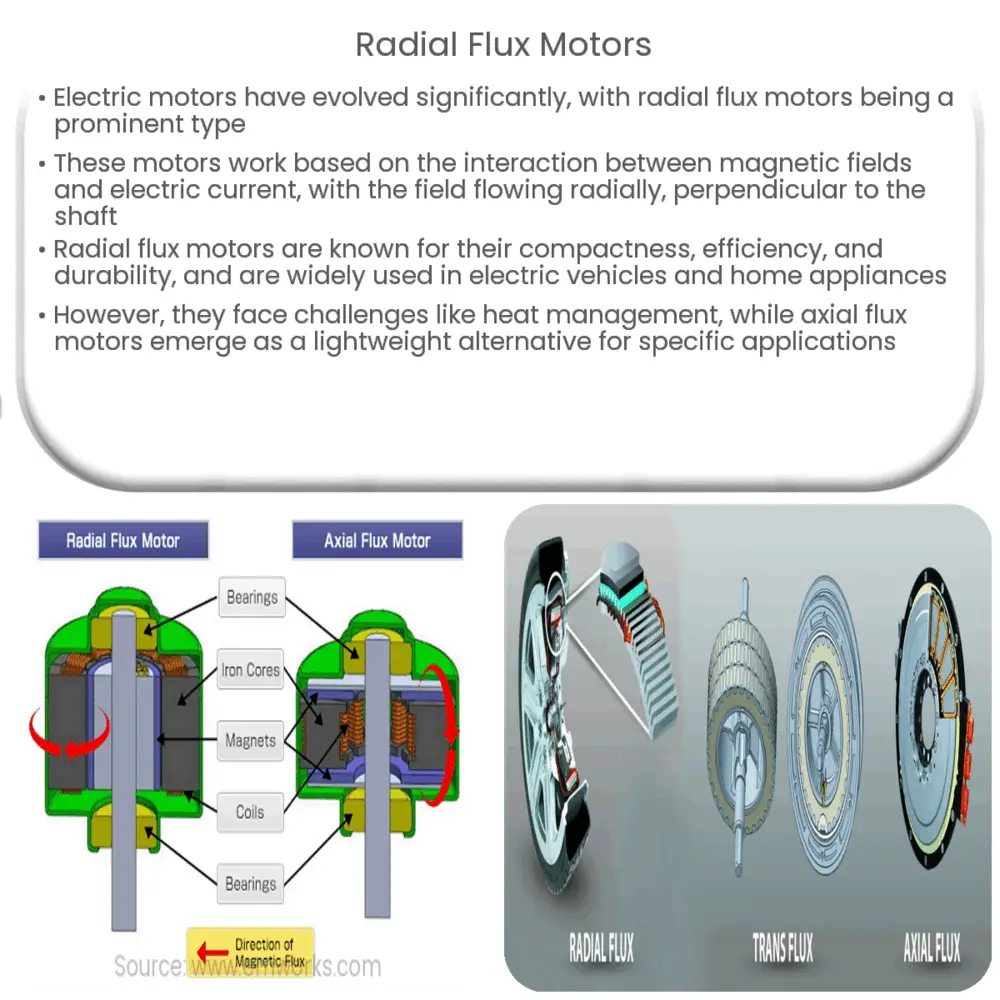
In the context of electric motors, the term ‘flux’ refers to the direction in which the magnetic field is flowing. There are two primary categories – axial and radial. In axial flux motors, the magnetic field flows along the axis of the motor, parallel to the shaft. In contrast, in radial flux motors, the magnetic field flows radially, that is, perpendicular to the shaft.
Design and Operation of Radial Flux Motors
Most conventional electric motors used today are of the radial flux type. In these motors, the stator (the stationary part of the motor) is designed around the rotor (the rotating part of the motor). The magnetic field generated by the stator windings travels radially across the air gap between the stator and rotor, thereby inducing a torque that makes the rotor turn. This radial flow of magnetic field gives these motors their name.
Advantages of Radial Flux Motors
- Compactness: The radial design often allows for a more compact motor, fitting into smaller spaces.
- Efficiency: With a well-designed radial flux motor, higher efficiency can be achieved, which can lead to significant energy savings over time.
- Robustness: Thanks to their design, radial flux motors are generally more robust and durable than other types of motors.
The above mentioned are just a few advantages of radial flux motors. These motors have a broad range of applications and are found in many electric devices and machinery. However, as technology progresses, other types of motors, such as the axial flux motor, are gaining popularity for certain applications. It’s important to understand the strengths and weaknesses of each to determine the best fit for a specific application.
Applications of Radial Flux Motors
Radial flux motors are extensively used in numerous applications, owing to their high power density and cost-effectiveness. These applications range from home appliances such as washing machines and fans to electric vehicles and industrial machinery. In fact, most electric vehicles on the road today use radial flux motors due to their high torque capabilities and efficiency.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite the numerous advantages, radial flux motors are not without their challenges. The primary hurdle pertains to heat management. Given that the windings and core are located close to each other, excess heat produced can be problematic. Moreover, the radial configuration necessitates a strong supporting structure to withstand the forces during operation, adding to the motor’s weight and size.
However, technological advancements are progressively overcoming these challenges. Innovations in materials, cooling systems, and motor design are continually pushing the boundaries of what is possible with radial flux motors.
Axial Flux Motors: An Emerging Competitor
While radial flux motors have long held dominance in many applications, axial flux motors are emerging as a promising alternative for specific use cases. These motors, wherein the magnetic field flows parallel to the shaft, offer advantages such as improved power-to-weight ratio, which makes them attractive for electric vehicle and renewable energy applications.
- Lighter: An axial flux motor can often be lighter than a radial flux motor of comparable power.
- Flexible Design: The flat and disk-like form factor of axial flux motors allows for unique design possibilities.
Nevertheless, each technology has its unique advantages and application areas, and the choice between the two ultimately depends on the specific requirements of the application.
Conclusion
In conclusion, radial flux motors, with their compact design, efficiency, and robustness, have been and continue to be a cornerstone of the electric motor industry. Despite the challenges associated with heat management and structural integrity, ongoing technological advancements are continuously improving their performance and reliability. While the emergence of axial flux motors introduces exciting prospects, radial flux motors are expected to retain their relevance and continue to drive the evolution of electric motor technology in the foreseeable future.

