PMLMs are direct drive linear motors using permanent magnets for precise motion control, high efficiency, and low maintenance in various industries.
Permanent Magnet Linear Motor (PMLM): An Introduction
Overview
Permanent Magnet Linear Motors (PMLMs) are a type of direct drive linear motor that utilizes permanent magnets in their construction to produce linear motion. These innovative motors have become increasingly popular in various industries due to their high efficiency, precise motion control, and reduced maintenance requirements. In this article, we will delve into the fundamental principles of PMLMs, their advantages and disadvantages, and some common applications.
Principles of Operation
Permanent Magnet Linear Motors operate based on the principles of electromagnetic attraction and repulsion. They consist of two main components: the primary part, which contains the permanent magnets, and the secondary part, which is made up of a series of conductive coils. When an alternating current (AC) is applied to the coils, it generates a magnetic field that interacts with the magnetic field produced by the permanent magnets. This interaction creates a linear force that drives the primary and secondary parts relative to each other, resulting in precise linear motion.
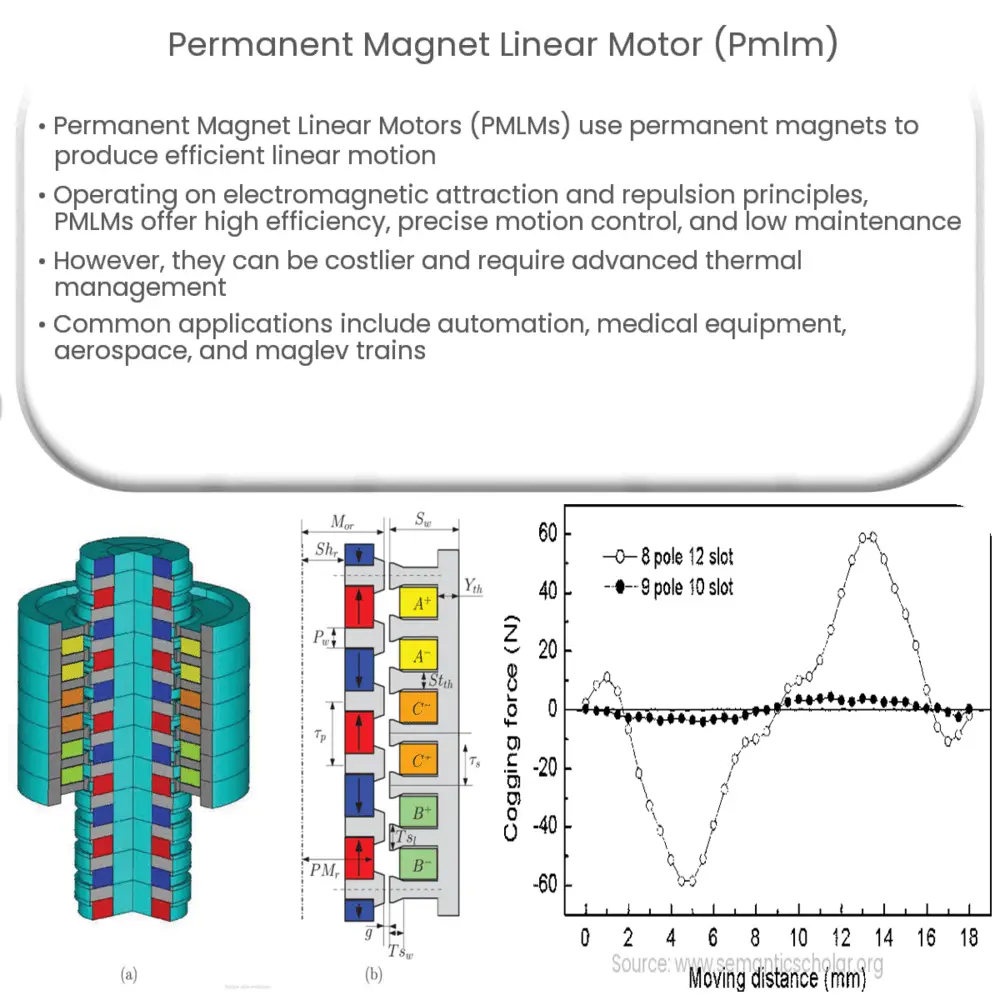
There are two primary configurations of PMLMs: the ironless and iron-core designs. In the ironless configuration, the primary part is composed of an array of permanent magnets arranged in a Halbach array, while the secondary part contains the windings. This design eliminates the need for an iron core, resulting in a lighter motor with zero cogging force and reduced eddy current losses. Conversely, the iron-core configuration uses an iron core to support the primary part, leading to increased force density but also increased cogging force and eddy current losses.
Advantages of PMLMs
Permanent Magnet Linear Motors offer several advantages over traditional rotary motors and other linear motor technologies:
- High efficiency: The direct drive nature of PMLMs results in minimal energy loss, as there are no mechanical transmission components such as gears, belts, or screws involved. This leads to higher overall efficiency.
- Precise motion control: PMLMs provide excellent motion control with high acceleration, deceleration, and positioning accuracy. Their cogging-free design, particularly in ironless configurations, enables smooth motion even at low speeds.
- Low maintenance: The absence of mechanical transmission components also means that PMLMs require less maintenance, as there are no parts that wear out or need lubrication.
- Compact and lightweight: PMLMs can be designed to be compact and lightweight, making them suitable for applications with limited space or weight constraints.
Disadvantages of PMLMs
While Permanent Magnet Linear Motors offer many advantages, they also come with some drawbacks:
- Cost: The use of permanent magnets and specialized components can make PMLMs more expensive than traditional rotary motors and other linear motor technologies.
- Thermal management: PMLMs may require more advanced thermal management systems due to the concentration of heat in the coils and the magnets. This is particularly true for iron-core configurations, which experience higher eddy current losses.
- Force variation: In iron-core configurations, the cogging force can result in force variation, which may affect the motion quality and positioning accuracy of the motor.
Applications of PMLMs
Permanent Magnet Linear Motors have found use in a wide range of industries and applications due to their unique benefits. Some common applications include:
- Automation and robotics: PMLMs are widely used in automated manufacturing processes, assembly lines, and robotics for precise positioning and high-speed operation.
- Medical and laboratory equipment: The high precision and reliability of PMLMs make them ideal for use in medical devices and laboratory equipment, such as medical imaging systems, diagnostic devices, and sample handling systems.
- Aerospace and defense: PMLMs have been employed in satellite positioning systems, missile guidance systems, and other aerospace applications where precision and reliability are of paramount importance.
- Transportation: PMLMs are used in magnetic levitation (maglev) trains, providing propulsion and precise control of the train’s movement.
Conclusion
Permanent Magnet Linear Motors (PMLMs) have emerged as a powerful alternative to traditional rotary motors and other linear motor technologies. Their high efficiency, precise motion control, and low maintenance requirements make them an attractive option for a wide range of industries and applications. While PMLMs do have some disadvantages, such as cost and thermal management challenges, ongoing research and development in this field continue to improve their performance and reduce their limitations. As a result, PMLMs are poised to play an increasingly significant role in the future of motion control and automation systems.

