Permanent magnet gears transmit torque using magnetic forces, offering high efficiency, compact design, and low noise for various industries.
Understanding Permanent Magnet Gears: An Innovative Solution for Power Transmission
As the world continues to embrace the need for renewable energy and advanced technologies, permanent magnet gears are emerging as an attractive option for efficient power transmission. These innovative devices have the potential to revolutionize various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and renewable energy sectors, due to their unique properties and benefits. In this article, we will explore the fundamentals of permanent magnet gears, how they work, and their applications across different fields.
What are Permanent Magnet Gears?
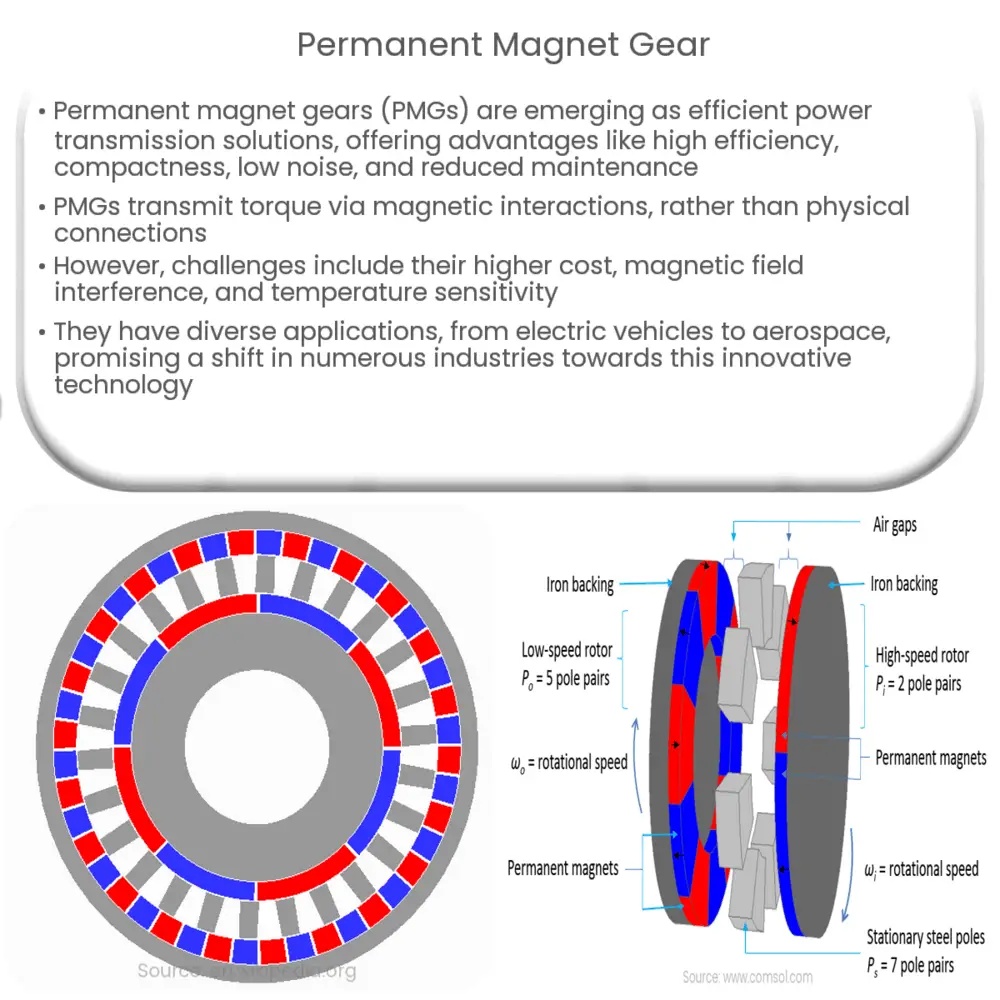
Permanent magnet gears (PMGs) are a type of mechanical power transmission device that relies on the interaction between magnetic fields to transmit torque and motion. They consist of two or more concentric rings or discs with permanent magnets mounted on their surfaces. The magnets on one disc are arranged in a specific pattern that complements the pattern on the other disc, allowing them to interact with one another and create a force that causes the discs to rotate in unison.
How Do Permanent Magnet Gears Work?
The primary operating principle of a PMG is based on magnetic attraction and repulsion. When two magnets with opposite poles face each other, they attract and create a force that pulls them together. Conversely, when magnets with the same poles face each other, they repel and create a force that pushes them apart. By strategically arranging the magnets on the gear discs, it is possible to generate a continuous rotational force that drives the gear system.
PMGs are typically classified as either synchronous or asynchronous gears. In synchronous PMGs, the input and output shafts rotate at the same speed, while asynchronous PMGs have input and output shafts that rotate at different speeds. The specific arrangement of magnets and the number of poles on each disc determine the gear ratio, which is the ratio of the input shaft speed to the output shaft speed.
Advantages of Permanent Magnet Gears
There are several key advantages to using permanent magnet gears in power transmission applications, some of which include:
- High Efficiency: PMGs have fewer mechanical components and generate less friction compared to traditional gear systems, resulting in higher overall efficiency and reduced energy loss.
- Compact Design: Due to the use of magnetic forces for power transmission, PMGs can be designed with a smaller footprint and lower weight than conventional gear systems, making them ideal for applications with space constraints.
- Low Noise and Vibration: The absence of physical contact between gear teeth in PMGs significantly reduces noise and vibration levels, leading to a quieter and smoother operation.
- Maintenance-Free Operation: The non-contact nature of PMGs minimizes wear and tear on components, resulting in longer service life and reduced maintenance requirements.
Disadvantages of Permanent Magnet Gears
Despite their numerous advantages, there are some drawbacks to using permanent magnet gears, which include:
- Cost: The production and assembly of permanent magnet gears can be more expensive than traditional gear systems, mainly due to the cost of high-performance magnets and the precise manufacturing process required.
- Magnetic Field Interference: PMGs can generate strong magnetic fields, which may interfere with other components or devices in close proximity, necessitating additional shielding or isolation measures.
- Temperature Sensitivity: The performance of permanent magnets can degrade at high temperatures, potentially affecting the efficiency and reliability of the gear system. This may require the use of specialized cooling systems or materials to maintain optimal performance.
Applications of Permanent Magnet Gears
Permanent magnet gears are versatile and can be employed in a wide range of applications across various industries, such as:
- Electric Vehicles: PMGs can be used in the drivetrain of electric vehicles, providing efficient power transmission and reduced weight compared to traditional gear systems, contributing to improved vehicle performance and range.
- Wind Turbines: By replacing conventional gearboxes with PMGs in wind turbines, energy conversion efficiency can be increased, leading to higher power generation and reduced maintenance requirements.
- Industrial Automation: Permanent magnet gears can be used in robotic systems and other automated machinery, offering high precision, low noise, and reduced maintenance needs.
- Aerospace: PMGs can provide lightweight, compact, and efficient power transmission solutions for various aerospace applications, such as actuators and propulsion systems.
Conclusion
Permanent magnet gears offer a promising alternative to traditional mechanical gear systems, with their high efficiency, compact design, and reduced maintenance requirements. While there are some challenges to overcome, such as cost and temperature sensitivity, the numerous benefits and wide range of applications make PMGs an attractive solution for various industries. As research and development in this field continue, we can expect to see further improvements in performance and a broader adoption of permanent magnet gear technology in the near future.




