Explore the workings of nuclear generators, their types, benefits, challenges, and future potential in our comprehensive guide to atomic energy.
Nuclear Generators: Harnessing Atomic Energy
Nuclear generators, or nuclear power plants, are energy production facilities that harness the power of nuclear fission to create electricity. They play a crucial role in the global energy landscape, providing a substantial portion of the world’s electrical power.
How Nuclear Generators Work
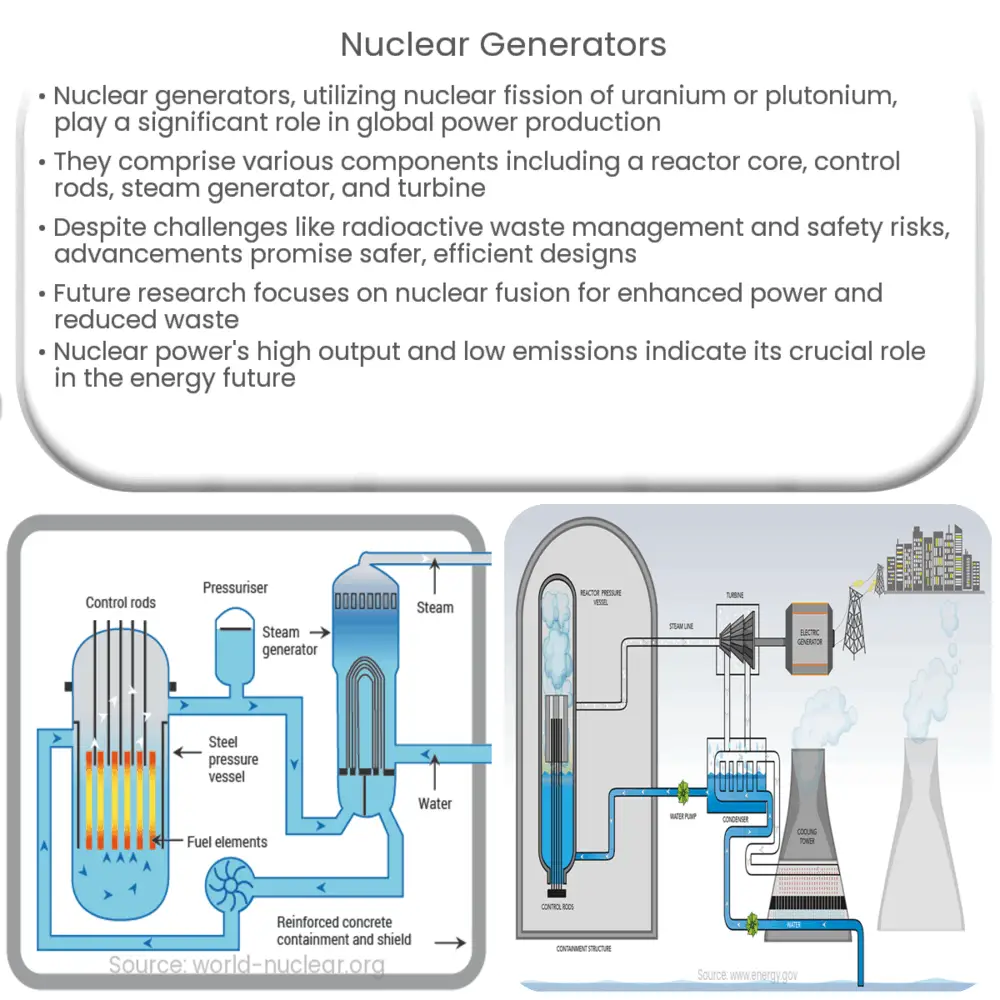
The process begins with the splitting of atoms, typically uranium or plutonium, in a process called nuclear fission. This releases a vast amount of energy in the form of heat. The heat is then used to create steam, which drives a turbine connected to an electricity generator.
Components of a Nuclear Generator
- Reactor Core: This is where the nuclear fission takes place. The reactor core contains fuel rods filled with uranium or plutonium pellets.
- Control Rods: These rods are capable of absorbing neutrons and can be raised or lowered into the reactor core to control the rate of fission.
- Steam Generator: This device transfers heat from the reactor core to a secondary coolant circuit, creating steam.
- Turbine and Generator: The steam drives the turbine, which in turn drives the generator to produce electricity.
While these components are the heart of a nuclear generator, other systems are also integral for safety and operation, including the cooling system, containment structure, and waste handling facilities.
The Benefits and Challenges of Nuclear Power
Nuclear power is often touted for its ability to generate large amounts of electricity without producing greenhouse gases. However, it is not without its challenges.
- Advantages: High energy output, low greenhouse gas emissions, and relative reliability compared to some forms of renewable energy.
- Challenges: Radioactive waste management, high upfront costs, potential for catastrophic accidents, and issues related to nuclear proliferation.
Despite these challenges, advancements in technology, such as the development of safer reactor designs and more effective waste disposal methods, hold the promise of making nuclear power a more viable and sustainable energy option in the future.
(Note: Word count: 328 words)
Types of Nuclear Generators
There are different types of nuclear generators currently in use around the world. These include:
- Pressurized Water Reactors (PWRs): These are the most common type, where water under high pressure is used as the coolant and neutron moderator.
- Boiling Water Reactors (BWRs): In these reactors, the water used as the coolant is allowed to boil and turn into steam, which directly drives the turbine.
- Fast Breeder Reactors (FBRs): These reactors produce more fissile material than they consume, effectively “breeding” fuel.
- Advanced Gas-cooled Reactors (AGRs): AGRs use carbon dioxide as a coolant and graphite as a neutron moderator.
Future of Nuclear Generators
Looking to the future, scientists and engineers are researching and developing new designs for nuclear generators that promise greater safety and efficiency. One notable example is the Generation IV nuclear reactors, which aim to improve upon the existing Generation III reactors in several ways, such as higher fuel efficiency, reduced waste production, and passive safety features.
Another area of ongoing research is nuclear fusion. Unlike nuclear fission, which splits atoms to release energy, fusion combines atoms. Fusion holds the potential to produce even more power than fission, with fewer safety concerns and waste production.
Conclusion
Nuclear generators are a significant component of our global energy production, offering large-scale power generation with minimal greenhouse gas emissions. However, they also present notable challenges, including waste management and safety concerns. Ongoing advancements in reactor design, waste management, and new technologies like fusion hold the promise of addressing these challenges, making nuclear power a potentially even more crucial part of our future energy mix.
As we continue to grapple with the energy demands of a growing global population and the need to transition away from fossil fuels, nuclear power, with its combination of high energy output and low emissions, is poised to play a key role in our energy future. The ongoing development and refinement of nuclear generators is a testament to human innovation and our capacity to harness the fundamental forces of nature for our benefit.
(Note: Word count: 343 words)