Explore the working principle, key components, and diverse applications of Monostable Multivibrators in digital electronics.
Introduction to Monostable Multivibrators
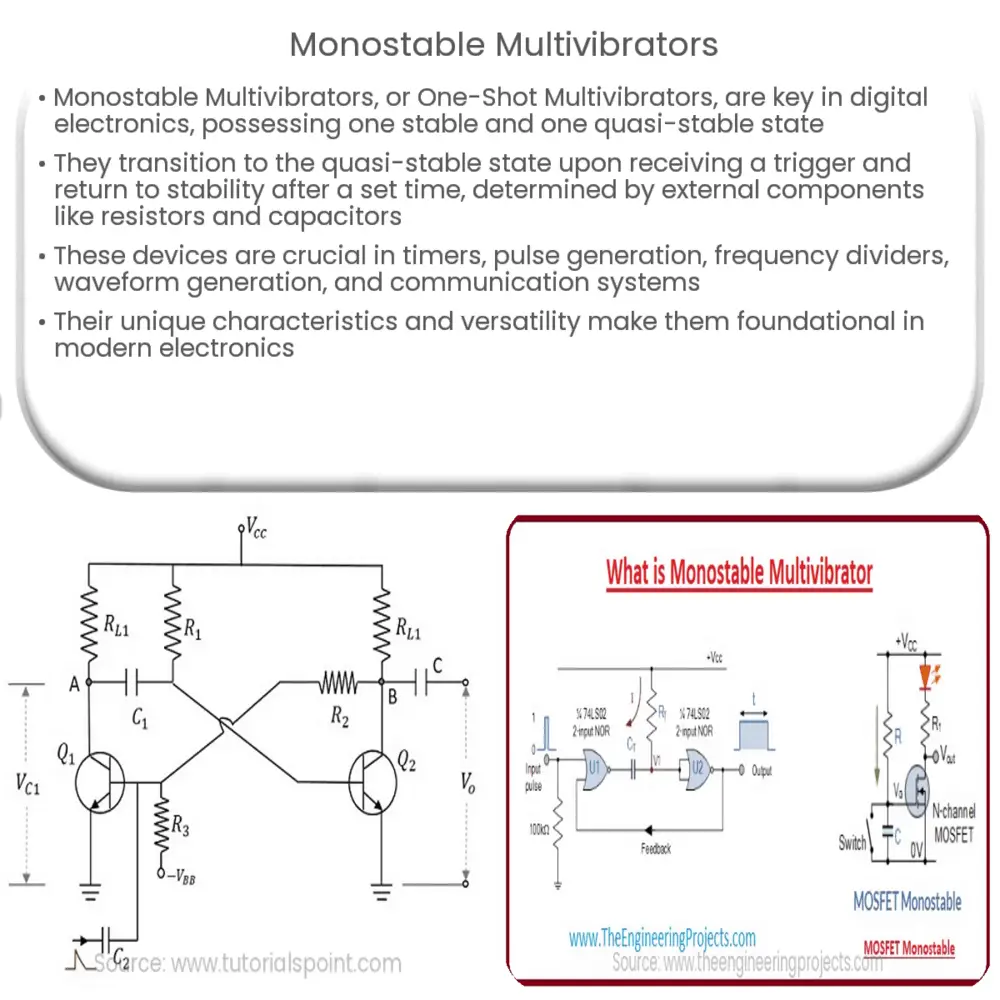
A Monostable Multivibrator, also known as a One-Shot Multivibrator, is a significant component in digital electronics. As the name suggests, this device has one stable state and another quasi-stable state. It is a type of flip-flop circuit, used frequently in timing applications.
Working Principle
The fundamental principle of a Monostable Multivibrator revolves around the fact that it has one stable state and can be triggered to a second state for a predetermined amount of time. The duration of this period is typically controlled by external components like resistors and capacitors.
Under normal conditions, the output of a monostable multivibrator remains in its stable state. However, when a triggering signal is applied, it flips to its quasi-stable state. After the lapse of a certain time period (determined by the external RC network), the circuit automatically returns to its original stable state without requiring an external trigger.
Key Components
- Resistors: These are passive electronic components that implement electrical resistance in the circuit. They limit the current flow, divide voltages, and, in a Monostable Multivibrator, are often used to set the time delay.
- Capacitors: Capacitors store and release electrical energy in the circuit. In a Monostable Multivibrator, they help determine the duration the circuit will remain in the quasi-stable state.
- Transistors: Transistors are semi-conductor devices used to amplify or switch electronic signals. In the context of a Monostable Multivibrator, they serve as the flip-flop element, switching between stable and quasi-stable states.
Applications of Monostable Multivibrators
Monostable Multivibrators find their utility in various applications, owing to their time-delay features. They are extensively used in timers, frequency dividers, and pulse generation. Furthermore, they serve crucial roles in digital sequential logic circuits, communication systems, and waveform generators. The next section will provide a deeper understanding of how these applications are achieved.
Deeper Understanding of Monostable Multivibrator Applications
Let’s delve into some specific applications of Monostable Multivibrators:
- Timers and Delays: The property of returning to a stable state after a defined period makes these circuits apt for creating precise time delays and timers in digital circuits.
- Frequency Division: They are also used for frequency division in digital electronics, where the output frequency is a submultiple of the input frequency.
- Pulse Generation: These multivibrators are used in generating a pulse of a specific width. The width of the output pulse is controlled by the RC time constant in the circuit.
- Waveform Generators: They serve a crucial role in generating different types of waveforms in electronic systems, which are further used in various signal processing applications.
- Sequential Logic Circuits: In digital sequential logic circuits, Monostable Multivibrators are often used as bistable latches and flip flops.
- Communication Systems: They are used in communication systems for various modulation techniques like Frequency Shift Keying (FSK) and Phase Shift Keying (PSK).
Conclusion
In conclusion, Monostable Multivibrators are a cornerstone in digital electronics, demonstrating a wide range of applications. The unique characteristic of one stable state and one quasi-stable state makes them essential in timing and sequential circuits. The flexibility in determining the duration of the quasi-stable state through external components enhances their utility in diverse applications, from waveform generation to communication systems.
The importance of understanding Monostable Multivibrators becomes apparent when we consider the foundational role they play in modern electronics. As we continue to evolve and innovate within the realm of digital technology, the relevance and use of Monostable Multivibrators is likely to expand even further.

